by Bruce Wells | Jun 26, 2024 | Petroleum Companies
Arkansas oilfield discoveries as early as the 1920s created boom towns and launched the state’s petroleum industry. In the 1950s, Arkansas Oil Ventures would try but fail to be part of a resurgence in drilling.
Arkansas’ first commercial oil well was drilled in 1921 at El Dorado in Union County, 15 miles north of the Louisiana border. The 68-square-mile field led U.S. oil output by 1925 with production reaching 70 million barrels of oil. (more…)
by Bruce Wells | Jun 11, 2024 | Petroleum Companies
When Edwin L. Drake drilled the first U.S. oil well in 1859 along a creek at Titusville, Pennsylvania, he transformed the landscape of the Allegheny River valley — and America’s energy future. The former railroad conductor’s discovery launched a new industry as investors and drillers rushed to cash in on the new resource for making kerosene for lamps.
Wallace Oil Company would be among the earliest U.S. petroleum companies, and the venture’s fate would presage the riskiness of America’s new exploration and production industry.

Grocery store owner John Wallace formed the Wallace Oil Company in 1865 to drill for “black gold.” Detail from Wallace Oil Company stock certificate.
The ensuing scramble fueled the nation’s first petroleum drilling boom. Newspapers reported discoveries on farms clustered in Northwestern Pennsylvania’s “oil region.”
Newly incorporated oil companies rushed to construct wooden derricks with steam-powered cable tools for “making hole.”

Drillers came to John Rynd’s farm at the junction of Oil Creek and Cherry Tree Run, the Blood farm to the north, and the widow McClintock farm to the south.
Pennsylvania Oil Fever
Operating a grocery store on the Rynd farm in 1859, Irish immigrant John Wallace witnessed the excitement firsthand. When the first of many wells found oil on the farm in 1861, derricks already crowded nearby hillsides. Four years later, the 24-year-old entrepreneur caught oil fever and incorporated Wallace Oil Company in 1865 with an office at 319 Walnut Street in Philadelphia.
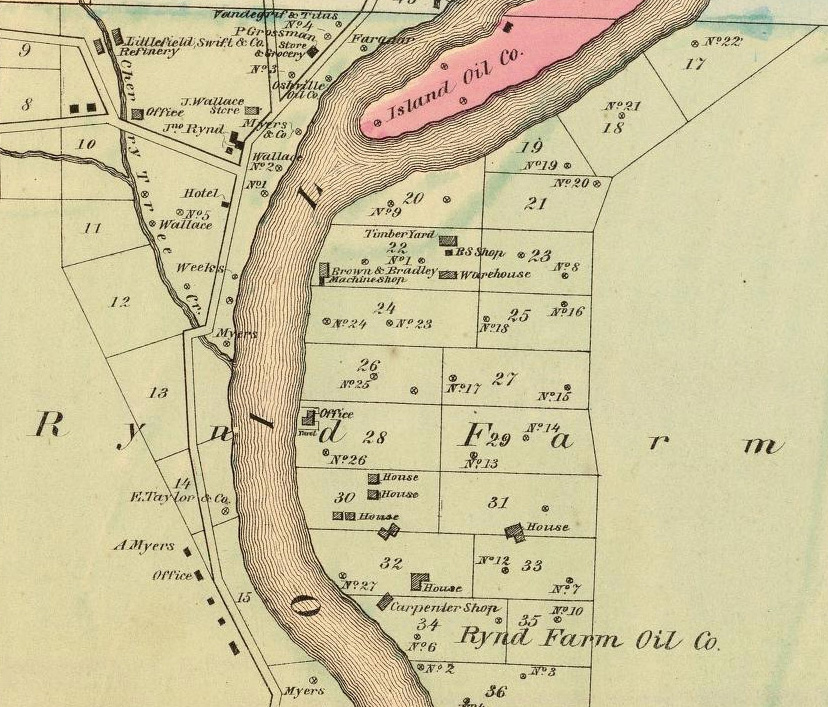
After witnessing the oil region’s drilling boom from his Rynd farm grocery store, John Wallace caught oil fever. “Oil Region of Pennsylvania,1865” map courtesy David Rumsey Historical Map Collection, F.W. Beers & Co.
With the science of petroleum geology in its infancy, “creekology” and oil seeps often were the only tools for finding promising locations to drill. Some exploration companies turned to dowsing (hazel or peach tree rods preferred) to find oil.
Wallace’s company sold stock certificates and acquired a 3/32 royalty interest in a 200-acre tract on the neighboring McClintock farm (previously owned by investors Curtiss, Haldeman, and Fawcett).
Although records offer no evidence of Wallace Oil Company actually drilling and completing a well, Wallace’s lease trading speculations, financed by his 3/32 royalty income, and energetic sales of stock, made the company money.

A circa 1875 building at Rouseville in the Pennsylvania oil region hosted an attorney, lease agents, a small oil exchange, and petroleum companies like Wallace Oil Company. Detail from stereograph “Pleasant morning – Rouseville,” courtesy Library of Congress.
Purchasers of Wallace’s stock stood to gain from both royalties and appreciation. The financial horizon looked promising. In 1865, a 42-gallon barrel of oil sold for $6.59 a barrel (nearly $100 in 2013 dollars).
Boom and Bust
As the gamble to find oil spread, Pithole Creek and other oilfield discoveries inspired more drilling — and speculation at oil exchanges in Titusville, Oil City, and elsewhere.

Those seeking petroleum riches in 1864 included John Wilkes Booth, whose Dramatic Oil Company drilled on a 3.5-acre lease on the Fuller farm.
By the end of 1869, Wallace Oil Company ‘s McClintock farm leases still produced an average of 200 barrels of oil daily from 32 wells. It took three more years before Wallace Oil Company paid its first and only dividend to investors, who received one cent per share in 1874. But by then, one industry publication noted, “oil had left the territory.”
The company dutifully paid the state an annual “Tax on Stock,” and in 1871 paid its first “Tax on Income.”
A circa 1875 Library of Congress stereograph of a small building includes signs for the “Wallace Oil Company,” the “Allegheny & Pittsburgh Oil Co.,” the “Oil Basin Petroleum Co.,” the “Buchanan Royalty Oil Co.,” and the “Rouseville Oil Co.”
Rouseville in 1861 had been the scene of a deadly oil well fire, one the earliest fatal conflagrations of the U.S. oil and natural gas industry.
By the early 1890s, Wallace Oil Company’s expanded oil-region holdings were reduced to the original 3/32 royalty from its McClintock property, which no longer produced commercial quantities of oil. Overproduction had drained profitability from the countryside.

In August 1895, American Investor reported Wallace Oil Company had lost its wells and property and could not even muster resources to pay legal fees associated with formal dissolution of the company. The grim assessment concluded, “The company is in a hopeless condition. The stock has no market value.”
Visit the Drake Well Museum and Park in Titusville.
The stories of exploration and production companies joining petroleum booms (and avoiding busts) can be found in Is my Old Oil Stock worth Anything?
_______________________
Recommended Reading: Trek of the Oil Finders: A History of Exploration for Petroleum (1975); Myth, Legend, Reality: Edwin Laurentine Drake and the Early Oil Industry (2009). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(2009). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Please become an AOGHS annual supporter and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. © 2024 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
Citation Information – Article Title: “Wallace Oil Company.” Authors: B.A. Wells and K.L. Wells. Website Name: American Oil & Gas Historical Society. URL: https: https://aoghs.org/old-oil-stocks/wallace-oil-company. Last Updated: June 11, 2024. Original Published Date: June 17, 2021.
by Bruce Wells | May 15, 2024 | Petroleum Companies
Widely publicized drilling booms attracted investors seeking “black gold” riches — real or imagined.
Exaggerated, questionable, and sometimes fraudulent claims by shady business ventures seeking investors grew in the years following World War I. As the Great Depression approached, many states passed “blue sky laws” to regulate securities sales and protect the public from fraud.
It would take an act of Congress in 1934 to stop skilled business hucksters from taking advantage of unwary investors seeking often fictional profits. Federal lawmakers established the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to help rein in exaggerated claims found in newspaper advertisements, mail solicitations, and other stock promotions.

Widely publicized giant oilfield discoveries at Burkburnett, Texas, in 1918 (above) and nearby “Roaring Ranger” one year earlier led to many inexperienced exploration ventures and exaggerated promotions. Photo courtesy Library of Congress
Since the U.S. petroleum industry’s earliest booms and busts in Pennsylvania following the Civil War, the need for dependable information and early financial centers — petroleum exchanges — led to a new profession — the oil scout.

As demand for refined kerosene for lamps grew, the search for new oilfields moved to mid-continent. Thousands of exploration and production companies were established. Most drilled dry holes. When wildcat wells (remote) revealed giant oil and natural fields in Texas and Oklahoma, a new generation of business financing hucksters took advantage.
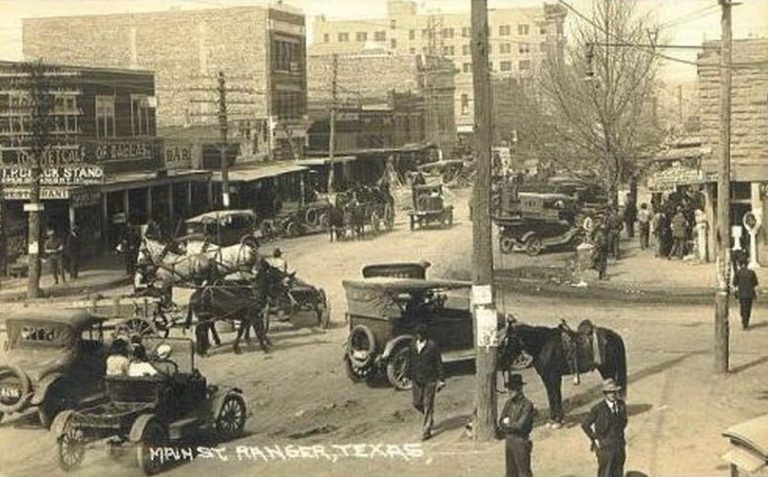

The J.H. McCleskey No. 1 discovery well of October 1917 created a massive oil boom at Ranger and across Eastland County, Texas. Photo courtesy Library of Congress.
Giant oilfield discoveries in North Texas made headlines, leading to the hundreds of new exploration companies (see Is my Old Oil Stock worth Anything?). Many began by seeking capital from local investors, often banks, doctors, and civic leaders. Financial swindlers saw opportunities to take advantage of oilfield discoveries and the resulting oil fever.
Newspapers nationwide reported wells with geysers of oil at Electra (1911), Ranger (1917), and the “World’s Wonder Oilfield” of Boom Town Burkburnett (1918). Publicity about these oil booms rekindled enthusiasm for Texas petroleum riches not seen since the giant oilfield discovery at Spindletop Hill in 1901, the famous “Lucas Gusher.”

Sudden, unexpected “black gold” or “Texas tea” wealth brought prosperity to struggling farming communities. Thanks to the Ranger oilfield, Eastland County’s Merriman Baptist Church (and graveyard) was once declared the richest church in America.
Black Gold Dreams
Criminals specializing in financial deception joined the influx of drilling contractors, workers, equipment suppliers, lease brokers, and associated oilfield service companies. In part to combat fraud in North Texas, the American Association of Petroleum Geologists (AAPG), founded in 1917, American Petroleum Institute (API), founded in 1919, and other industry associations organized.
With so many oil boom-inspired companies forming so quickly, the rapid printing of eye-catching but boiler-plate stock certificates often occurred (see Oil Prospects Inc. for one of the most common certificate vignettes).

In a rush to find investors, quickly formed exploration companies ended up using the same oilfield scene for stock certificates. It might have saved time and money by choosing a printer’s common vignette.
Already iconic U.S. boom towns and busts (see the remarkable 1865 rise and fall of Pithole, Pennsylvania) would help launch major companies like Marathon and Texaco, as did the first California oil wells. New petroleum discoveries attracted experienced companies — and many more inexperienced exploration and production ventures that aggressively sought leases, equipment and men, and investors.
However, with little knowledge of the new science of petroleum geology and drilling technologies, few of newly formed companies would find oil. Most did not survive long in the highly competitive oilfields.

Crowding too many wells on leases and a lack of infrastructure for storing and transporting oil harmed the environment. Many companies learned from hard experience, but more went bankrupt without ever finding oil.
Competing exploration companies, lacking petroleum engineers and efficient production technologies, often overproduced geological formations. Unchecked drilling and oversupply in the oil market led prices to collapse as low as 15 cents per 42-gallon oil barrel in the giant East Texas oilfield of the 1930s.
Huckster of Hog Creek
The lure black gold also attracted skilled confidence men who could create oil companies on paper. J.W. “Hog Creek” Carruth was among the most notorious.
Financial World in 1912 described “Hog Creek” Carruth as a con man who made a fortune selling worthless oil stocks. The magazine also cited the far better known infamous explorer Dr. Frederick Cook (learn more in Arctic Explorer turned Oil Promoter).
In September 1918 a discovery well near Desdemona blew in after reaching a depth of 2,960 feet, initially producing 2,000 barrels of oil a day. “Unlike Ranger, Desdemona was a small operator’s field. Production reached a peak of 7,375,825 barrels in 1919, and then dropped sharply, chiefly because of over drilling,” according to the Handbook of Texas Online.
“Hog Creek” Carruth proclaimed himself to be the discoverer of the Desdemona oilfield (he was not). He advertised expansively to sell worthless stocks inflated by his phony reputation.
Pilgrim Oil Company
Pilgrim Oil Company formed as a common law trust estate (unincorporated business managed by trustees) in Fort Worth, Texas, on December 20, 1920. The company’s trustees included George M. Richardson and Warren H. Hollister. and was capitalized at $1 million with 100,000 shares offered at par value of $10.
The petroleum company, another fraudulent enterprise of J.W. “Hog Creek” Carruth, would be his last.

J.W. “Hog Creek” Carruth falsely claimed to have discovered the Desdemona, oilfield, along Hogg Creek. Detail from circa 1919 panoramic photo courtesy Library of Congress.
The oilfield along Hog Creek had been discovered in 1918, just one year after the famous Ranger well. This new field at Desdemona (once called Hog Town) attracted the usual rush of new exploration companies, many with little or no drilling experience.

Among the Eastland County startups, a wily financial conman’s Hog Creek Carruth Oil Company profited by colorful stock sale advertisements to attract investors.
The skillfully exaggerated promotions of Carruth prompted one contemporary writer to admire the crook’s audacity. “Any reader who cannot get a thrill out of Carruth’s highly colored advertising literature is indeed phlegmatic,” the observer declared.
But harm to many small, unwary investors was real. Most of the stock sales’ dollars went into Carruth’s pockets instead of his companies. Even the failure of his oil companies became part of his schemes.
Hogg Oil + Hog Creek Carruth Oil
Carruth merged two of his insolvent petroleum companies — Hogg Oil Company and Hogg Creek Carruth Oil Company — to create the Pilgrim Oil Company. His latest venture attracted some skeptical attention from financial magazine editors. The Pilgrim Oil Company, “makes a business of gathering in defunct oil companies,” reported Financial World.
As part of his connived merger game plan, stockholders of the two bankrupt Carruth oil ventures had to buy an additional 25 percent of Pilgrim Oil Company shares (in cash) or lose their investments entirely. Carruth used this money to pay dividends, thereby luring more buyers into his petroleum company Ponzi scheme.
Financial World noted, “This is a promoter’s way of reloading old stockholders with additional $25 worth of stock for every $100 they hold in a defunct company.”

J.W. Carruth merged his fraudulent Hogg Creek Carruth Oil with his other fraudulent oil company to create Pilgrim Oil company, a Ponzi scheme using investors’ purchase money to pay dividends and lure more buyers.
In 1923, a federal court indicted J.W. “Hog Creek” Carruth for mail fraud. Also indicted were Pilgrim Oil Company trustees Richardson and Hollister. Eighty-nine other shady characters also were named in a sweeping indictment aimed at stock hucksters.
U.S. Penitentiary, Leavenworth
Federal prosecutors reviewed financial harm to innocent Pilgrim Oil Company shareholders, who pleaded to the court for justice.
“False, fraudulent, and untrue representations were made for the purpose of inducing plaintiffs to buy the said stock of the said two companies, and for the purpose of cheating, swindling, and defrauding plaintiffs out of their money, and did cheat, swindle, and defraud plaintiffs out of their said money,” the attorneys declared.

“That in 1922, and for a long time prior and subsequent thereto, defendant was engaged in handling and selling oil stock certificates and owned and controlled interests in various oil companies and concerns in this state,” the prosecutors added. Dozens of convictions followed.
Carruth earned a one-year sentence in Leavenworth, Kansas. He joined the federal penitentiary’s oil-scheme alumni Dr. Frederick Cook, the fraudulent Arctic explorer turned oil well promoter. Pilgrim Oil Company and the other Carruth company shareholders were left with stock certificates of no value, except perhaps as a family stories and heirlooms.
Convicted felon “Hog Creek” Carruth, who died in obscurity in 1932, should not be confused with former Texas Governor James S. “Big Jim” Hogg, who helped discover the important West Columbia oilfield in 1917 — learn more in Governor Hogg’s Texas Oil Wells.
New Jersey Oilfield?
A West Coast newspaper in 1916 reported on a rare attempt to find an East Coast oilfield. “Lewis Steelman, the man who has been prospecting for oil near Millville, N.J., for some time, has begun active work to locate an oil well and he confidently expects to strike the fluid,” reported California’s Santa Ana Register.
In New Jersey, the recently established Steelman Realty Gas & Oil Company was selling stock buttressed by the declarations of Dr. H. J. von Hagen, who company executives cited as “one of the world’s greatest living geologists and petroleum engineers.” Learn more in Fake New Jersey Oil Well.
More articles about U.S. exploration and production companies and links for further research can be found in Oil Stock Certificates.
_______________________
Recommended Reading (October 9): The Prize: The Epic Quest for Oil, Money & Power (2008); The Extraction State, A History of Natural Gas in America (2021); The Birth of the Oil Industry (1936); Trek of the Oil Finders: A History of Exploration for Petroleum (1975). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(2008); The Extraction State, A History of Natural Gas in America (2021); The Birth of the Oil Industry (1936); Trek of the Oil Finders: A History of Exploration for Petroleum (1975). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society preserves U.S. petroleum history. Please become an annual AOGHS annual supporter. Help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2024 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
Citation Information – Article Title: “Exploiting North Texas Oil Fever.” Authors: B.A. Wells and K.L. Wells. Website Name: American Oil & Gas Historical Society. URL: https://aoghs.org/stocks/pilgrim-oil-company-exploiting-oil-fever. Last Updated: May 4, 2024. Original Published Date: September 9, 2021.
.
by Bruce Wells | Apr 23, 2024 | Petroleum Companies
Post-World War II rise and fall of the amazing Harry Stonehill.
According to the man who envisioned Spider-Man, the life story of Harry S. Stonehill “would make a great movie by someone like Oliver Stone.”
Stonehill returned to the Philippines after his Army service in the Pacific during World War II. He became wealthy from a variety of business ventures, but eventually was forced to flee the Philippines — and several other countries. Stan Lee, creator of the comic book web-slinger in 1962, was an old Army buddy of Lt. Harry Stonehill.
In 2011, Lee told Forbes magazine:
After the war, he said to me, “Hey Stan Come to the Philippines with me.” I said, “Why?” And he said, “I found out that they don’t have Christmas cards there. I’m going to buy a batch of Christmas cards and start a business.” I said, “I love ya, Harry, but you’re a lunatic.” And I went back to my comics and he went off to the Philippines.

By 1957, Stonehill was a multimillionaire when he organized American-Asiatic Oil Corporation. He had built a $50 million fortune in more than a dozen enterprises, including cotton, textiles and real-estate development. He also owned U.S. Tobacco, which held a virtual cigarette monopoly in the country; it would lead to his troubles. (more…)
by Bruce Wells | Mar 25, 2024 | Petroleum Companies
Chicago business sought risky shale opportunities during WWI.
At the end of the 20th century, record-breaking petroleum production from shale oil grew thanks to drilling and production technologies that produced from low permeability “tight oil” formations. But a century ago, the shale was an unconventional resource mined, crushed and transported to a retorting facility.
Mining shale began as an extraction process that converted organic matter within the rock (kerogen) into synthetic oil and gas, which could be used as a fuel or upgraded for an oil refinery feedstock.
The strategic importance of America’s mined shale production led to establishment of the Naval Petroleum and Oil Shale Reserves in 1912, “to insulate the United States from foreign dependency on oil during times of war.”

Commissioned in 1914 with coal-powered boilers, the battleship USS Texas was converted to use fuel oil in 1925. Photo courtesy Texas Parks and Wildlife Department.
Meanwhile, fuel oil also began replacing coal in U.S. warships (See Petroleum and Sea Power), as World War I erupted in Europe. After more than three years of neutrality, America entered the war on April 2, 1917.
Recognizing wartime demand for oil, Van H. Manning, director, U.S. Bureau of Mines, declared, “We have as yet untouched our great reserves of shale that contain oil…and are conservatively estimated to contain many times the amount of oil that has been or will have been produced from all the porous formations in this country.”

Central Oil Shale Refining Company formed with $500,000 capitalization and set up offices in Chicago. The venture saw a financial opportunity in mining shale and secured leases on 480 acres in Garfield County, Colorado, an area with known deposits.
Central Oil Shale Refining also leased a total of about 5,000 acres in Kentucky, Kansas, and Texas. These investments were a gamble on the margins of supply and demand.
Despite the risks, Central Oil Shale Refining presented “Expert Information on Oil Shale” to stockholders and potential investors at Chicago’s Palmer House hotel. Company executives promoted the mining and distillation of Colorado oil shales as an opportunity not to be missed. It helped that publications like Oil Field Engineering (December 1917) proclaimed shales as “A New Source of Gasoline.”
Shale Business Model
Oil shale operator Joseph Bellis presented a business model to the Palmer House audience, describing oil shale production process and economics. Bellis, a veteran of Colorado shale mining in the Piceance Creek Basin, later published a paper in the Colorado School of Mines’ quarterly magazine.
The paper may have helped Central Oil Shale Refining stock sales, but the company’s trajectory had already been determined on a farm near Ranger, Texas.
Concerns about U.S. wartime oil supplies declined — along with oil prices — soon after an October 17, 1917, gusher halfway between Abilene and Dallas. Still annually celebrated by area residents, “Roaring Ranger” J. McCleskey No. 1 well produced 1,600 barrels of oil a day. Other wells in the oilfield would yield up to 10,000 barrels of oil daily.
The North Texas drilling boom opened giant fields near Desdemona and Breckenridge (Conrad Hilton would buy his first hotel in Cisco). An even bigger oilfield was found in 1918 at Burkburnett, near Wichita Falls. With suddenly abundant supplies, oil sold for less than $2 per barrel — five cents a gallon.

Central Oil Shale Refining was in deep trouble. Even if every ton mined resulted in 50 gallons of oil, it would take more than 1,300 tons of shale every day to match the McCleskey’s well production alone. The numbers didn’t work and debts needed to be paid.
In one last effort to survive, Central Oil Shale Refining reorganized with the same officers, moved its offices, and subtly changed its name to Central Oil Shale and Refining Company. The new company quickly failed, leaving a brief shadow in financial records.
Another example of producing commercial quantities of petroleum from shale can be found in Ute Oil Company – Oil Shale Pioneer. By the 1980s, new technologies revolutionized petroleum production from low-permeability shales — especially for natural gas.
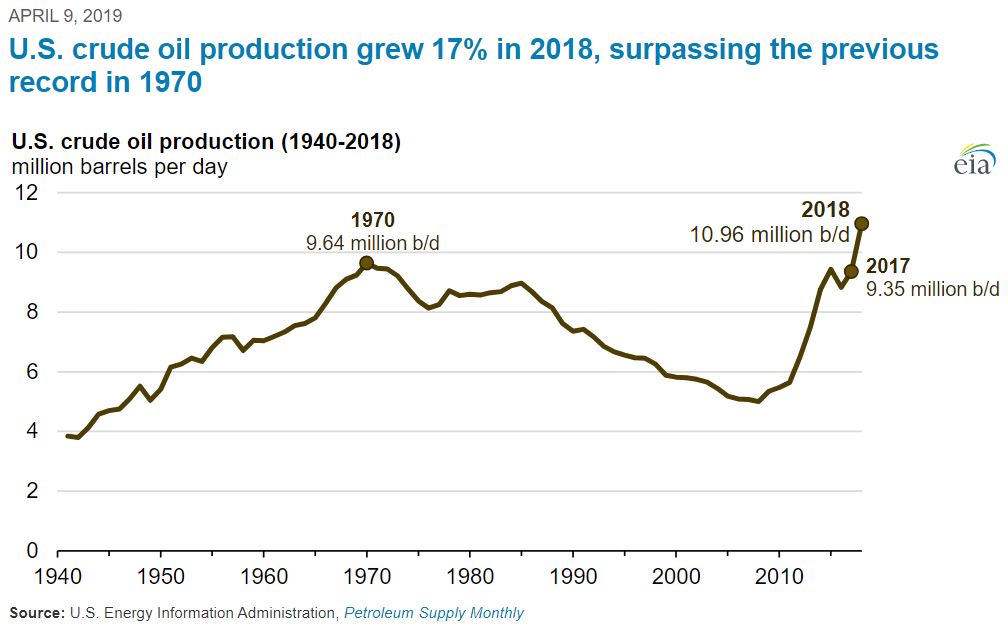
Annual U.S. crude oil production reached a record level of 10.96 million barrels per day in 2018, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration.
Although geologists had known of the potential of drilling in these “tight oil” formations, only one percent of U.S. natural gas production came from shale as late as 2000. But by applying horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing techniques, in 2010 shale gas accounted for more than 20 percent of U.S. natural gas production, according to the Energy Information Administration (EIA).
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Become an AOGHS annual supporting member and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. © 2024 Bruce A. Wells.
Citation Information – Article Title: “Central Oil Shale Refining Company.” Authors: B.A. Wells and K.L. Wells. Website Name: American Oil & Gas Historical Society. URL: https:https://aoghs.org/old-oil-stocks/central-oil-shale-refining-company. Last Updated: March 31, 2024. Original Published Date: April 1, 2019.
by Bruce Wells | Mar 11, 2024 | Petroleum Companies
Updated research and articles about the histories of old oil company stock and petroleum company histories.
Found an old oil company stock certificate and hoping for a petroleum financial gusher?
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society’s research and accompanying forum depend upon your individual financial support. The historical society is an independent, energy education organization — unaffiliated with upstream or downstream petroleum companies, state or federal government, or industry advocacy groups.

A petroleum company’s old oil stock certificate vignette sometimes has value for collectors of scripophily – the buying and selling of certificates after they have no redeemable value as a security.
Although use of fossil fuels today is highly controversial, the history of U.S. petroleum exploration, production, and transportation provides context for modern energy debates.

From 19th-century kerosene for lamps, 20th-century gasoline for cars, and modern plastic polymers for everyday products, the petroleum industry’s huge social, economic and technological heritage should be preserved.
A Popular Vignette
Collectors have found a surprising number of examples where quickly formed exploration companies picked the exact same oilfield scene for stock certificates.

In the rush to print stock certificates during oil booms, new companies often chose to print certificates using a vignette of derricks!
It might have saved time and money by choosing a common vignette today found on shares of Centralized Oil & Gas Company; Double Standard Oil & Gas Company; Evangeline Oil Company; Texas Production Company; Tulsa Producing and Refining Company; Hecla-Wyoming Oil Company; Oil Prospectors Inc.; Craven Oil & Refining; Buck Run Oil and Refining; Home Oil & Gas; Hog Creek Carruth Company; Buffalo-Texas Oil Company; and the Champion Oil Company (see links to them below).

Can you tell me anything about this old petroleum company (for free)? I found its stock certificate in an attic. Am I rich? Probably not. Since first commercial U.S. oil well in 1859, the petroleum industry’s boom and bust cycles have left many casualties.
The vast majority of old oil stock certificates (especially prior to U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), simply become family mementos — and not connected to any modern company. For one that led to extended court battles, see Not a Millionaire from Old Oil Stock.

America’s first oil company – the Pennsylvania Rock Oil Company of New York – organized it 1855.
Unfortunately, this small historical society cannot grant requests for free research regarding individual company histories and the potential value of stock certificates. As you may have discovered, financial research is difficult and time consuming. If you are fortunate, a visitor to this website or a society volunteer may have posted helpful information.
If your certificate is not listed here, and to share further research experiences, you are invited to submit your query in the current Stock Certificate Q&A Forum.
(more…)
















