by Bruce Wells | Mar 5, 2024 | Petroleum Pioneers
Oil derricks in the Oklahoma City Field in 1930 stood silent for one hour in tribute to Tom Slick.
Once known as “Dry Hole Slick,” wildcatter Thomas B. Slick discovered Oklahoma’s giant Cushing oilfield in 1912 and became known as the “King of the Wildcatters.” Today Cushing is the “Pipeline Crossroads of the World,” the trading hub for oil in North America – and the daily settlement point for prices, including West Texas Intermediate.
The owner of Spurlock Petroleum Company, Alexander Massey, enjoyed great success in the Kansas oilfields after finding oil or natural gas in 25 consecutive wells. In 1904, Massey hired an inexperienced 21-year-old “lease man” named Thomas Baker Slick for a 25 percent share in all the leases the young man could secure. They went to Tryon, Oklahoma, to look for oil.
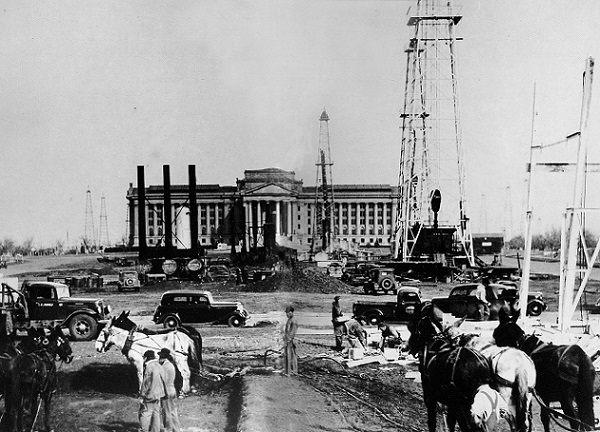

When Oklahoma’s “King of the Wildcatters” Thomas B. Slick suddenly died from a stroke at age 46 in 1930, the oil derricks in the Oklahoma City field stood silent for one hour in tribute. Photo courtesy Library of Congress.
Massey later recalled that Slick, born in Shippenville, Pennsylvania, in 1883, showed a talent for securing petroleum leases. “Tom would go out and lease most of a territory as yet unproved or doubtful as to oil prospects,” Massey noted. “But he’d spread as clean a bunch of leases before a capitalist as you’d wish to see…He certainly knew what a good oil lease was.”

Spurlock Petroleum Company spudded an exploratory well on the farm of M.C. Teegarden near Tryon. As Slick continued securing leases that eventually totaled more than 27,000 acres, drilling generated excitement in the local newspaper and with other Oklahoma wildcatters.

Once known as “Dry Hole Slick” by many, on March 12, 1912, Thomas B. Slick discovered Oklahoma’s giant Cushing oilfield.
However, at a depth of 2,800 feet with no signs of oil, Spurlock Petroleum and owner Massey ran out of money. Tom Slick’s first well was a dry hole. It was the first of many.
Dry Hole Slick
In 1907, after another dry hole near Kendrick, Oklahoma, Slick left the employ of Massey and headed for Chicago, Illinois. Charles B. Shaffer of the Shaffer & Smathers Company hired Slick for $100 per month (and expenses) to find and secure promising oil leases.
Slick traveled to Illinois, Kentucky, western Canada, and eventually, back to Oklahoma. While leasing for Shaffer & Smathers, the young oilman drilled at least ten dry holes in Oklahoma, earning his unenviable nickname, “Dry Hole Slick.”
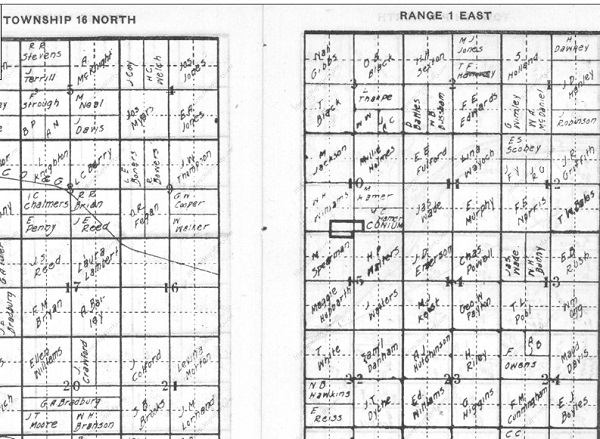
An example of township leases similar to those negotiated by Tom Slick, from the Atlas of North Central Oklahoma 1917 Oil Fields and Landowners: Oklahoma, M. P. Burke, 1917.
The Bristow Record newspaper reported that Slick, “continues to gamble on wild cat stuff. Few men have stuck to the wildcatting longer and harder than Slick and associates. It is said he has spent $150,000 mostly on dry holes.” Now also known as “Mad Tom” Slick, he tried his luck again just 35 miles down the road, in Cushing.
As “Mad Tom” pursued new leases in 1912, publications like the Cushing Independent encouraged readers to take advantage of leasing opportunities. “Land owners have everything to gain and no risk to themselves in making leases,” the newspaper reported on January 25.

“It costs from $8,000 to $10,000 to put down a single hole,” the newspaper noted. “Unless the promoters can get the leases they want they will not chance their money here, while other localities are eager to give leases and even bonuses in money to get prospecting done.”
The Cushing Democrat added, “We would repeat that we believe it to the best interests of the individuals and all that these leases be granted…And just a word of warning. If you make a lease see that the lessees name is not left blank, but that the name of Thomas B. Slick is there.”
Slick and Charles Shaffer spudded a wildcat well on the farm of Frank M. Wheeler in January 1912.
Cushing Gusher and Crafty Moves
On March 12, 1912, the Wheeler No. 1 well struck oil, producing about 400 barrels a day from a depth between 2,319 and 2,347 feet. It marked Tom Slick’s first gusher — and a giant oilfield discovery. Slick was so secretive about his find that he even cut the phone line to the Wheeler house to prevent word from spreading.
Knowing that exploration companies and speculators would descend in droves on the town once word got out, Slick protected his investment. Just how he did so would be described by a frustrated competing lease man to his boss:
You see, sir, Slick and Shaffer roped off their well on the Wheeler farm and posted guards and nobody can get near it…I got a call yesterday at the hotel in Cushing from a friend who said they had struck oil out there. A friend of his was listening in on the party line and heard the driller call Tom Slick at the farm where he’s been boarding and said they’d hit.

Pump stations in the Cushing oilfield, 1910-1918, from the Oklahoma Historical Society. More than 50 refineries once operated in the Cushing area about 50 miles west of Tulsa. Pipelines and storage facilities have since made it “the pipeline crossroads of the world.”
Well, I rushed down to the livery stable to get a rig to go out and do some leasing and damned if Slick hadn’t already been there and hired every rig. Not only there, but every other stable in town. They all had the barns locked and the horses out to pasture. There’s 25 rigs for hire in Cushing and he had them all for ten days at $4.50 a day apiece, so you know he really thinks he’s got something.

I went looking for a farm wagon to hire and had to walk three miles. Some other scouts had already gotten the wagons on the first farms I hit. Soon as I got one I beat it back to town to pick up a notary public to carry along with me to get leases — and damned if Slick hadn’t hired every notary in town, too.
Eleven days later the news had spread. As a leasing frenzy grew the Tryon Star reported, “Our old friend Tom Slick the oilman has struck it rich…Slick has been plugging away for several years and has put down several dry holes…He deserves this success and here’s hoping that it will make Tom his millions.”
New King of the Wildcatters
Tom Slick’s No. 1 Wheeler was the discovery well for the prolific Drumright-Cushing oilfield, which produced for the next 35 years, reaching 330,000 barrels every day at its peak.

Oklahoma’s Drumright Historical Society Museum includes the town’s 1915 Santa Fe Railroad Depot, which is listed in the National Register of Historic Places.
Slick was suddenly a very rich man. After his dramatic success in Drumright and Cushing, he began an incredible 18-year streak of discoveries in some of the nation’s most prolific oilfields. Visit the Drumright Historical Society Museum.
Slick was active in the Seminole Area, especially the oilfields of Pioneer, Tonkawa, Papoose, and Seminole. He secured leases and drilled wells that consistently paid off.
Slick’s oil gushers were spectacular: No. 4 Eakin — 10,000 barrels per day; No. 1 Laura Endicott — 4,500 barrels per day; No. 1 Walker — 5,000 barrels per day; No. 1 Franks — 5,000 barrels per day (see Greater Seminole Oil Boom).

Reflecting on his fortunes late in his career, he noted, “If I strike oil everyone calls it Tom Slick’s luck, (but) I call it largely judgment based upon experience. Some folks don’t recognize good luck when they meet it in the middle of the road. So I have been fortunate, or lucky, whichever you call it, but I’ve also done a lot of calling good luck to bring it my way.”

Newly discovered oilfields of the mid-1920s brought prosperity — and traffic jams — to Seminole, Oklahoma. Photo courtesy the Oklahoma Oil Museum.
Slick’s leases in Oklahoma, Kansas, and Texas produced millions of barrels of oil. Production from his wells reached 35,000 barrels of oil a day 1929, and he was proclaimed the largest independent oil operator in the United States with a net worth estimated from $35 million and up to $100 million.
By 1930, in the Oklahoma City field alone, Slick had 45 wells being drilled, more than 30 wells completed, and the capacity to produce 200,000 barrels of crude daily. Across the Mid-Continent, stories of Tom Slick’s business acumen and integrity grew with his fortune.
It was often told how Slick once closed a $100,000 deal for a prized Seminole lease on a street corner. He met the owner on the street and inquired, “What do you want for that lease’ ‘A hundred thousand dollars,’ replied the owner. ‘It’s a sale, bring in your deeds,’ said Slick.”

Thomas B. Slick is among those honored at an outdoor plaza at the Sam Noble Museum, University of Oklahoma, in Norman.
Thomas B. Slick’s death from a stroke in August 1930 at the age of 46 abruptly ended a career that had helped supply an energy hungry nation with the petroleum it needed to grow.
“Oil derricks in the Oklahoma City Field stood silent for one hour in tribute,” reported the Oklahoma Historical Society. Slick’s biggest strike came a week after he died when his Campbell No. 1 well in Oklahoma City produced 43,200 barrels of oil per day.

Stories about the “King of the Wildcatters” and his oilfield discoveries would spread across the Mid-Continent. Thomas B. Slick, — no longer known as “Mad Tom” or “Dry Hole Slick” — joined other Oklahoma petroleum industry leaders honored at the Conoco Oil Pioneers of Oklahoma Plaza.
By the end of the 20th century, more than one-half million Oklahoma oil and natural gas wells were drilled since an oilfield discovery at Bartlesville in 1897 (learn more in First Oklahoma Oil Well).
More about Slick and his extraordinary oilfield career can be found King of the Wildcatters, the Life and Times of Tom Slick, 1883–1930 by Ray Miles, professor of history and dean of the college of liberal arts at McNeese State University, Lake Charles, Louisiana.
For example, Miles relates that in 1933, a friend and business partner of the Oklahoma wildcatter was kidnapped and held for ransom. Once released, Charles Urschel assisted the FBI in catching his abductors, including George “Machine Gun” Kelly, who was sentenced to life in Alcatraz.
_______________________
Recommended Reading: King of the Wildcatters, the Life and Times of Tom Slick, 1883–1930. (2004); The Oklahoma City Oil Field in Pictures (2005); The Oklahoma Petroleum Industry
(2005); The Oklahoma Petroleum Industry (1980). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(1980). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Become an AOGHS annual supporting member and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. © 2024 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
Citation Information – Article Title: “Oklahoma’s King of the Wildcatters.” Authors: B.A. Wells and K.L. Wells. Website Name: American Oil & Gas Historical Society. URL: https://aoghs.org/petroleum-pioneers/wildcatter-tom-slick. Last Updated: December 30, 2023. Original Published Date: December 1, 2004.
by Bruce Wells | Mar 4, 2024 | This Week in Petroleum History
March 4, 1918 – West Virginia Well sets World Depth Record –
Hope Natural Gas Company completed an oil well at a depth of 7,386 feet on the Martha Goff farm in Harrison County, West Virginia. The well, drilled northeast of Clarksburg using cable-tools, was the world’s deepest at the time — until surpassed by a 1919 well drilled in nearby Marion County. The previous world depth record had been 7,345 feet for a well in Germany.

This 1918 West Virginia oil well was the world’s deepest. Photo courtesy West Virginia Oil and Natural Gas Association.
In 1953, the New York State Natural Gas Corporation claimed the world’s deepest cable-tool well at a depth of 11,145 feet near the New York town of Van Etten. By 2018, a rotary rig depth record was reached by a Russian well drilled 40,502 feet deep on Sakhalin Island.

March 4, 1933 – Oklahoma City Oilfield under Martial Law
Oklahoma Governor William H. “Alfalfa Bill” Murray declared martial law to enforce his regulations strictly limiting production in the Oklahoma City oilfield, discovered in December 1928. Two years earlier, Murray had called a meeting of fellow governors from Texas, Kansas and New Mexico to create an Oil States Advisory Committee, “to study the present distressed condition of the petroleum industry.”

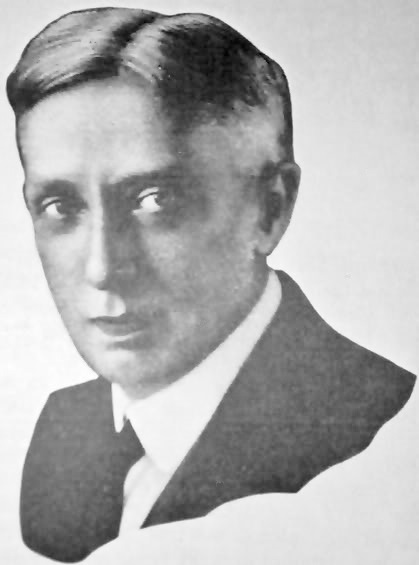
William “Alfalfa Bill” Murray in 1932.
Elected in 1930, the controversial politician was called “Alfalfa Bill” because of speeches urging farmers to plant alfalfa to restore nitrogen to the soil. By the end of his administration, Murray had called out the National Guard 47 times and declared martial law more than 30 times. He was succeeded as Oklahoma governor by E.W. Marland in 1935.
March 4, 1938 – Giant Oilfield discovery in Arkansas
The Kerr-Lynn Oil Company (a Kerr-McGee predecessor) completed its Barnett No. 1 well east of Magnolia, Arkansas, discovering the giant Magnolia oilfield, which would become the largest producing field (in volume) during the early years of World War II, helping to fuel the American war effort.

Crew members stand in front of their 1938 giant oilfield discovery well at Magnolia, Arkansas. Photo courtesy W.B. “Buzz” Sawyer.
The southern Arkansas gusher launched a Columbia County oil boom similar to Union County’s Busey-Armstrong No. 1 well southwest of El Dorado in January 1921.
March 5, 1895 – First Wyoming Refinery produces Lubricants
Near the Chicago & North Western railroad tracks in Casper, Civil War veteran Philip “Mark” Shannon and his Pennsylvania investors opened Wyoming’s first refinery. It could produce 100 barrels a day of 15 different grades of lubricant, from “light cylinder oil” to heavy grease. Shannon and his associates incorporated as Pennsylvania Oil and Gas Company.

The original Casper oil refinery in Wyoming, circa 1895. Photo courtesy Wyoming Tales and Trails.
By 1904, Shannon’s company owned 14 wells in the Salt Creek field, about 45 miles from the company’s refinery (two days by wagon). Each well produced up to 40 barrels of oil per day. Despite Casper’s improved railroad access, transportation costs meant Wyoming oil could not compete for eastern markets. The state’s first petroleum boom would have to wait until 1908, when Salt Creek’s “Big Dutch” well was completed.
Learn more in First Wyoming Oil Wells.

March 6, 1935 – Search for First Utah Oil proves Deadly
More than a decade before Utah’s first commercial oil wells, residents of St. George had hoped the “shooting” of a well drilled by Arrowhead Petroleum Company would bring black gold prosperity. A crowd had gathered to watch as workers prepared six, 10-foot-long explosive canisters to fracture the 3,200-foot-deep Escalante No. 1 well.
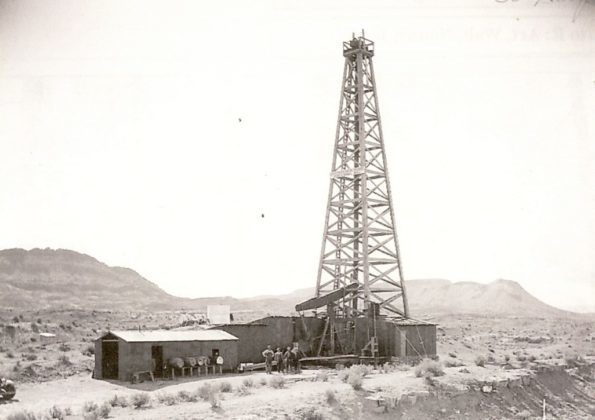

A 1935 attempt to find oil in Utah proved deadly. Photo courtesy Washington County Historical Society.
An explosion occurred as the torpedoes, “each loaded with nitroglycerin and TNT and hanging from the derrick,” were being lowered into the well. Ten people died from the detonations, which “sent a shaft of fire into the night that was seen as far as 18 miles away.”
The 1935 accident has remained the worst oil-related disaster in Utah, according to The Escalante Well Incident, a 2007 historical account.
March 6, 1981 — Shale Revolution begins in North Texas
Mitchell Energy and Development Corporation drilled its C.W. Slay No. 1 well, the first commercial natural gas well of the Barnett shale formation. Over the next four years, the vertical well in North Texas produced nearly a billion cubic feet of gas, but it would take almost two decades to perfect cost-effective shale fracturing methods combined with horizontal drilling.
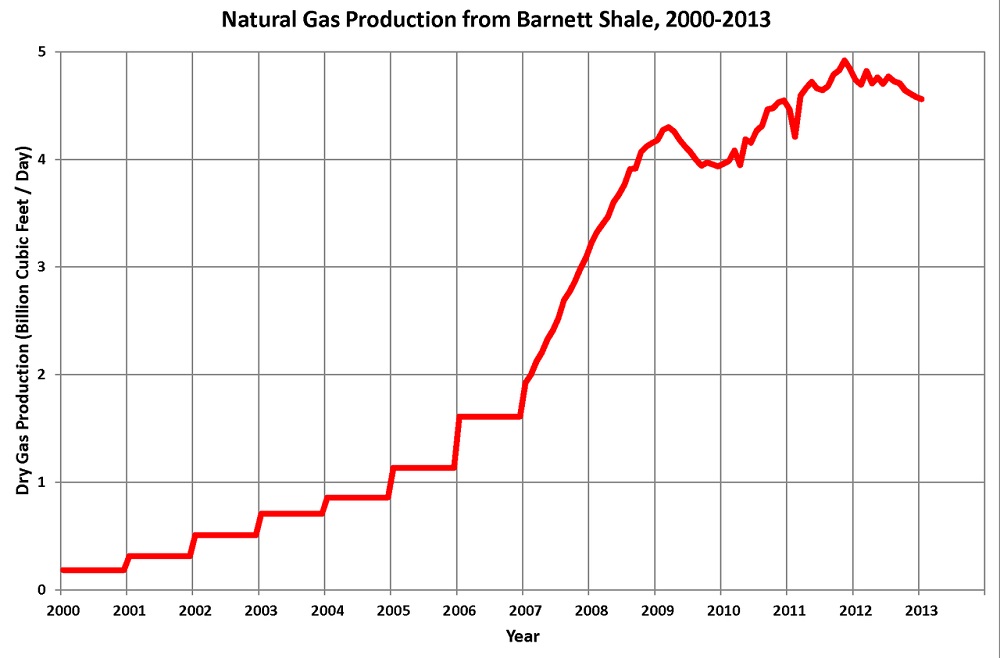
Production from the Barnett shale formation extends from Dallas west and south, covering 5,000 square miles, according to the Texas Railroad Commission. Chart courtesy Dan Plazak.
Mitchell Energy’s 7,500-foot-deep well and others in Wise County helped evaluate seismic and fracturing data to understand deep shale structures. “The C.W. Slay No. 1 and the subsequent wells drilled into the Barnett formation laid the foundation for the shale revolution, proving that natural gas could be extracted from the dense, black rock thousands of feet underground,” the Dallas Morning News later declared.
By the end of 2012, with almost 14,000 wells drilled in the largest gas field in Texas, production started to decline, but the Barnett field still accounted for 6.1 percent of Texas natural gas production and 1.8 percent of the U.S. supply, according to the Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas.
March 7, 1902 – Oil discovered at Sour Lake, Texas
Adding to the giant oilfields of Texas, the Sour Lake field was discovered about 20 miles west of the world-famous Spindletop gusher of January 1901. The spa town of Sour Lake quickly became a boom town where major oil companies, including Texaco, got their start.

“The resort town of Sour Lake, 20 miles northwest of Beaumont, was transformed into an oil boom town when a gusher was hit in 1902,” notes the Texas State Library and Archives Commission.
Originally settled in 1835 and called Sour Lake Springs because of its “sulphureus spring water” known for healing, the sulfur wells attracted many exploration companies. Some petroleum geologists predicted a Sour Lake salt dome formation similar to that revealed by Pattillo Higgins, the Prophet of Spindletop.
Sour Lake’s 1902 discovery well was the second attempt of the Great Western Company. The well, drilled “north of the old hotel building,” penetrated 40 feet of oil sands before reaching a total depth of about 700 feet. The Hardin County’s salt dome oilfield yielded almost nine million barrels of oil by 1903, when the Texas Company made its first major oil find at Sour Lake.
Learn more in Sour Lake produces Texaco.

March 7, 2007 – National Artificial Reef Plan updated
The National Marine Fisheries Service of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), approved a comprehensive update of the 1985 National Artificial Reef Plan, popularly known as the “rigs to reefs” program.

A typical platform provides almost three acres of feeding habitat for thousands of species. Photo courtesy U.S. Bureau of Safety and Environmental Enforcement.
The agency worked with interstate marine commissions and state artificial reef programs, “to promote and facilitate responsible and effective artificial reef use based on the best scientific information available.” The revised National Artificial Reef Plan included guidelines for converting old platforms into reefs. A typical four-leg structure provides up to three acres of habitat for hundreds of marine species.
“As of December 2021, 573 platforms previously installed on the U.S. Outer Continental Shelf have been reefed in the Gulf of Mexico,” according to the Bureau of Safety and Environmental Enforcement (BSEE).
Learn more in Rigs to Reefs.
March 9, 1930 – Prototype Oil Tanker is Electrically Welded
The world’s first electrically welded commercial vessel, the Texas Company (later Texaco) tanker M/S Carolinian, was completed in Charleston, South Carolina. The World War I shipbuilding boom had encouraged new electric welding technologies. The oil company’s 226-ton vessel was a prototype designed by naval architect Richard Smith.

Construction of M/S Carolinian began in 1929. The M/S designation meant it used an internal combustion engine. Photo courtesy Z.P. Liollio.
The tanker — the first electrically welded ship — eliminated the need for about 85,000 pounds of rivets, according to a 2017 article for the International Committee for the Conservation of the Industrial Heritage (TICCIH). Success of the prototype led to “the standard of welded hulls and internal combustion engines would become universal in construction of new vessels.”

March 9, 1959 – Barbie is a Petroleum Doll
Mattel revealed the Barbie Doll at the American Toy Fair in New York City. More than one billion “dolls in the Barbie family” have been sold since. Eleven inches tall, Barbie owes her existence to petroleum products and the science of polymerization, including several plastic acronyms: ABS, EVA, PBT, and PVC.

Petroleum-based polymers are part of Barbie’s DNA.
Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS) is known for strength and flexibility. This thermoplastic polymer is used in Barbie’s torso to provide impact and heat resistance. EVA (Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate), a copolymer made up of ethylene and vinyl acetate, protects Barbie’s smooth surface.
The Mattel doll also includes Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT), a thermoplastic polymer often used as an electrical insulator. A mineral component facilitates PBT injection molding of her “full figure,” according to the company. Barbie’s hair and many of her designer outfits are made from the world’s first synthetic fiber, nylon, invented in 1935 (see Nylon, a Petroleum Polymer).
_______________________
Recommended Reading: Where it all began: The story of the people and places where the oil & gas industry began: West Virginia and southeastern Ohio (1994); Kettles and Crackers – A History of Wyoming Oil Refineries
(1994); Kettles and Crackers – A History of Wyoming Oil Refineries (2016); Utah Oil Shale: Science, Technology, and Policy Perspectives
(2016); Utah Oil Shale: Science, Technology, and Policy Perspectives (2016); George P. Mitchell: Fracking, Sustainability, and an Unorthodox Quest to Save the Planet (2019); Sour Lake, Texas: From Mud Baths to Millionaires, 1835-1909
(2016); George P. Mitchell: Fracking, Sustainability, and an Unorthodox Quest to Save the Planet (2019); Sour Lake, Texas: From Mud Baths to Millionaires, 1835-1909 (1995); Rigs-to-reefs: the use of obsolete petroleum structures as artificial reefs
(1995); Rigs-to-reefs: the use of obsolete petroleum structures as artificial reefs (1987); Plastic: The Making of a Synthetic Century Hardcover
(1987); Plastic: The Making of a Synthetic Century Hardcover (1996); American Fads
(1996); American Fads (1985). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(1985). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Please become an AOGHS annual supporter and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2024 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
by Bruce Wells | Mar 1, 2024 | Petroleum Pioneers
As drillers and speculators rushed to Spindletop Hill, the Texas Company organized in 1902.
A series of oil and natural gas discoveries at Sour Lake, Texas — near the famous 1901 gusher at Beaumont — helped launch the major oil company Texaco.
Originally known as Sour Lake Springs because of sulfurous spring water popular for its healing properties, a series of oil discoveries brought wealth and new petroleum companies to Hardin County in southeastern Texas.

“A forest of oil well derricks at Sour Lake, Texas,” is from the W.D. Hornaday Collection, Texas State Library and Archives Commission, Austin. Oil discoveries at the resort town northwest of the world-famous Spindletop gusher of 1901 would transform the Texas Company.
As the science of petroleum exploration and production evolved, some geologists predicted oil was trapped at a salt dome at Sour Lake similar to that of Beaumont’s Spindletop Hill formation, which was producing massive amounts of oil.
According to Charles Warner in Texas Oil & Gas Since 1543, in November 1901 an exploratory well found “hot salt water impregnated with sulfur between 800 and 850 feet…and four oil sands about 10 feet thick at a depth of approximately 1,040 feet.”
Warner noted that the Sour Lake Springs field’s discovery well came four months later when a second attempt by the Great Western Company drilled “north of the old hotel building” in the vicinity of earlier shallow wells.

“This well secured gusher production at a depth of approximately 683 feet on March 7, 1902,” Warner reported. “The well penetrated 40 feet of oil sand. The flow of oil was accompanied by a considerable amount of loose sand, and it was necessary to close the well in from time to time and bail out the sand, after which the well would respond with excellent flows.”

A monument marks the site where in 1903 the Fee No. 3 well flowed at 5,000 barrels of oil a day, launching the Texas Company into becoming Texaco.
As more discoveries followed, Joseph “Buckskin Joe” Cullinan and Arnold Schlaet were among those who rushed to the area from their offices in Beaumont.
The Texas Company
The most significant company started during the Spindletop oil boom was The Texas Company, according to one historian.

“Cullinan worked in the Pennsylvania oil industry and later went to Corsicana, Texas, about 1898 when oil was first discovered in that district where he became the most prosperous operator in the field,” reported Elton Gish in his “History of the Texas Company and Port Arthur Works Refinery.”
Cullinan formed the Petroleum Iron Works, building oil storage tanks in the Beaumont area — where he was introduced to Schlaet. “When the Spindletop boom came in January 1901, Mr. Cullinan decided to visit Beaumont,” Gish noted. Schlaet managed the oil business of two brothers, New York leather merchants.

Named after its original New York City telegraph office address, Texaco’s name became official in 1959.
“Schlaet’s field superintendent, Charles Miller, traveled to Beaumont in 1901 to witness the Spindletop activity and met with Cullinan, whom he knew from the oil business in Pennsylvania. He liked Cullinan’s plans and asked Schlaet to join them in Beaumont.”
According to Texaco, Cullinan and Schlaet formed the Texas Company on April 7, 1902, by absorbing the Texas Fuel Company and inheriting its office in Beaumont. Texas Fuel had organized just one year earlier to purchase Spindletop oil, develop storage and transportation networks, and sell the oil to northern refineries.

By November 1902, the new Texas Company was establishing a new refinery in Port Arthur as well as 20 storage tanks, building its first marine vessel, and equipping an oil terminal to serve sugar plantations along the Mississippi River.
Fee No. 3 Discovery
The Texas Company struck oil at Sour Lake Springs in January 1903, “after gambling its future on the site’s drilling rights,” the company explained. “The discovery, during a heavy downpour near Sour Lake’s mineral springs, turned the company into a major oil producer overnight, validating the risk-taking insight of company co-founder J.S. Cullinan and the ability of driller Walter Sharp.”

A Texaco station was among the 2012 indoor exhibits featured at the National Route 66 Museum in Elk City, Oklahoma. Photo by Bruce Wells.
Their 1903 Hardin County discovery at Sour Lake Springs — the Fee No. 3 well — flowed at 5,000 barrels a day, securing the Texas Company’s success in petroleum exploration, production, transportation and refining. Sharp would found the Sharp-Hughes Tool Company in 1908 with Howard Hughes Sr.
High oil production levels from the Sour Lake field and other successful wells in the Humble oilfield (1905), secured the company’s financial base, according to L. W. Kemp and Cherie Voris in Handbook of Texas Online.

“In 1905 the Texas Company linked these two fields by pipelines to Port Arthur, ninety miles away, and built its first refinery there. That same year the company acquired an asphalt refinery at nearby Port Neches,” the authors noted.
“In 1908 the company completed the ambitious venture of a pipeline from the Glenn Pool, in the Indian Territory (now Oklahoma), to its Southeast Texas refineries,” added Kemp and Voris. “As early as 1905 the Texas Company had established marketing facilities not only throughout the United States, but also in Belgium, Luxembourg, and Panama.”

The Texas Company registered its “Texaco” trademark in 1909.
The telegraph address for the company’s New York office is “Texaco” — a name soon applied to its products. The company registered its first trademark, the original red star with a green capital letter “T” superimposed on it in 1909. The letter remained an essential component of the logo for decades. By 1928 the company operated more than 4,000 gasoline stations in 48 states.
The Texas Company officially renamed itself Texaco in 1959. It purchased Getty Oil Company in 1984. On October 9, 2001, Chevron Corp. and Texaco agreed to form a merger that created ChevronTexaco, renamed simply Chevron in 2005.

Although the Sour Lake Springs oil boom soon was surpassed by other Texas discoveries, Sour Lake proudly promotes itself as the birthplace of Texaco.
Learn more Spindletop history in Spindletop creates Modern Petroleum Industry. Also see Prophet of Spindletop.
_______________________
Recommended Reading: The Texaco Story, The First Fifty Years 1902 – 1952 by Texas Company (1952). Texaco’s Port Arthur Works, A Legacy of Spindletop and Sour Lake (2003); Giant Under the Hill: A History of the Spindletop Oil Discovery (2008). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(2008). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Become an AOGHS annual supporting member and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2024 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
Citation Information – Article Title: “Sour Lake produces Texaco.” Authors: B.A. Wells and K.L. Wells. Website Name: American Oil & Gas Historical Society. URL: https://aoghs.org/petroleum-pioneers/sour-lake-produces-texaco. Last Updated: March 1, 2024. Original Published Date: April 5, 2014.
by Bruce Wells | Feb 29, 2024 | Petroleum Companies
Although successful oil wells had been drilled as early as 1901, oil fever arrived in Montana with the October 1915 discovery of the Elk Basin oilfield in Carbon County.
More discoveries came at the Cat Creek oilfield in 1920 and in the Kevin-Sunburst oilfield of 1922, both of which motivated businessmen in Miles City to form the Montana Bell Oil & Gas Company. They filed to do business in the state on March 8, 1924, but their timing was terrible.
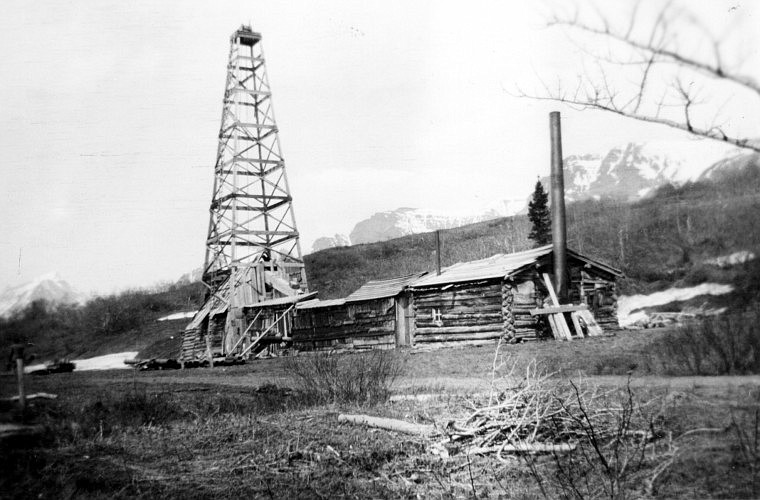

Montana’s first oil well was drilled in 1901 in the Kintla Lake area that’s now part of Glacier National Park. Photo courtesy Daily Inter Lake, Kalispell, Montana.
In the last few months of 1924 alone, a financial crisis described by Montana’s superintendent of banks as a “veritable nightmare” closed 191 banks.
Bankrupt in Montana
Between 1921 and 1926, no state had more bankruptcies than Montana. Newspapers reported in 1924 reported “the tremulous activity” of Montana Belle Oil that “may be expected in this country within the year, unless present plans halted.”

Nonetheless, Montana Belle Oil & Gas was able to secure a mineral lease from Adolph F. Loesch west of Miles City in April 1926. The company selected a drilling site for its first well in typically foreboding southeast Montana (see Public Land Survey System, Northeast Quarter of Section 28, Township 8 North, Range 45 East).
Drilling the wildcat well during hard financial times and in a remote location slowed progress. Legal issues also troubled the company, according to reports in the Billings Gazette.
“With the settlement of differences arising without recourse to the courts, the officers of the Montana Belle Oil & Gas company are preparing to proceed,” the newspaper noted in January 1928.
“Drilling in the Montana Belle Oil and Gas company well, located about twelve miles west of this city is proceeding 24 hours a day,” the reporter added.
Using dated cable-tool drilling technology, the company reached a depth of 1,035 feet. The Billings Gazette reported the company’s objective was a depth of 1,750 feet, “in accordance with the report of the geologist who has made a survey and examination of the earth strata, and at which it is expected that results will follow. Gas is also in evidence in the hole.”

Investors and stockholders were encouraged that the well was “showing some light oil though not in commercial quantities.” The drilling continued into deeper formations. On October 24, 1929 — “Black Thursday” — the U.S. stock market crashed, launching the Great Depression.
In December 1929, five years after incorporating, Montana Belle Oil and Gas Company’s only oil well shut down for the winter. It reportedly had reach the impressive depth of 4,562 feet, but drilling never resumed. Montana Belle Oil and Gas Company failed in 1930, as did Miles City’s oil refinery and many other oilfield businesses.
The first Montana oil well was drilled in 1901 in the Kintla Lake area, later part of Glacier National Park. More about the state’s petroleum history can be found in the 2011 article “Montana’s first oil well was drilled at Kintla Lake in 1901.”
_______________________
The stories of exploration and production companies joining petroleum booms (and avoiding busts) can be found updated in Is my Old Oil Stock worth Anything? Become an AOGHS annual supporting member and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2024Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
Citation Information – Article Title: “Montana Belle Oil & Gas Company.” Authors: B.A. Wells and K.L. Wells. Website Name: American Oil & Gas Historical Society. URL: https://aoghs.org/old-oil-stocks/montana-belle-oil-amp-gas-company. Last Updated: February 29, 2024. Original Published Date: April 13, 2022.
by Bruce Wells | Feb 14, 2024 | Petroleum Technology
Public fascination with mid-continent “black gold” discoveries briefly switched to natural gas in 1906.
As petroleum exploration wells reached deeper by the early 1900s, highly pressurized natural gas formations in Kansas and the Indian Territory challenged well-control technologies of the day.
Once ignited by a lightning bolt, the natural gas well of Caney, Kansas, towered 150 feet high and at night could be seen for 35 miles. The conflagration made national headlines, attracting a host of exploration companies to drill into Mid-Continent oilfields — even as well control technologies tried to catch up.
(more…)







(2005); The Oklahoma Petroleum Industry
(1980). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.


















