by Bruce Wells | Jun 17, 2025 | Petroleum Art
Alexandre Hogue and other artists depicted America’s oilfields during the Great Depression.
“Oil Fields of Graham,” a 1939 mural by Alexandre Hogue, can be found in its original Texas community’s U.S. Postal Service building, a Graham museum preserving the work of oil art.
During the Great Depression, when President Franklin Roosevelt created public projects like the New Deal Federal Arts Program, Alexandre Hogue and other artists received commissions to illustrate scenes of America and its history on the walls of public buildings.
Among his paintings, the artist’s petroleum-related works include “Oil Fields of Graham” (1939), a 12-foot mural now on exhibit in the city’s historic U.S. Post Office building.
(more…)
by Bruce Wells | Jun 4, 2025 | Petroleum Pioneers
Drilling for water in 1894, Corsicana discovered an oilfield and became the richest town in Texas.
In the summer of 1894, town leaders of Corsicana, Texas, hired a contractor to drill a water well on 12th Street. The driller found oil instead. The small community’s oilfield discovery launched the first Texas oil boom seven years before a more famous gusher at Spindletop Hill far to the southeast.
Corsicana’s first oil well produced less than three barrels of oil a day, but it quickly transformed the sleepy agricultural town into a petroleum and industrial center. The discovery launched industries, including service companies and manufacturers of the newly invented rotary drilling rig.

The first Texas oil boom arrived in 1894 with discovery of the Corsicana oilfield by a drilling contractor hired by the city to find water. An annual Derrick Day Chili & BBQ Cook-Off celebrates the discovery. Colorized postcard of Navarro County oil wells, circa 1910.
Corsicana local historians consider the 1894 discovery well, drilled on South 12th Street, the first significant commercial oil discovery west of the Mississippi (Kansans claim the same distinction for an 1892 Neodesha oil well).
Early Texas Oilfields
The American Well and Prospecting Company (from Kansas) made the oil strike on June 9, 1894, at a depth of 1,035 feet. The city council — angry and still wanting water for its growing community 55 miles south of Dallas — paid only half of the drilling contractor’s $1,000 fee. (more…)
by Bruce Wells | May 17, 2025 | Petroleum Pioneers
West Texas discoveries in the 1920s revealed a petroleum expanse 250 miles wide and 300 miles long.
A West Texas oil well blessed by nuns revealed the true size of the petroleum-rich Permian Basin in 1923. A small university in Austin owned the arid land, which had been deemed mostly worthless by experts.
Successful exploration of the Permian Basin, once known as a “petroleum graveyard,” began in February 1920 with a discovery by William H. Abrams in Mitchell County in West Texas. When completed after “shooting” the well with nitroglycerin in July, production averaged 20 barrels of oil a day.
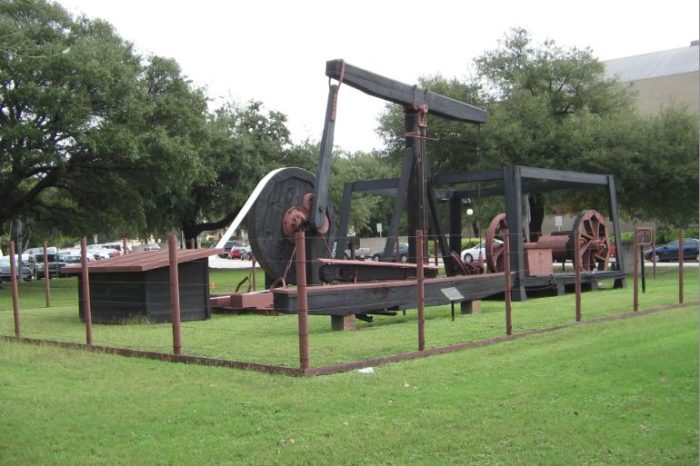

In 1958, the University of Texas moved the Santa Rita No. 1 well’s walking beam and other equipment to the Austin campus. The student newspaper described the well, “as one that made the difference between pine-shack classrooms and modern buildings.” Photo from 2007 by Bruce Wells.
The W.H. Abrams No. 1 oilfield discovery well of the Permian Basin would lead to the area’s first commercial oil pipeline in the Permian Basin, according to a Texas Historical Commission historic marker placed near the well in 1996 (reported missing in 2020).
Meanwhile, even with its limited production, the Abrams well began attracting oil exploration to the barren region.
West Texas Oil
It would be another Permian Basin discovery well that launched a stampede of wildcatters to explore the full 300-mile extent of the basin from West Texas into southeastern New Mexico.
Geologists remained unconvinced the Permian Basin contained commercial amounts of petroleum until the Santa Rita No. 1 well tapped a vast oilfield. The well, drilled by Texon Oil and Land Company near Big Lake, Texas, struck oil on May 28, 1923. The discovery came on land leased from the University of Texas.

It had not been easy for Texon Oil and Land Company. The well required 21 months of cable-tool drilling that averaged less than five feet per day to reach a total depth of 3,055 feet. Once completed, the well produced for the next 70 years.
Because state legislators had given the land and mineral rights to the University of Texas when it opened in 1883, the oilfield’s royalties would endow the University of Texas with $4 million.
Discovery of the Big Lake oil field in 1923 led to many boom towns, including Midland, which some called “Little Dallas.”
The Texas Board of Regents moved Santa Rita’s drilling equipment to the campus in 1958, “In order that it may stand as a symbol of a great era in the history of the university.” After the dedication, the student newspaper of the day described the well “as one that made the difference between pine-shack classrooms and modern buildings.”
Santa Rita No. 1
The historic well’s oil discovery began in 1919 when attorney and oil speculator Rupert Ricker applied to lease rights on more than 430,000 acres of arid land designated by the state for the financing of the University of Texas. As time ran out to pay a filing fee of about $43,000, Ricker failed to raise money from Fort Worth investors.
“Nobody seemed to have any interest in the deal so with the deadline looming he sold the entire scheme to El Pasoans Frank T. Pickrell and Haymon Krupp for the sum of $2,500,” noted a 2017 article in the Permian Basin Petroleum Association Magazine.
The two men had served in the same Army company during World War I. Their Santa Rita No. 1 well near Big Lake started “making hole” shortly before midnight on August 17, 1921 — on the last day before the 18-month drilling permit expired.

A 2007 University of Texas exhibit featured original Santa Rita cable-tool drilling equipment at San Jacinto Boulevard and 19th Street on the Austin campus. Photo by Bruce Wells.
Pickrell hired an experienced Pennsylvania driller, Carl Cromwell, to drill Texon Oil and Land’s test well. Cromwell had been born in 1889 not far from the first commercial U.S. oil well in Titusville, Pennsylvania.
Nuns and Roses
At the time, West Texas drilling crews, when available, “consisted mostly of cowboy roustabouts who were distinguished for high absenteeism and steady turnover,” notes one historian. The well often needed to be shut down because of a lack of cash to pay salaries or buy supplies.

Several months after the start of drilling, an increasingly concerned Pickrell climbed the derrick. At the top, he threw handfuls of rose petals that a group of Catholic women investors from New York had given him.
Pickrell christened his wildcat well for the church’s Patroness of Impossible Causes — Santa Rita. On May 25, 1923, early signs of oil and natural gas appeared. Three days later, Santa Rita No. 1 roared in as a West Texas gusher.
People as far away as Fort Worth traveled to see the well. Much-needed casing and other well equipment arrived a month later to bring the wild well under control, and the first commercial well in the Permian Basin went into production.

The Big Lake field — at 4.5 square miles — revealed that vast oil reserves in West Texas came from both shallow and deep formations. Exploration spread into other areas of the Permian Basin, still one of the largest oil-producing regions in the United States.
In the fall of 1923, Pickrell found an important investor, Michael L. Benedum, the highly successful independent oilman from Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Benedum and another Pittsburgh wildcatter, Joseph Trees, purchased Texon properties and formed the Big Lake Oil Company in 1924.
Big Lake Oilfield
The new company’s president, Levi Smith, would be instrumental in creating Big Lake — the first oil company town in the Permian Basin. Santa Rita No. 1 well, capped in May 1990, would be remembered with a replica erected in Reagan County Park.
The Big Lake oilfield proved to be 4.5 square miles and demonstrated that vast oil reserves in West Texas came from both shallow and deep horizons. Exploration spread into other areas of the Permian Basin, which would become one of the largest oil-producing regions in the United States.

Learn the story of the Permian Basin at the Petroleum Museum in Midland. Not far from the museum, in Odessa, an Ector County historical marker notes “the first Permian Basin dry hole” drilled in 1924.
Pennsylvania independent operators drilled the well to 900 feet and found only “Red Bed” rock, notes the 1965 marker. The 1924 well would be abandoned, but by 1964 Ector County would have 9,600 oil wells.
Hollywood at Big Lake
The 2002 movie “The Rookie” was filmed almost entirely in West Texas. It featured a Big Lake high-school teacher played by Dennis Quaid, who despite being in his mid-30s briefly makes it to the major leagues.

The opening scenes of the 2002 movie “The Rookie” included Catholic nuns christening the wildcat well with rose petals.
As the well is being drilled, Catholic nuns are shown carrying a basket of rose petals to christen it for the patron Saint of the Impossible – Santa Rita.
Learn more about baseball teams fielded by petroleum “company towns” in Oilfields of Dreams.
_______________________
Recommended Reading: Santa Rita: The University of Texas Oil Discovery (1958); Chronicles of an Oil Boom: Unlocking the Permian Basin
(1958); Chronicles of an Oil Boom: Unlocking the Permian Basin (2014). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(2014). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Please become an AOGHS annual supporter and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. © 2025 Bruce A. Wells.
Citation Information – Article Title: “Santa Rita taps Permian Basin.” Authors: B.A. Wells and K.L. Wells. Website Name: American Oil & Gas Historical Society. URL: https://aoghs.org/petroleum-pioneers/west-texas-petroleum. Last Updated: May 22, 2024. Original Published Date: November 1, 2004.









