This Week in Petroleum History: January 15 – 21
January 17, 1911 – Oilfield Discovery leads to North Texas Boom –
The Producers Oil Company discovered the Electra oilfield in North Texas, bringing the first commercial oil production to Wichita County. The Waggoner No. 5 well produced 50 barrels per day from a depth of 1,825 feet on land owned by local rancher William Waggoner, who had found traces of oil while drilling a water well for his cattle.

Named after rancher William Waggoner’s daughter, Electra, would become the “Pump Jack Capital of Texas.” Photo by Bruce Wells.
“At first, there weren’t any cars, and about the only thing oil was good for was to help repel chicken house mites,” noted a county historian about the discovery well, which brought more exploration. The Clayco No. 1 gusher of April 1 would send Electra’s oil fortunes further skyward, helping it become the Pump Jack Capital of Texas.
January 18, 1919 – Congregation rejects drilling in Cemetery
World War I had ended two months earlier as oil production continued to soar in North Texas. Reporting on “Roaring Ranger” oilfields, the New York Times noted that speculators had offered $1 million for rights to drill in the Merriman Baptist Church cemetery, but the congregation could not be persuaded to disturb the interred.
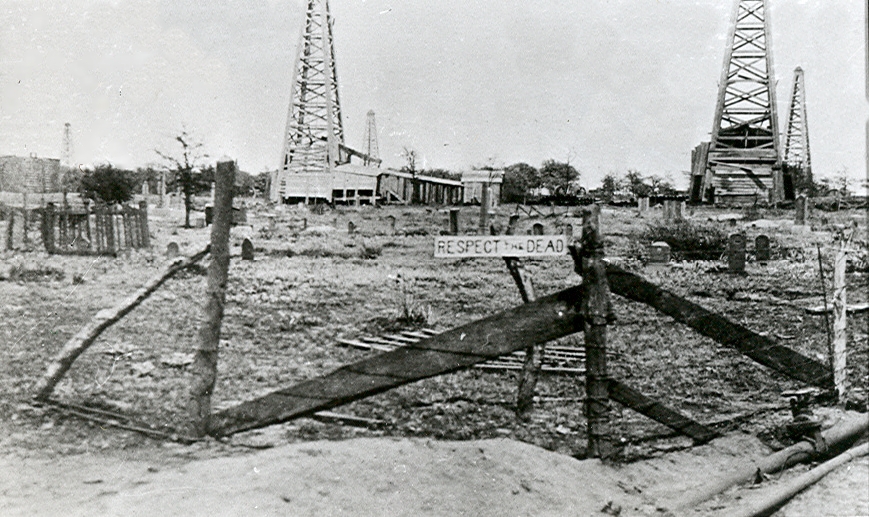

“Lone Star Bonanza, the Ranger Oil Boom of 1917-1923,” photograph of a North Texas church cemetery by Robert Vann.
Posted on a barbed-wire fence surrounding the graves not far from producing oil wells, a sign proclaimed, “Respect the Dead.” Today, the cemetery — and a new church — can be found three miles south of Ranger.
Learn more in Oil Riches of Merriman Baptist Church.
January 19, 1922 – Geological Survey predicts Oil Shortage
The U.S. Geological Survey predicted America’s oil supplies would run out in 20 years. It was not the first or last false alarm. Warnings of shortages had been made for most of the 20th century, according to geologist David Deming of the University of Oklahoma. His 1950 report, A Case History of Oil-Shortage Scares, documented six claims prior to 1950 alone.
Among the end of oil supplies predictions named in the report: The Model T Scare of 1916; the Gasless Sunday Scare of 1918; the John Bull (United Kingdom) Scare of 1920-1923; the Ickes (Interior Secretary Harold Ickes) Petroleum Reserves Scare of 1943-1944; and the Cold War Scare of 1946-1948.
Predictions of U.S. oil shortages began as early as 1879, when the Pennsylvania state geologist said remaining oil supplies would keep kerosene lamps burning for only four more years.
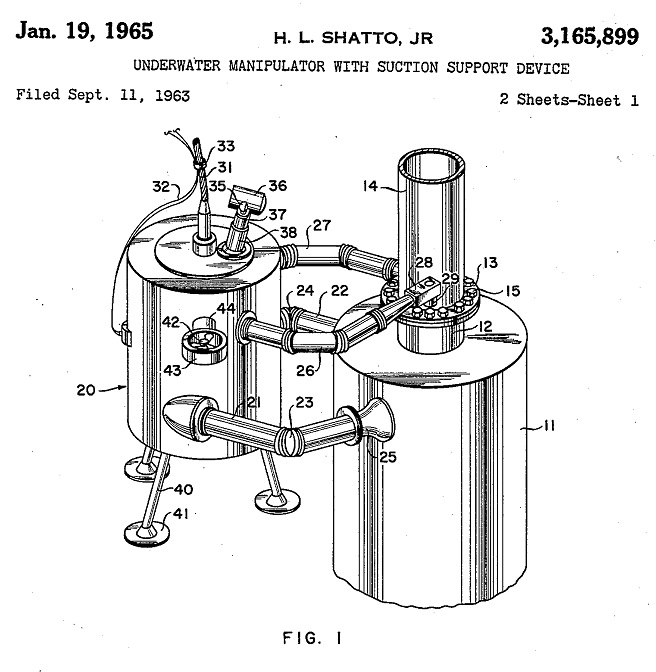
January 19, 1965 – “Underwater Manipulator” patented
Howard Shatto Jr. received a 1965 U.S. patent for his “underwater manipulator with suction support device.” His concept led to the modern remotely operated vehicle (ROV) now used most widely by the offshore petroleum industry. Shatto helped make Shell Oil Company an early leader in offshore oilfield technologies.
Howard Shatto Jr. would become “a world-respected innovator in the areas of dynamic positioning and remotely operated vehicles.”
Underwater robot technology can trace its roots to the late 1950s, when Hughes Aircraft developed a Manipulator Operated Robot — MOBOT — for the U.S. Atomic Energy Commission. Beginning in 1960, Shell Oil began transforming the landlocked MOBOT into a marine robot, “basically a swimming socket wrench,” noted one engineer.
In his 1965 patent — one of many he received — Shatto explained how his robot could install production equipment at greater depths than divers could safely work. The ROV inventor also would become known as the offshore industry’s father of dynamic positioning.
Learn more in ROV – Swimming Socket Wrench.
January 20, 1886 – Great Karg Well erupts Natural Gas in Ohio
The spectacular natural gas well – the “Great Karg Well” of Findlay, Ohio — erupted with an initial flow of 12 million cubic feet a day. The well’s gas pressure could not be controlled by technology of the day, and it ignited into a towering flame that burned for four months — becoming a popular Ohio tourist attraction. Eight years earlier, another natural gas well in Pennsylvania had made similar headlines (see Natural Gas is King in Pittsburgh).

A plaque dedicated in 1937 in Findlay, Ohio, commemorated the state’s giant natural gas discovery of 1886.
Although Ohio’s first natural gas well was drilled in Findlay in 1884 by Findlay Natural Gas Company, the Karg well launched the state’s first major gas boom and brought many new industries. Glass companies like the Richardson Glass Works were lured by the inexpensive gas.
New manufacturers included eight window glass factories, two bottle, two chimney lamp, one light bulb, one novelty, and five for tableware. By 1887, Findlay became known as the “City of Light,” according to a historical marker erected in 1987 at the first field office of the Ohio Oil Company, which adopted the name Marathon Oil in 1962.
The Hancock Historical Museum in Findlay includes Great Karg Well exhibits less than two miles from the site of the famous well.
January 21, 1865 – Roberts Torpedo detonated, improving oil production
Civil War veteran Col. Edward A.L. Roberts (1829-1881) conducted his first experiment to increase oil production by using an explosive charge deep in the well. Roberts twice detonated eight pounds of black powder 465 feet deep in the bore of the “Ladies Well” on Watson’s Flats south of Titusville, Pennsylvania.

Civil War veteran Col. E.A.L. Roberts demonstrated his oil well “torpedo” south of Titusville, Pennsylvania.
The “shooting” of the well was a success, increasing daily production from a few barrels of oil to more than 40 barrels, according to Pennsylvania Heritage Magazine.
In April 1865, Roberts received the first of many patents for his “exploding torpedo.” The Titusville Morning Herald in 1866 reported, “Our attention has been called to a series of experiments that have been made in the wells of various localities by Col. Roberts, with his newly patented torpedo. The results have in many cases been astonishing.”
By 1870, Roberts’ torpedo technology using nitroglycerin became common in oilfields (see Shooters – A “Fracking” History).
_______________________
Recommended Reading: Early Texas Oil: A Photographic History, 1866-1936 (2000); Ranger, Images of America
(2010); Diving & ROV: Commercial Diving offshore (2021); Myth, Legend, Reality: Edwin Laurentine Drake and the Early Oil Industry
(2009); Portrait in Oil: How Ohio Oil Company Grew to Become Marathon
(1962); Ohio Oil and Gas, Images of America
(2008); Trek of the Oil Finders: A History of Exploration for Petroleum (1975). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Become an AOGHS annual supporting member and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2024 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.






