by Bruce Wells | Feb 23, 2024 | Petroleum Technology
Reversing an earlier ban, voters in Long Beach, California, in 1962 approved petroleum exploration in their harbor. Five major oil companies formed a company called THUMS and built four artificial islands to produce the oil.
California’s headline-making 1921 oil discovery at Signal Hill launched a drilling boom that transformed the quiet residential area. So many derricks sprouted it became known as “Porcupine Hill.”
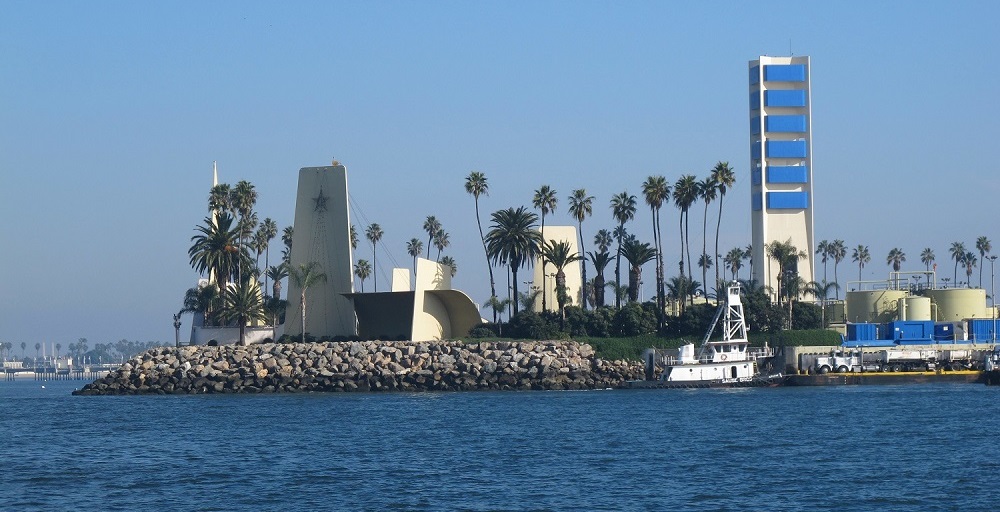

Island Grissom, one of the four THUMS islands at Long Beach, California, was named after NASA astronaut Col. Virgil “Gus” Grissom, who died in 1967 in the Apollo spacecraft fire. Photo courtesy U.S. Department of Energy.
With many homeowners aspiring to become drillers and oilfield speculators, much of Signal Hill’s land was sold and subdivided in real estate lots of a size described as “big enough to raise chickens.”
Derricks were so close to one cemetery that graves “generated royalty checks to next-of-kin when oil was drawn from beneath family plots,” noted one historian. Neighboring Long Beach joined the drilling boom.

By 1923, oil production reached more than one-quarter million barrels of oil per day. When Long Beach instituted a per-barrel oil tax, Signal Hill residents voted to incorporate in 1924.
At the time, “the law of capture” for petroleum production ensured the formerly scenic landscape would be transformed. Competing exploration and production companies crowded around newly completed wells and chased any signs of oil to the Pacific Ocean.
The islands are among the most innovative oilfield designs in the world. Circa 1965 illustration courtesy Oxy Petroleum.
By the early 1930s, the massive Wilmington oilfield extended through Long Beach as reservoir management concerns remained in the future. Naturally produced California oil seeps had led to many discoveries south of the 1892 Los Angeles City field.
Onshore and offshore tax revenues generated by production of more than one billion barrels of oil and one trillion cubic feet of natural gas helped underwrite much of the Los Angeles area’s economic growth. But not without consequences.
Long Beach: A Sinking City
The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers reported, “Subsidence, the sinking of the ground surface, is typically caused by extracting fluids from the subsurface.”

Petroleum reserves brought drilling booms to southern California. By 1923, oil production reached more than one-quarter million barrels of oil per day from Signal Hill, seen in the distance in this detail from a panorama from the Library of Congress.
Californians had a lot of experience dealing with groundwater induced subsidence and the building damage it caused, but by 1951, Long Beach was sinking at the alarming rate of about two feet each year.
Earth scientists noted that between 1928 and 1965, the community sank almost 30 feet. TIME magazine call the bustling port “America’s Sinking City.”

After decades of prospering from petroleum production, the city prohibited “offshore area” drilling to slow the subsidence as the community looked for a solution.
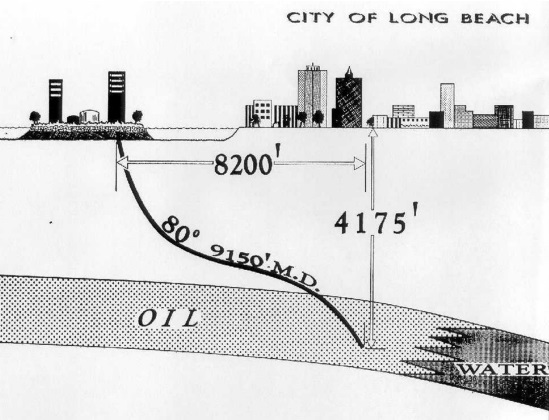
On February 27, 1962, Long Beach voters approved “controlled exploration and exploitation of the oil and gas reserves” underlying their harbor. The city’s charter had prohibited such drilling since a 1956 referendum. Advancements in oilfield technologies enabled Long Beach to stay afloat.
Directional drilling and water injection opened another 6,500 acres of the Wilmington field — and saved the sinking city.
THUMS: Texaco, Humble, Union and Shell
Five oil companies formed a Long Beach company called THUMS: Texaco (now Chevron), Humble (now ExxonMobil), Union Oil (now Chevron), Mobil (now ExxonMobil) and Shell Oil Company. They built four artificial islands at a cost of $22 million in 1965 (more than $200 in 2024 dollars).
The islands — named in 1967 Grissom, White, Chaffee, and Freemen in honor of lost NASA astronauts would include 42 acres for about 1,000 active wells producing 46,000 barrels of oil and 9 million cubic feet of natural gas a day.

The prospering but “sinking city” of Long Beach would solve its subsidence problem with four islands and advanced drilling and production technologies. Photo by Roger Coar, 1959, courtesy Long Beach Historical Society.
To counter subsidence, five 1,750-horsepower motors on White Island drive water injection pumps to offset extracted petroleum, sustain reservoir pressures, and extend oil recovery. The challenge was once described as “a massive Rubik’s Cube of oil pockets, fault blocks, fluid pressures and piping systems.”
Meanwhile, all of this happens amidst the scenic boating and tourist waters in Long Beach Harbor.
The California Resources Corporation operates the offshore part on the islands of the Wilmington field, the fourth-largest U.S. oilfield, according to the Los Angeles Association of Professional Landmen, whose members toured the facilities in November 2017.
Producing in Plain Sight
“Most interestingly, the islands were designed to blend in with the surrounding coastal environment,” explained LAAPL Education Chair Blake W.E. Barton of Signal Hill Petroleum.
“The drilling rigs and other above-ground equipment are camouflaged and sound-proofed with faux skyscraper skins and waterfalls,” Barton noted.
Most people simply do not realize the islands are petroleum production facilities. From the shore, the man-made islands appear occupied by upscale condos and lush vegetation. Many of the creative disguises came courtesy of Joseph Linesch, a pioneering designer who helped landscape Disneyland.

The THUMs islands required exceptional designs, and “the people who were involved at the time were very creative visionaries,” said Frank Komin, executive vice president for southern operations of the California Resources Corporation (CRC), owner of the islands.
About 80 percent of the company’s properties would overlie the Wilmington oilfield, according to CRC, noting that from 2003 to 2018, CRC operations generated over $5.2 billion in revenues, taxes and fees for the City of Long Beach and the state.
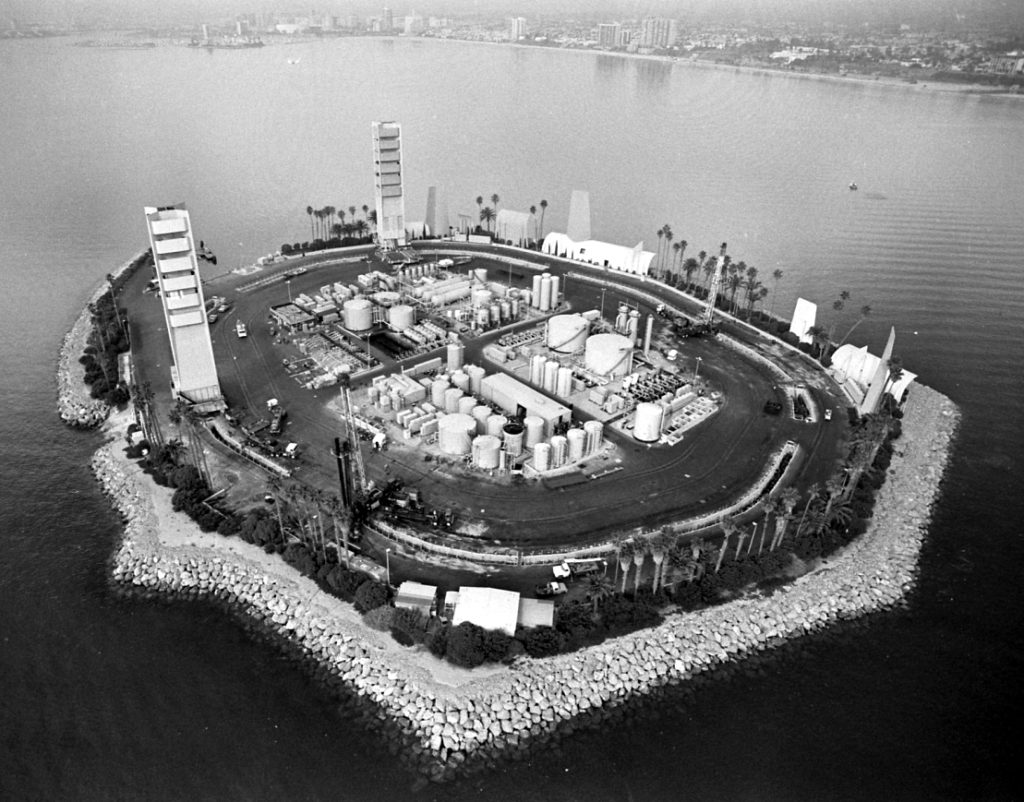

THUMS Island White, named for Col. Edward White II, the first American to walk in space, who died in 1967 along with NASA astronauts “Gus” Grissom and Roger B. Chaffee. A fourth island was named for NASA test pilot Ted Freeman, who in 1963 was the first fatality among the astronauts. Photo courtesy UCLA Library.
“Even today, those islands are viewed as one of the most innovative oil field designs in the world,” CRC executive Komin declared in a 2015 Long Beach Business Journal article. “The islands have grown to become icons in which the City of Long Beach takes a great deal of pride.”
The Journal explained that 640,000 tons of boulders, some as large as five tons, were mined and placed to build up the perimeters of the islands. “Concrete facades constructed for aesthetic purposes also divert industrial noise away from nearby residents,” the article added. For more noise abatement, electricity has provided nearly all the power for the islands.

The THUMS aesthetic integration of 175-foot derricks and production structures has been described by the Los Angeles Times as, “part Disney, part Jetsons, part Swiss Family Robinson.”
_______________________
Recommended Reading: An Ocean of Oil: A Century of Political Struggle over Petroleum Off the California Coast (1998); Black Gold in California: The Story of California Petroleum Industry  (2016); Early California Oil: A Photographic History, 1865-1940
(2016); Early California Oil: A Photographic History, 1865-1940 (1985). Your Amazon purchases benefit the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(1985). Your Amazon purchases benefit the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Become an AOGHS annual supporting member and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2023 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
Citation Information – Article Title: “THUMS – California’s Hidden Oil Islands.” Authors: B.A. Wells and K.L. Wells. Website Name: American Oil & Gas Historical Society. URL: https://aoghs.org/technology/thums-california-hidden-oil-islands. Last Updated: February 23, 2024. Original Published Date: March 8, 2018.
by Bruce Wells | Jan 20, 2024 | Offshore History
Exploring the 1969 offshore disaster and the geology of ancient natural petroleum seeps.
A 1969 oil spill from a California offshore platform transformed the public’s view of the U.S. petroleum industry and helped launch the modern environmental movement — and the Environmental Protection Agency. Ancient natural seeps continue to produce thousands of tons of oil every day.
On January 28, 1969, after drilling 3,500 feet below the ocean floor, a Union Oil Company drilling platform six miles off Santa Barbara, suffered a blowout. Between 80,000 and 100,000 barrels of oil flowed into the Pacific Ocean and onto beaches, including at Summerland, where the U.S. offshore industry began in 1896 with drilling on oil well piers. (more…)
by Bruce Wells | Jan 1, 2024 | Petroleum Companies
The rush for “black gold” took off in 1886, after William Rowland and partner William Lacy completed several producing oil wells at Rancho La Puente. Their company, Rowland & Lacy (later called the Puente Oil Company), revealed the Puente oilfield. News spread, launching a drilling boom.
By 1912, a host of inexperienced exploration companies were drilling more than 100 wells in the Fullerton area alone. According to reports, two of the inevitable dry hole holes that resulted were drilled by a new venture, the Puente Crude Oil Company.
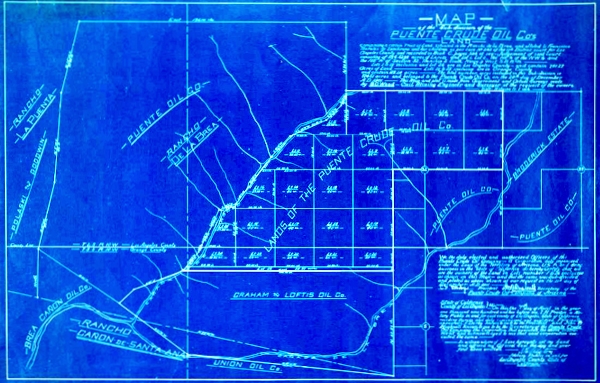
Puente Crude Oil Company was one of many small ventures that hoped to find oil in southern California’s prolific oil fields near Brea Canyon and Fullerton at the turn of the century.
Puente Crude Oil Company was capitalized at only $500,000 and offered stock to the public at 10 cents a share in 1900, but its two unsuccessful wells in the Puente field’s eastern extension brought the company to a quick financial crisis. One well was lost to a “crooked hole” and the other found only traces of oil and natural gas.
Enthusiastic advertisements solicited investment. Some ads referred to the better known Sunset oil field, discovered in 1892 in Kern County to the north. By May 1901 company stock was offered at two cents per share to relieve indebtedness and enable further drilling on the company’s 870 acres in Rodeo Canyon.
One year later, San Bernardino newspapers reported the company in trouble.

“This history of misadventure has not been pleasing to the stockholders of the Puente Crude Oil Company,” noted one article. “An auditing committee was appointed for the purpose of examining the books and accounts of the company,” it added.
Further reports in 1902 noted the company had issued no statements, “financial or otherwise,” for a year. Puente Crude Oil Company is absent from records thereafter.
South of Los Angeles, in Orange County, the Brea Museum and Heritage Center tells the story of the Olinda Oil Well No. 1 well of 1898 – one of many important California petroleum discoveries. Visit the Olinda Oil Museum and Trail at 4025 Santa Fe Road in Brea.
The stories of exploration and production (E&P) companies joining U.S. petroleum booms (and avoiding busts) can be found updated in Is my Old Oil Stock worth Anything?
___________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society preserves U.S. petroleum history. Join today as an AOGHS supporting member. Help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2021 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.

Much of the Puente Oil’s former oil producing land has long since been managed by the Puente Hills Landfill Native Habitat Preservation Authority, and in 2022 the Port of Los Angeles handled more than 220 million metric tons — 20 percent of all incoming cargo for the United States.
_______________________
Recommended Reading: Los Angeles, California, Images of America (2001). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(2001). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Become an AOGHS annual supporting member and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2024 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
Citation Information – Article Title: “Puente Crude Oil Company.” Authors: B.A. Wells and K.L. Wells. Website Name: American Oil & Gas Historical Society. URL: https://aoghs.org/old-oil-stocks/puente-crude-oil-company. Last Updated: January 4, 2024. Original Published Date: July 2, 2013.
.
by Bruce Wells | Dec 4, 2023 | Petroleum Companies
Oilfield discovery in 1908 at Cat Canyon, California, began company’s lengthy corporate convolution.
In the Solomon Hills of central Santa Barbara County, California, the search for oil and natural gas began in 1904 at Cat Canyon. Exploration companies unsuccessfully drilled there for four years before Palmer Oil Company discovered an oilfield about 10 miles southeast of Santa Maria.
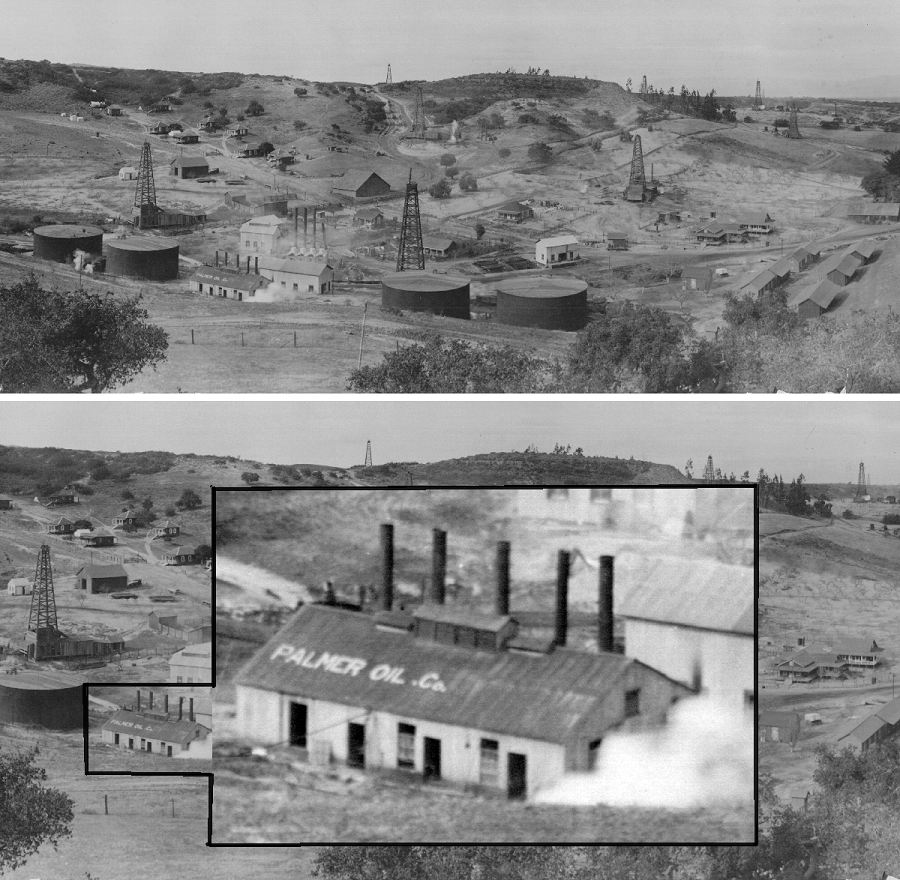

Palmer Oil Company derricks and refinery in Santa Barbara County, California, circa 1920s.
Palmer Oil’s Santa Maria well initially produced 150 barrels of oil a day, but within a few months it jumped to 10,000 barrels a day. The company completed a second well that also proved to be a true gusher. With it and other 1908 discoveries, Palmer Oil opened the Cat Canyon oilfield — the largest in Santa Barbara County at the time.

“The Palmer Oil Company is generally concluded to have opened one of the biggest and richest oil fields in California by the bringing in of its two gushers in the Cat Canyon District, now doing 10,000 barrels per day between them,” declared the trade publication “Oil Age Weekly” on September 9, 1910.
Although the Cat Canyon oilfield produced “heavy oil” with a high sulfur content, the success of Palmer Oil brought new investors, and the company was capitalized at $10 million by the beginning of 1911. The latest oil boom (see First California Oil Wells) attracted 26 exploration companies that completed 35 producing wells.
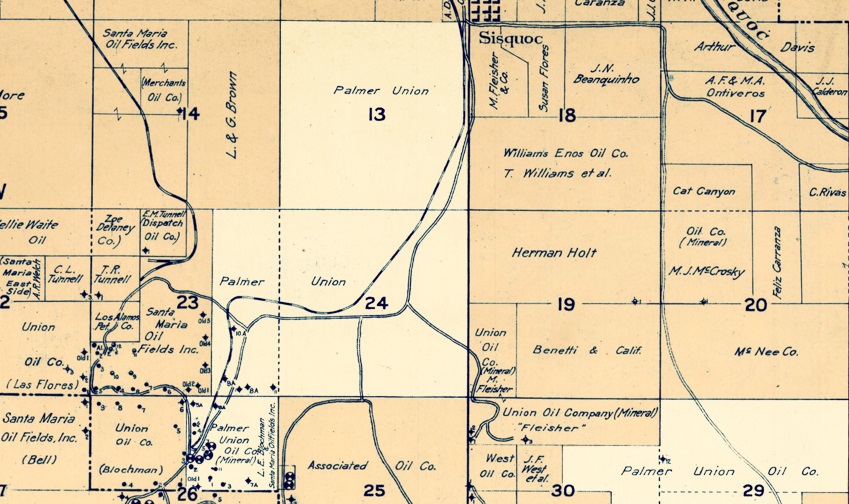
By 1927, Palmer Oil Company had reorganized into Palmer Union Oil Company as it continued to drill on Santa Barbara, California, leases.
By 1927, despite Cat Canyon’s proven oil reserves, drilling and production challenges of the heavy, high sulfur content prompted investors to look for better returns on their investments.
Palmer Oil to Coca-Cola
New drilling in Cat Canyon stalled — as did Palmer Oil, which began the first of its many corporate convolutions by becoming the Palmer Union Oil Company.
In January 1932, Palmer Union Oil became Palmer Stendel Oil Corporation, beginning decades of mergers and acquisitions: Palmer Stendel Oil Company – Petrocarbon Chemicals Incorporated – Great Western Producers – Pleasant Valley Wine Company – Taylor Wine Company – Coca-Cola Company.
After the Great Depression and World War II, water-flooding technology resurrected the Cat Canyon field’s production capability to a peak in 1953. Millions of barrels of oil were recovered and even in 1983, production was still about 350 barrels a day.

One century after its discovery by Palmer Oil Company, the Cat Canyon oilfield had 243 active oil wells. In a state long known for its natural oil seeps, enhanced recovery technologies revived oil production in Santa Barbara County and California’s other heavy oil-producing regions.
To extract reserves previously considered unrecoverable, companies like HVI Cat Canyon (Greka Energy), ERG Resources, and others used tertiary thermal recovery techniques. Improved technologies have dramatically lessened dangers to the environment, but not eliminated them.

A 1927 Palmer Union Oil Company stock certificate purchased at a garage sale in 2008 sparked a legal battle with Coca-Cola.
In 2023, a U.S. District Court found HVI Cat Canyon Inc. (formerly Greka Oil & Gas Company) liable for oil spills and ordered the company to pay $40 million in civil penalties for the spills; $15 million for violations of federal regulations, and $2.5 million in cleanup costs.
The U. S. Energy Information Administration in 2013 ranked Cat Canyon as 17th on its list of the nation’s top 100 producing oilfields — with no company having partial ownership in Coca-Cola Company (see Not a Millionaire from Old Oil Stock).
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Become an AOGHS annual supporting member and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2023 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
Citation Information – Article Title: “Palmer Oil Company.” Authors: B.A. Wells and K.L. Wells. Website Name: American Oil & Gas Historical Society. URL:https://aoghs.org/old-oil-stocks/palmer-oil-company. Last Updated: December 7, 2023. Original Published Date: December 7, 2023.












