by Bruce Wells | Jun 30, 2025 | This Week in Petroleum History
June 30, 1864 – Oil Tax funds Civil War –
The federal government taxed oil for the first time when it levied a $1 per barrel tax on production from Pennsylvania oilfields.

Seeking ways to pay for the Civil War, Treasury Secretary Salmon Chase advocated an oil tax of $6.30 per barrel.
Desperate for revenue to fund the Civil War as early as 1862, Treasury Secretary Salmon Chase advocated a $6.30 tax per barrel of oil and $10.50 per barrel on refined products. Angry oil producers rallied against the tax in Oil City, Pennsylvania, and sent delegates to Washington, D.C., where they negotiated a tax of $1 per 42-gallon barrel of oil.
July 1, 1919 – Top Independent Producers associate in Tulsa –
The two-year-old Mid-Continent Oil & Gas Association established its Kansas-Oklahoma Division in boom town Tulsa. Members were a “who’s who” of top independent oil and natural gas producers.

Alf Landon served as Kansas governor and was the 1936 Republican presidential candidate.
Today the U.S. Oil & Gas Association, membership in 1919 included Frank Phillips of Phillips Petroleum; E.W. Marland, whose company became Conoco; W.G. Skelly, founder of Skelly Oil; H.H. Champlin, founder of Champlin Oil; and Alf Landon, the 1936 Republican presidential candidate. Robert Kerr of Kerr-McGee Oil Company presided as president of the Mid-Continent Division from 1935 through 1941.
July 1, 1922 – Smackover Field brings Arkansas Drilling Boom
First settled by French fur trappers in 1844, Smackover, Arkansas, had a population of just 90 people in 1922 when a wildcat well erupted oil. The well, drilled to 2,066 feet by sawmill owner Sidney Umsted, discovered the 25,000-acre Smackover field. Within six months, 1,000 wells were drilled with a success rate of 92 percent.
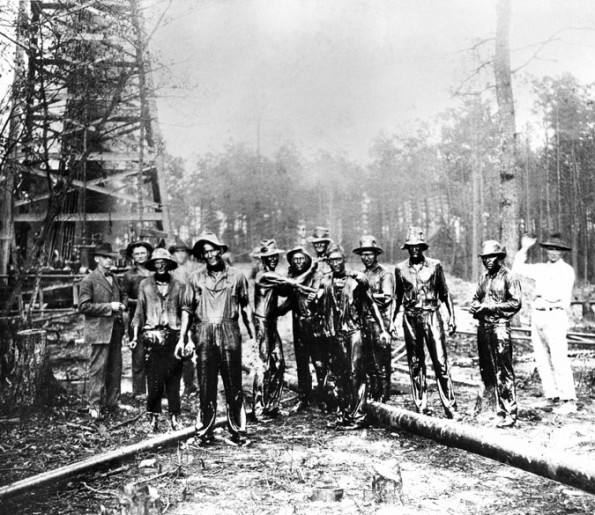

Roughnecks photographed following the July 1, 1922, discovery of the Smackover (Richardson) field in Union County. Photo courtesy of the Southwest Arkansas Regional Archives.
Smackover’s population grew to 25,000 and its uncommon name quickly attained national attention. Nearby less than two years earlier, the first commercial oil well in Arkansas, the Busey-Armstrong No. 1, had revealed the giant El Dorado field and launched the career of a young H.L. Hunt.
Learn more in First Arkansas Oil Wells.
July 1, 1938 – The Texas Company discovers Illinois Oilfield
Using a newly introduced technology of seismic exploration, petroleum geologists found hidden anticlines with commercial quantities of oil in Marion County, Illinois. By January 1939 the Salem field was ranked seventh in U.S. daily production. In one year the field produced more than 20 million barrels of oil.
Natural gas production in Illinois began as early as 1853 when marsh or “drift gas” was produced from two water wells drilled near Champaign. The state’s first drilling boom arrived in 1906, thanks to the John Shore No. 1 oil well in Crawford County, according to the Illinois Oilfield Museum.
July 2, 1910 – President Taft establishes Naval Petroleum Reserves
As the Navy converted from coal to oil-burning ships, President William Howard Taft established three Naval Petroleum Reserves.

“As a prospective large consumer of oil by reason of the increasing use of fuel oil by the Navy, the federal government is directly concerned both in encouraging rational development and at the same time ensuring the longest possible life to the oil supply,” the president declared in a message to Congress.

Commissioned in 1914 with coal-powered boilers that were converted to use fuel oil in 1925, the U.S.S. Texas “was the most powerful weapon in the world.”
The last U.S. battleship to be built with coal-fired boilers, the U.S.S. Texas, was launched in 1912 and converted to oil-fired boilers in 1926.
Learn more in Petroleum and Sea Power.
July 2, 1913 – First Gasoline-Electric Hybrid Locomotive
While most U.S. trains were still steam-powered, General Electric built the first commercially successful gasoline-powered engine locomotive. Two General Motors 175-horsepower V-8s powered two 600-volt, direct current generators to propel the 57-ton locomotive to a top speed of 51 miles per hour.

Many consider the locomotive “Dan Patch” the first successful internal combustion engine locomotive in the United States.
The Electric Line of Minnesota Company purchased the new gasoline-powered electric hybrid for $34,500, naming it “Dan Patch” in honor of the world’s champion harness horse of the time. By 1930, diesel engines with G.E. generators launched the modern train industry with Streamliners.
July 2, 1920 – West Columbia Oilfield discovered in Texas
The Abrams No. 1 well erupted oil in Brazoria County, Texas, revealing the West Columbia oilfield southwest of Houston. Drilled by the Texas Company (the future Texaco), the well initially produced up to 30,000 barrels of oil a day. The well was completed on a 1,650-acre tract owned by railroad official William H. Abrams (1843–1926), who administered millions of acres for the Texas Pacific Land Trust.
Abrams also invested in Mitchell County leases in West Texas, where another 1920 wildcat well discovered the first oil production of the Permian Basin. Three years later, drillers from El Paso completed the Santa Rita No. 1 well.
July 5, 1900 – Edison films New Jersey Refinery Fire
An early morning lightning strike at the Standard Oil Company refinery at Bayonne, New Jersey, set off explosions in three storage tanks, each with a capacity of 40,000 barrels of oil. Within minutes, the company’s fire department and tugboats rushed to fight the blaze.

Screenshots from Thomas Edison’s film of the destruction of Standard Oil Company’s refinery at Bayonne, New Jersey, on July 5, 1900, courtesy Library of Congress.
“The tugboats moved the company ships and oil-filled barges away from its burning docks to safe waters,” noted the Jersey Journal in 2017. The Bayonne refinery fire was one of the first newsreels produced by the Thomas A. Edison Company (it can be viewed here). As bad as the conflagration was, there were no fatalities.
July 6, 1988 – Piper Alpha North Sea Tragedy
An explosion and fire on Occidental Petroleum’s Piper Alpha offshore production platform in the North Sea resulted in the deaths of 167 out of 224 personnel. It remains the most deadly offshore disaster in petroleum history.

“Smoke pouring from Piper Alpha throws a pall over the North Sea 18 hours after the explosion,” reported The Daily Telegraph of London on July 8, 1988.
Piper Alpha had been receiving natural gas from two platforms while exporting gas to a compression platform. The initial explosion was caused “by a misunderstanding of the readiness of a gas condensate pump that had been removed from service for maintenance of its pressure safety valve,” according to safety expert Gary Karasek.
Improved offshore platform designs, operations engineering, evacuation technologies, and safety procedures emerged following the official inquiry, noted Karasek. “It was a ground-breaking effort, with numerous detailed findings and 106 recommendations, which were readily accepted by industry.”
_______________________
Recommended Reading: Tulsa Where the Streets Were Paved With Gold – Images of America (2000); The Discovery of Oil in South Arkansas, 1920-1924 (1974); Historic Battleship Texas: The Last Dreadnought
(2000); The Discovery of Oil in South Arkansas, 1920-1924 (1974); Historic Battleship Texas: The Last Dreadnought (2007); Evolution of the American Diesel Locomotive, Railroads Past and Present
(2007); Evolution of the American Diesel Locomotive, Railroads Past and Present (2007); Early Texas Oil: A Photographic History, 1866-1936
(2007); Early Texas Oil: A Photographic History, 1866-1936 (2000) Death and Oil: A True Story of the Piper Alpha Disaster on the North Sea
(2000) Death and Oil: A True Story of the Piper Alpha Disaster on the North Sea (2011). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(2011). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Please become an AOGHS annual supporter and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. © 2025 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
by Bruce Wells | Jun 23, 2025 | This Week in Petroleum History
June 23, 1921 – Signal Hill brings California Oil Boom –
Another southern California drilling boom began when a geyser of “black gold” erupted 114 feet high at Signal Hill. The Alamitos No. 1 well, which revealed a giant oilfield, produced about 600 barrels of oil a day when it was completed.

The Signal Hill oil discovery helped make California the source of one-quarter of the world’s oil output. “Porcupine Hill” and the Long Beach field produced 260,000 barrels of oil a day by 1923. Photo courtesy of Los Angeles Museum of Natural History.
Soon known as “Porcupine Hill,” the Signal Hill oilfield 20 miles south of Los Angeles produced almost 260,000 barrels of oil a day by 1923. Combined with the 1892 Los Angeles Oilfield discovery and the 1920 Huntington Beach oilfield, California produced one-fourth of the world’s oil. A monument dedicated in 1952 at Signal Hill’s Discovery Well Park has served “as a tribute to the petroleum pioneers for their success here.”
Learn more in Signal Hill Oil Boom.
June 23, 1947 – Supreme Court limits State Rights to Continental Shelf
The U.S. Supreme Court ruled California could not claim rights to the continental shelf beyond three nautical miles. Litigation resulted from President Harry Truman’s September 1945 Continental Shelf Proclamation, which placed control with the federal government. The Supreme Court ruling on the Truman Proclamation affirmed federal jurisdiction “with respect to the natural resources of the subsoil and seabed of the continental shelf.” Similar rulings affecting Louisiana and Texas would be made in 1950.
June 24, 1937 – Traces of Oil found in Minnesota
In far western Minnesota, a remote wildcat well drilled in Traverse County began producing three barrels of oil a day from a depth of 864 feet. The unlikely discovery prompted more leasing, but no commercial quantities of oil.
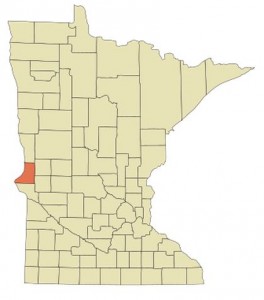
Traverse County, Minnesota, where oil production peaked in 1937.
The lack of an oilfield reaffirmed geologists’ conclusions since 1889 that conditions for significant petroleum deposits did not exist in Minnesota, despite some water wells in southern Minnesota containing small amounts of natural gas.
“Not much oil and gas is obtained from Precambrian rocks, with which Minnesota is very amply blessed,” noted the 1984 book Minnesota’s Geology.
June 25, 1889 – First Oil Tanker catches Fire in California
The first oil tanker built for that purpose, a schooner named W.L. Hardison, burned at its wharf in Ventura, California. The Hardison & Stewart Oil Company (later Union Oil) commissioned the experimental vessel, which offered an alternative to paying for railroad oil tank cars charging one dollar per oil barrel to reach markets in San Francisco.
With oil-fired steam boilers and supplemental sails, the schooner could ship up to 6,500 barrels of oil below deck in specially constructed steel tanks. After the fire, the tanks were recovered and used at the company’s Santa Paula refinery. It took 11 years before the company launched a replacement tanker, the Santa Paula.

Rare photographs of the doomed oil tanker W.L. Hardison and Ventura pier courtesy the Museum of Ventura County.
The Ventura Wharf Company by April 1898 had exported 518,204 barrels of bulk oil during the previous year, according to the Los Angeles Times. The pier remained a working wharf until 1936 when it became the longest recreational wooden pier in California.
Designated a Ventura Historic Landmark in 1976 and now 1,600 feet long, California’s oldest pier was refurbished for $2.2 million in 2000, according to the Museum of Ventura County, which also operates archaeological and agricultural museums. In nearby Santa Paula, the 1890 headquarters building of Union Oil Company is home to the California Oil Museum.
June 25, 1901 – Red Fork Discovery leads to Tulsa Boom
Six years before statehood, Oklahoma witnessed a second oil discovery (some say the third — see Another First Oklahoma Oil Well) when two drillers from the Pennsylvania oil regions discovered an oilfield at Red Fork in the Creek Indian Nation.
John Wick and Jesse Heydrick drilled the Sue A. Bland No. 1 well near the Creek village across the Arkansas River from Tulsa. Sue Bland, a Creek citizen, was the wife of homesteader Dr. John C. W. Bland. Their Red Fork well produced just 10 barrels of oil a day from a depth of 550 feet, but created a drilling boom attracting petroleum companies to nearby Tulsa.
Learn more in Red Fork Gusher.

June 25, 1999 – Texas Post Office named Historic Place
The former U.S. Post Office building in Graham, Texas, with its Great Depression-era oilfield mural by Alexandre Hogue, joined the National Register of Historic Places. Hogue’s 1939 “Oil Fields of Graham” has been joined by other art exhibits in its historic Art Deco building on Third Street.

“Oil Fields of Graham” by Alexandre Hogue, a 1939 mural in the Old Post Office Museum & Art Center of Graham, Texas. The white-haired gentleman was the mayor of Graham.
Hogue’s artwork included many southwestern scenes as part of the New Deal Federal Arts Program. His murals on the walls of public buildings often portrayed scenes of the Texas petroleum industry. In Graham’s historic building on Third Street, “Oil Fields of Graham,” 12 feet wide and 7 feet high, is among exhibits at the Old Post Office Museum & Art Center, which opened in 2002.
Learn more in Oil Art of Graham, Texas.
June 26, 1885 – Natural Gas Utility established in Pennsylvania
Peoples Natural Gas Company incorporated — the first Pennsylvania natural gas company chartered by the state to regulate production, transmission, and distribution of natural gas. A similar utility incorporation had taken place a year earlier in New York City when six competing companies combined to form Consolidated Edison.
By 1891, the Pittsburgh-based limited liability company had consolidated pipelines and facilities of Pittsburgh Natural Gas, Lawrence Natural Gas, Conemaugh Gas, and Columbia Natural Gas companies. More than a dozen more companies would be acquired between 1903 and 1961. The large utility added Saxonburg Heat and Light in 1979 and Equitable Gas in 2017, expanding natural gas services in West Virginia and Kentucky.
June 28, 1887 – Kansans celebrate First Natural Gas Jubilee
After erecting flambeau arches at the four corners of the town square, Paola, Kansas, hosted what local leaders described as “the first natural gas celebration ever held in the West.” Excursion trains from Kansas City brought about 2,000 people, “to witness the wonders of natural gas,” according to the Miami County Historical Museum, which preserves the region’s petroleum history.
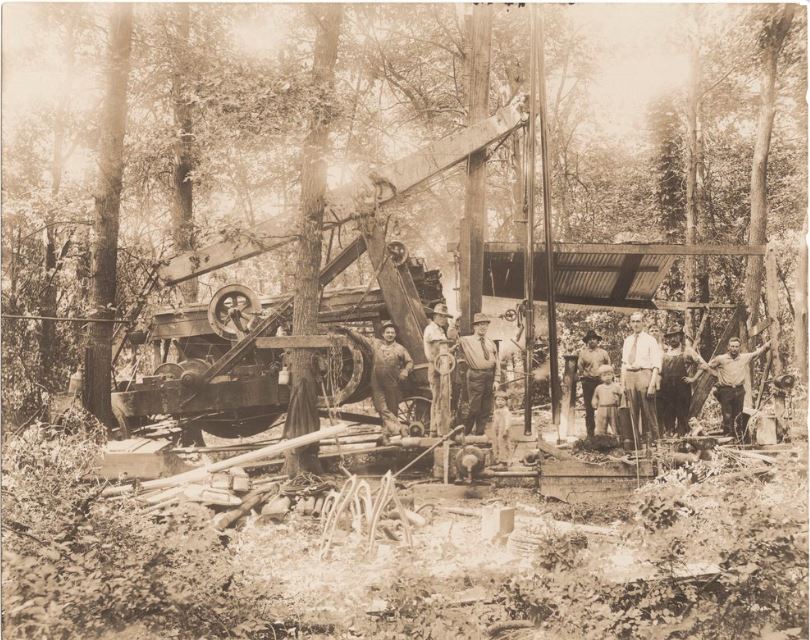

Paola’s giant natural gas field attracted more petroleum exploration to Miami County, including this circa 1920 oil well. Photo courtesy Kansas Historical Society.
The town’s special event included a “grand illumination” of natural gas street lights, where “gas was attached to a yard sprinkler by a rubber hose, and when it was ignited there appeared nests of small blazes which were beautiful and attractive.”
Learn more in First Kansas Oil Well.

June 28, 1967 – Hall of Petroleum opens in Smithsonian Museum
The Hall of Petroleum opened at the Smithsonian Institution’s Museum of History and Technology in Washington, D.C. Exhibits included cable-tool and rotary rig drilling technologies and counterbalanced pumping units, The Hall of Petroleum also featured 1967 developments in offshore exploration and production.
Visitors to what in 1980 became the National Museum of American History were greeted by a mural painted by Delbert Jackson of Tulsa, Oklahoma. Jackson spent two years creating his 13-foot by 56-foot painting with scenes of oil and natural gas exploration, production, refining, and transportation.

A “Panorama of Petroleum” once greeted visitors to the Smithsonian’s American History Museum in Washington, D.C. The 13-foot by 56-foot mural today is exhibited inside Tulsa International Airport.
Jackson’s “Panorama of Petroleum” featured industry pioneers and served as a visual map to the hall’s oilfield technology exhibits. “If the hall can increase the public’s knowledge of and respect for the technical skill and know-how of those who make this energy available, it will have served its purpose,” noted the exhibit’s 1967 catalog. The mural ended up in storage for three decades, until finding a home at Tulsa International Airport.
Learn more in Smithsonian’s “Hall of Petroleum.“

June 29, 1956 – Interstate Highway System enacted
The Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1956, popularly known as the National Interstate and Defense Highways Act, became law. Passed at the urging of President Dwight D. Eisenhower, the act provided 90 percent federal funding for a “system of interstate and defense highways,” and authorized spending $25 billion through 1969 for construction of about 41,000 miles of interstates.
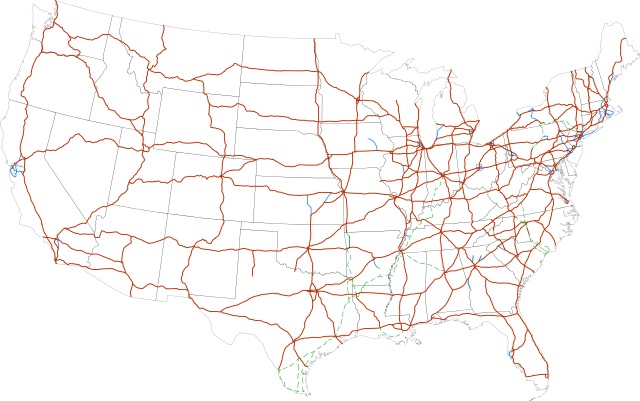
The interstate system reached 48,191 miles in 2016. Federal regulations banned collecting tolls but that would change.
“Of all his domestic programs, Eisenhower’s favorite by far was the Interstate System,” noted historian Stephen Ambrose. The thirty-fourth president urged passage of the act for national defense; interstates would be needed for evacuating major cities during a nuclear war.
_______________________
Recommended Reading: Signal Hill, California, Images of America (2006); Minnesota’s Geology (1982) Tulsa Oil Capital of the World, Images of America
(2006); Minnesota’s Geology (1982) Tulsa Oil Capital of the World, Images of America (2004); Oil in West Texas and New Mexico
(2004); Oil in West Texas and New Mexico (1982); Minnesota’s Geology (1982); Black Gold in California: The Story of California Petroleum Industry
(1982); Minnesota’s Geology (1982); Black Gold in California: The Story of California Petroleum Industry  (2016); Early California Oil: A Photographic History, 1865-1940
(2016); Early California Oil: A Photographic History, 1865-1940 (1985); Tulsa Oil Capital of the World, Images of America
(1985); Tulsa Oil Capital of the World, Images of America (2004); Oil in West Texas and New Mexico
(2004); Oil in West Texas and New Mexico (1982); Official Guide to the Smithsonian
(1982); Official Guide to the Smithsonian (2016); Eisenhower: Soldier and President
(2016); Eisenhower: Soldier and President (1968). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(1968). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Please become an AOGHS annual supporter and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. © 2025 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
by Bruce Wells | Jun 16, 2025 | This Week in Petroleum History
June 16, 1903 – Ford Motor Company Incorporated –
After successfully testing his gasoline-powered Quadricycle in 1896, Henry Ford and a group of investors (including machinist John Dodge) filed articles of association for the Ford Motor Company. Ford’s contributions included machinery, drawings, and several patents. The first sale was a Ford Model A to a Chicago physician in July as the Detroit-based automaker began ordering carriages, wheels, and tires for a low-cost car that would become the Model T by 1908, according to the Henry Ford Heritage Association (HFHA).
June 18, 1889 – Standard Oil of New Jersey adds Indiana
Standard Oil Company of New Jersey incorporated a subsidiary, Standard Oil Company of Indiana, and began processing oil at its new refinery in Whiting, Indiana, southeast of Chicago. In 1910, the refinery added pipelines connecting it to Kansas and Oklahoma oilfields. When the Supreme Court mandated the break up of John D. Rockefeller’s empire in 1911, Standard Oil of Indiana emerged as an independent company. Amoco branded service stations arrived in the 1950s. Amoco merged with British Petroleum (BP) in 1998, the largest foreign takeover of a U.S. company at the time.
June 18, 1946 – Truman establishes National Petroleum Council
At the request of President Harry S. Truman, the Department of the Interior established the National Petroleum Council to make policy recommendations relating to oil and natural gas. Transferred to the new Department of Energy in 1977, the Council became a privately funded advisory committee with 200 members appointed by the Secretary of Energy. “The NPC does not concern itself with trade practices, nor does it engage in any of the usual trade association activities,” notes the NPC, which held its 134th meeting on April 23, 2024, in Washington, D.C.

June 18, 1948 – Service Company celebrates 100,000th Perforation
Fifteen years after its first well-perforation job, the Lane-Wells Company returned to the well at Montebello, California, to perform its 100,000th perforation. The return to Union Oil Company’s La Merced No. 17 well included a ceremony hosted by Walter Wells, chairman and company co-founder.
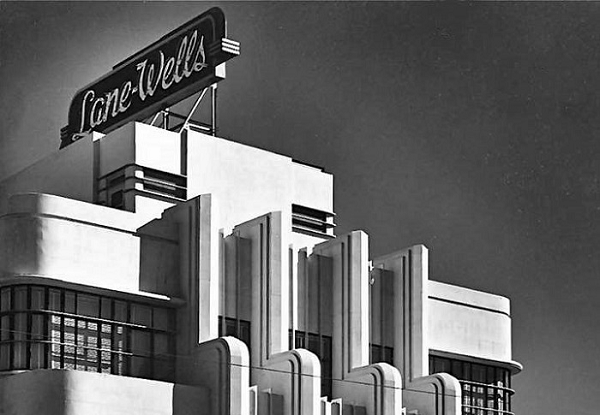

Los Angeles headquarters of Lane-Wells by architect William Mayer, completed in 1937. Photo courtesy Water and Power Associates.
In 1930, Wells and oilfield tool salesman Bill Lane developed a practical multiple-shot perforator that could shoot steel bullets through casing. After many tests, success came at the La Merced No. 17 well. By late 1935, Lane-Wells established a small fleet of trucks for well-perforation services. The company merged with Dresser Industries in 1956 and later became part of Baker-Atlas.
Learn more in Lane-Wells 100,000th Perforation.
June 20, 1977 – Oil begins Flowing in Trans-Alaska Pipeline
The Trans-Alaska Pipeline began carrying oil 800 miles from Prudhoe Bay to the Port of Valdez at Prince William Sound. The oil arrived 38 days later, culminating the world’s largest privately funded construction project. The Prudhoe Bay field had been discovered in 1968 by Atlantic Richfield and Exxon about 250 miles north of the Arctic Circle.

Construction of the controversial pipeline began in 1974. Photo courtesy Alaska Pipeline Authority.
After years of controversy, construction of the 48-inch-wide pipeline began in April 1974. Above-ground sections of the pipeline (420 miles) were built in a zigzag configuration to allow for expansion or contraction and include heat pipes. Oil throughput of the $8 billion pipeline peaked in 1988 at just over 2 million barrels per day, according to the Energy Information Administration (EIA), adding that since 2003, deliveries have been less than 1 million barrels per day and averaged a record low of 464,748 barrels per day in 2024.
“That creates challenges for the pipeline’s operators, including the formation of ice and the buildup of wax that is in the oil on the inside pipeline wall, EIA notes. “The amount of time it takes for oil to travel the 800 miles through the pipeline from the North Slope to the Valdez port increased from 4.5 days in 1988 to about 19 days in recent years.”
Learn more in Trans-Alaska Pipeline History.
June 21, 1893 – Submersible Pump Inventor born
Armais Arutunoff, inventor of the electric submersible pump for oil wells, was born to Armenian parents in Tiflis, Russia. He invented the world’s first electrical centrifugal submersible pump in 1916. At first, Arutunoff could not find financial support for his oilfield production technology after emigrating to the United States in 1923.

Russian engineer Armais Arutunoff, inventor of the first electric submersible pumps.
Thanks to help from Frank Phillips, president of Phillips Petroleum, Arutunoff moved to Bartlesville, Oklahoma, in 1928 and established a manufacturing company. The Tulsa World described the Arutunoff pump as “An electric motor with the proportions of a slim fencepost which stands on its head at the bottom of a well and kicks oil to the surface with its feet.”
REDA Pump Company manufactured pump and motor devices — and employed hundreds during the Great Depression. The name stands for Russian Electrical Dynamo of Arutunoff, the cable address of his first company in Germany and since 1998 a subsidiary of SLB (Schlumberger).
Learn more in Inventing the Electric Submersible Pump.

June 21, 1932 – Oklahoma Governor battles “Hot Oil”
Thirty National Guardsmen marched into the Oklahoma City oilfield when Governor William H. “Alfalfa Bill” Murray took control of oil production after creating a proration board despite objections from independent producers.

The Oklahoma History Center in Oklahoma City includes petroleum equipment on display in the Devon Energy Park, which opened in 2005. Photo by Bruce Wells.
Murray declared martial law again in March 1933 to enforce his regulations preventing the sale or transport of oil produced in excess of the quota, referred to as “hot oil.”
The state legislature passed a law in April giving the Oklahoma Corporation Commission authority to enforce its rules — taking away Murray’s power to regulate the petroleum industry. The commission had been established in 1907 to regulate railroad, telephone, and telegraph companies.
June 21, 1937 – “Great Karg Well” Marker dedicated in Ohio
Similar to the Indiana natural gas boom, discoveries in Ohio brought petroleum prosperity as evidenced by a 1937 historic marker at one well — “erected in humble pride by the people of Findlay, Ohio,” in celebration of the “Great Karg Well” that revealed a giant natural gas field in January 1886.

Marker dedicated in 1937 at the wellhead of the famous 1886 natural gas discovery at Findlay, Ohio. Photo by Michael Baker, courtesy Historical Marker Database.
“At that time gas was simply a by-product of oil drilling, and with no way to store it they ended up piping it away for free to heat homes and drive industrial machinery,” notes the historic marker inscription at the wellhead. Many companies promoted Ohio’s natural gas supplies, which “attracted glass companies from around the world” — until the gas ran out.
Learn more in Indiana Natural Gas Boom.
_______________________
Recommended Reading: From Here to Obscurity: An Illustrated History of the Model T Ford, 1909 – 1927 (1971); Standard Oil Company: The Rise and Fall of America’s Most Famous Monopoly
(1971); Standard Oil Company: The Rise and Fall of America’s Most Famous Monopoly (2016); The Prize: The Epic Quest for Oil, Money & Power
(2016); The Prize: The Epic Quest for Oil, Money & Power (2008); Wireline: A History of the Well Logging and Perforating Business in the Oil Fields
(2008); Wireline: A History of the Well Logging and Perforating Business in the Oil Fields (1990)
(1990) ; The Great Alaska Pipeline
; The Great Alaska Pipeline (1988); Artificial Lift-down Hole Pumping Systems
(1988); Artificial Lift-down Hole Pumping Systems (1984); Oil in Oklahoma
(1984); Oil in Oklahoma (1976); Ohio Oil and Gas, Images of America
(1976); Ohio Oil and Gas, Images of America (2008). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(2008). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Please become an AOGHS annual supporter and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2025. Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
by Bruce Wells | Jun 9, 2025 | This Week in Petroleum History
June 9, 1894 – Water Well finds Oil in Corsicana, Texas –
A contractor hired by the town of Corsicana to drill a water well on 12th Street found oil instead, launching the Texas petroleum industry seven years before the more famous Spindletop Hill gusher hundreds of miles to the southeast. Corsicana’s well produced just 2.5 barrels of oil a day from a depth of 1,035 feet, but inspired a rush of exploration companies.

A colorized postcard depicts the Corsicana oilfield circa 1910. The boom town, which became an oilfield service and manufacturing center, today annually celebrates its oil patch heritage.
By 1898, about 300 produced oil in and around the boom town, which also became a center for technological innovation. A Corsicana company patented and manufactured the rotary rig that drilled the 1901 Spindletop discovery well near Beaumont.
Despite Corsicana’s oilfield discovery well bringing petroleum riches and a drilling boom, city officials paid the contractor only half of the $1,000 fee, citing the agreement for completing a water well. Corsicana has hosted an annual Derrick Days since 1976.
Learn more in First Texas Oil Boom.
June 9, 2023 — California Pump Jack added to Historic Register
An eccentric-wheel oilfield pumping unit that operated in California’s largest oilfield joined the National Register of Historic Places, thanks to research by Mark Smith, who submitted the application. Installed by the Engineers Oil Company in 1913, the Kern County jack plant’s eccentric wheels pumped oil until 1990.
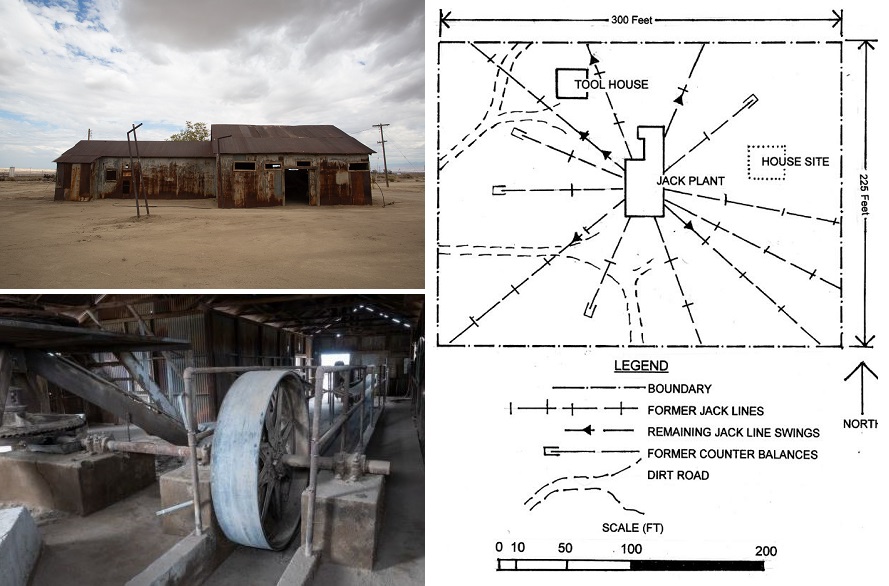
In operation until 1990, California’s Midway-Sunset Jack Plant used eccentric-wheel technologies from the late 19th century. The Kern County plant pumped more than 1.5 million barrels of oil. Photos courtesy John Harte. Illustration courtesy San Joaquin Geological Society.
“The Midway-Sunset Jack Plant is an extremely rare example of central power and ‘jack-line’ oil pumping technology on its original site and housed in its original building,” Smith noted in his 45-page draft application to the State Historical Resources Commission and later approved by the National Park Service. “Its design and operational history reflect significant advancements in oil extraction technology.”

June 11, 1816 – Manufactured Gas lights Art Museum in Baltimore
The first commercial gas lighting of residences, streets and businesses began when Rembrandt Peale impressed Baltimore civic leaders by illuminating a room in his Holliday Street Museum by burning “manufactured gas.” His display (using gas distilled from coal, tar or wood) dazzled them with a “ring beset with gems of light.”
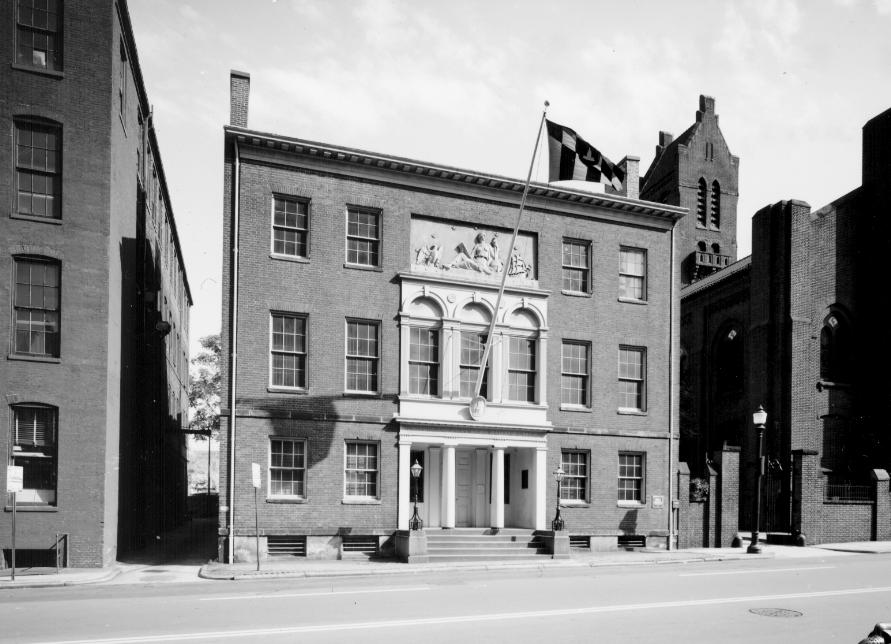

Lighted with manufactured gas, this Baltimore museum opened in 1814, America’s first building erected as a museum. Photo courtesy Maryland Historical Trust.
The Baltimore museum became the first U.S. public building to use gas lighting, according to the Maryland Historical Trust. Within a week, the city council approved plans to illuminate the city’s streets. Peale and a group of investors founded the Gas Light Company of Baltimore — the first gas company in America (today Baltimore Gas and Electric).
Learn more about “town gas” in Illuminating Gaslight.
June 11, 1911 – E.W. Marland discovers Ponca Nation Oilfield
Ernest W. Marland, founder of the 101 Ranch Oil Company in 1908, discovered an oilfield near Ponca City, Oklahoma, after reorganizing the company in his hometown of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Almost broke after drilling eight uneconomical wells, Marland had turned to childhood friend John McCaskey of Pittsburgh, known as the “Sauerkraut King.”
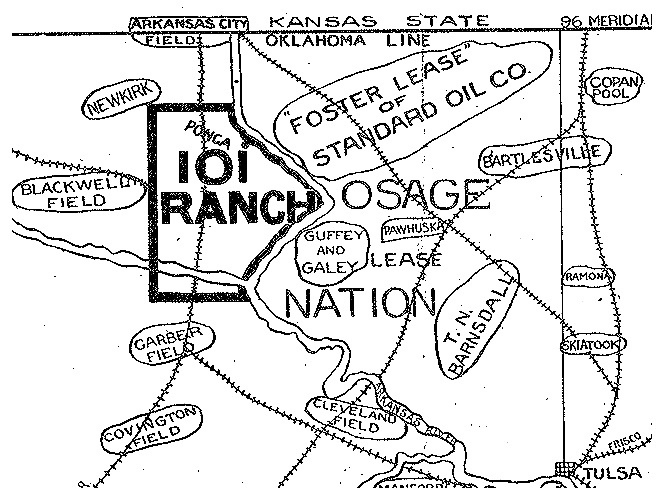
Circa 1910 newspaper promotion of the 101 Ranch Oil Company following discoveries near Ponca (City), west of Osage Nation leases and oilfields.
Partnered with McCaskey and the owners of the 101 Ranch, Marland received permission from White Eagle, chief of the Ponca Nation, to drill near a reservation burial ground. The oilfield discovery well and many that followed produced oil on a reservation allotment owned by Willie-Cries-For-War, age 19, who had leased his 160 acres to Marland for $1,000 a year and 12.5 cents a barrel of oil produced.
Marland would found Marland Oil Company in 1917, merge it with Continental Oil in 1928, and become governor of Oklahoma in 1935. ConocoPhillips opened a Conoco Museum in Ponca City in 2007.
June 11, 1929 – Independent Producers get Organized
Ninety-five years ago, Wirt Franklin of Ardmore, Oklahoma, spoke on behalf of small exploration and production companies during President Herbert Hoover’s Oil Conservation Conference at the Broadmoor Hotel in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Franklin and other independent producers opposed creating a federal commission that could restrict production and allow more imported foreign oil.
“If this condition should be brought about, it would mean the annihilation and destruction of the small producer of crude oil, ” proclaimed Franklin, who had found success in the shallow but prolific Healdton oilfield. Before returning to Ardmore, Franklin and other independents established today’s Washington, D.C.-based Independent Petroleum Association of America (IPAA).

June 12, 1879 – Allegheny Oilfield discovered by O.P. Taylor
Orville “O.P.” Taylor completed the Triangle No. 1 well at a depth of 1,177 feet in Allegheny County, New York, revealing an oilfield that extended into Pennsylvania. His discovery came after two failed wells drilled near oil seeps first reported by a French missionary in 1627. O.P.’s Allegheny oilfield launched a drilling boom that created the town of Petrolia.
The Confederate Army veteran had worked in the cigar manufacturing business in Virginia before catching “oil fever” after reading of oil discoveries along the Allegheny River (see Derricks of Triumph Hill). Early success led to his election as mayor of Wellsville, New York, and the title of “Father of the Allegheny Oilfield.” A Liberty Ship would be named for him during World War II.
June 13, 1917 – Phillips Petroleum Company founded
During the early months of America’s entry into World War I, as oil prices rose above $1 per barrel, Phillips Petroleum Company was founded in Bartlesville, Oklahoma. Brothers Frank and Lee Eldas “L.E.” Phillips consolidated their oil companies and began operating throughout Oklahoma and Kansas. Assets rose from $3 million to $100 million within a few years.

Brothers L.E. Phillips (left) and Frank Phillips established Phillips Petroleum Company in Bartlesville in 1917. Photo courtesy ConocoPhillips.
In 1927, Phillips Petroleum began selling its gasoline in Wichita, Kansas, the first of more than 10,000 Phillips 66 service stations. Phillips chemists received thousands of U.S. patents, including one in 1954 for Marlex, a high-density polyethylene. Wham-O toy company was the first to buy the new plastic (see Petroleum Product Hoopla). The oil company’s high-octane Nu-Aviation fuel played an important role in winning World War II.
Phillips Petroleum merged with Conoco in 2002 to become ConocoPhillips, which in 2007 established petroleum museums in Ponca City and Bartlesville as part of the 100th anniversary of Oklahoma statehood.
June 13, 1928 – Hobbs Oilfield discovered in New Mexico
The New Mexico petroleum industry was launched with the discovery of the Hobbs oilfield near the southeastern corner of the state. After months of difficult cable-tool drilling, the Midwest State No. 1 well produced oil for the Midwest Refining Company, which had drilled the state’s first oil well in 1922.

A June 1928 oilfield discovery brought many decades of petroleum prosperity to downtown Hobbs, New Mexico.
The Hobbs well revealed a giant field, later cited by the New Mexico Bureau of Mines & Mineral Resources as “the most important single discovery of oil in New Mexico’s history.” But after months of drilling, the well had reached a depth of 1,500 feet when an engine house fire consumed the wooden derrick. “Men with less vision would have given up, but not the drillers of Midwest,” noted the state geologist.
As the Great Depression approached, oil production from the Hobbs field attracted investors and drilling companies, quickly transforming Hobbs from “sand, mesquite, bear grass and jackrabbits” to the fastest-growing town in the nation.
Learn more in First New Mexico Oil Wells.

June 14, 1865 – First Daily Oil Region Newspaper
Pennsylvania’s oil region got its first daily newspaper when brothers William and Henry Bloss published a four-page broadsheet, which exceeded a circulation of 300 as the Titusville Herald. The first edition’s articles included a reference to John Wilkes Booth’s visits to the region and his August 1864 oil interests.

The “First Daily Newspaper in the Pennsylvania Oil Region” noted John Wilkes Booth’s petroleum interests.
“John Wilkes Booth purchased a one-thirteenth interest in the territory in August 1864,” the newspaper reported. “We are credibly informed that this Homestead well (see Dramatic Oil Company) in which Booth was interested was destroyed by fire on the day he assassinated President Lincoln.”
June 14, 1938 – United States regulates Natural Gas
The federal government for the first time assumed regulatory control of U.S. natural gas sales to limit the growing market power of interstate pipeline companies.
Although the Natural Gas Act of 1938 did not apply to production, gathering or local distribution, it sought to establish “just and reasonable rates” for pipeline company transmission or sales of natural gas in interstate commerce. Regulatory functions were assigned to the Federal Power Commission (established in 1920), which became the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) in 1977.
June 15, 1954 – Launch of First Mobile Offshore Rig
The offshore barge oil drilling platform, Mr. Charlie left its Louisiana shipyard and went to work for Shell Oil Company in a new oilfield in East Bay, near the mouth of the Mississippi River. The vessel’s design, which would revolutionize the offshore industry, originated with Alden “Doc” Laborde, a marine superintendent for the Kerr-McGee Company in Morgan City, Louisiana.

Beginning in 1954 and capable of drilling wells in water up to 40 feet in depth, Mr. Charlie became the first mobile offshore drilling unit (MODU). Photos courtesy Murphy Oil Corp.
Despite Kerr-McGee’s experience with many post-World War II offshore technologies, including drilling the first oil well out of sight of land in 1947, the company decided against Laborde’s idea for a transportable, submersible drilling barge. The inventor, a Navy veteran, eventually found support from Charles Murphy Jr., founder of Murphy Oil Company.

A self-sufficient drilling rig on a barge, Mr. Charlie in 1954 became an offshore technology milestone with its transportable, column-stabilized design.
LaBorde established Ocean Drilling & Exploration and contracted with J. Ray McDermott Company to convert a 220-foot barge into a drilling platform — the world’s first mobile offshore drilling unit (MODU). Today moored in Morgan City as an international petroleum museum, in December 2024 the Secretary of the Interior added Mr. Charlie to the National Register of Historic Places.
Learn more in Mr. Charlie, First Mobile Offshore Drilling Rig.
_______________________
Recommended Reading: Corsicana (2010); Texas Oil and Gas Postcard History (2013); Black Gold in California: The Story of California Petroleum Industry  (2016); In Pursuit of Fame: Rembrandt Peale, 1778-1860 (1993); The Extraction State, A History of Natural Gas in America (2021); Oil And Gas In Oklahoma: Petroleum Geology In Oklahoma
(2016); In Pursuit of Fame: Rembrandt Peale, 1778-1860 (1993); The Extraction State, A History of Natural Gas in America (2021); Oil And Gas In Oklahoma: Petroleum Geology In Oklahoma (2013); Oil Man: The Story of Frank Phillips and the Birth of Phillips Petroleum
(2013); Oil Man: The Story of Frank Phillips and the Birth of Phillips Petroleum (2014); Oil in West Texas and New Mexico
(2014); Oil in West Texas and New Mexico (1982); Around Titusville, Pa., Images of America
(1982); Around Titusville, Pa., Images of America (2004); Offshore Pioneers: Brown & Root and the History of Offshore Oil and Gas
(2004); Offshore Pioneers: Brown & Root and the History of Offshore Oil and Gas (2011); Breaking the Gas Ceiling: Women in the Offshore Oil and Gas Industry (2019);. Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(2011); Breaking the Gas Ceiling: Women in the Offshore Oil and Gas Industry (2019);. Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Please become an AOGHS annual supporter and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2025 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
by Bruce Wells | Jun 2, 2025 | This Week in Petroleum History
June 2, 1908 – Goose Creek Oilfield discovered –
Drilled on Galveston Bay wetlands, the first offshore well in Texas revealed a giant oilfield 20 miles southeast of Houston, according to the Texas State Historical Association (TSHA). Inspired by reports of bubbles on the surface where Goose Creek emptied into the bay, the Houston-based syndicate Goose Creek Production Company made the discovery at a depth of 1,600 feet.

A single well of the Goose Creek field in 1917 produced 35,000 barrels of oil a day from a depth of 3,050 feet. Circa 1919 photo by Frank Schlueter courtesy Library of Congress Prints and Photographs Division.
“Within days the syndicate sold out to a subsidiary of the Texas Company, the future Texaco,” notes TSHA, adding the Goose Creek field, “spurred exploration for deep-seated (salt) domes, and led to the discovery of some of the largest oilfields in the United States.”
In 1909, Howard Hughes Sr. secretly tested an experimental dual-cone rock bit at Goose Creek. Humble Oil and Refining Company constructed a refinery adjacent to the field In 1921, naming the site Baytown.
June 3, 1979 – Bay of Campeche Oil Spill
Drilling in about 150 feet of water, the semi-submersible platform Sedco 135 suffered a blowout 50 miles off Mexico’s Gulf Coast. The Pemex well Ixtoc 1 spilled 3.4 million barrels of oil before being controlled nine months later. Considering the spill’s size, the environmental impact proved less than expected, according to a 1981 report by the Coordinated Program of Ecological Studies in the Bay of Campeche. Surveys of Campeche Sound conducted in 1980 reported, “Evaporation, dispersion, photo-oxidation and biodegradation processes played a major role in attenuating the harmful environmental effects of the oil spill.”
June 4, 1872 – Pennsylvania Oilfields bring Petroleum Jelly
A young chemist living in New York City, Robert Chesebrough, patented “a new and useful product from petroleum,” which he named “Vaseline.” His patent proclaimed the virtues of this purified extract of petroleum distillation residue as a lubricant, hair treatment, and balm for chapped hands.
patented “a new and useful product from petroleum,” which he named “Vaseline.” His patent proclaimed the virtues of this purified extract of petroleum distillation residue as a lubricant, hair treatment, and balm for chapped hands.

Robert Chesebrough consumed a spoonful of Vaseline each day and lived to be 96 years old. Photo courtesy Drake Well Museum.
When the 22-year-old chemist visited the new Pennsylvania oilfields in 1865, he noted drilling was often confounded by a paraffin-like substance that clogged the wellhead. Drillers used the “rod wax” as a quick first aid for abrasions.
Chesebrough returned to New York City and worked in his laboratory to purify the well byproduct, which he first called “petroleum jelly.” Female customers would discover that mixing lamp black with Vaseline made an impromptu mascara. In 1913, Mabel Williams employed just such a concoction and it led to the founding of a cosmetic company.
Learn more in The Crude History of Mabel’s Eyelashes.

June 4, 1892 – Devastation of Pennsylvania Oil Regions
After weeks of thunderstorms in Pennsylvania’s Oil Creek Valley, the Spartansburg Dam on Oil Creek burst, sending torrents of water that killed more than 100 people and destroyed homes and businesses in Titusville and Oil City. The disaster was compounded when fires broke out.

Titusville, Pennsylvania, residents used the “Colonel Drake Steam Pumper” during the great flood and fire of 1892. Photo by John Mather courtesy Drake Well Museum and Park.
“This city during the past twenty-four hours has been visited by one of the most appalling fires and overwhelming floods in the history of this country,” reported the New York Times from Oil City. Oilfield photographer John A. Mather documented the devastation, which included his Titusville studio and 16,000 glass-plate negatives.
Learn more in Oilfield photographer John Mather.
June 4, 1896 – Henry Ford drives his “Quadricycle”
Driving the first car he ever built, Henry Ford left a workshop behind his home on Bagley Avenue in Detroit, Michigan. He had designed his “Quadricycle” in his spare time while working as an engineer for Edison Illuminating Company. Ford chose the name because his handmade, 500-pound “horseless carriage” ran on four bicycle tires. Inspired by advancements in gasoline-fueled engines, he founded the Henry Ford Company in 1903.
June 4, 1921 – Petroleum Seismograph tested
A team of earth scientists tested an experimental seismograph device on a farm three miles north of Oklahoma City and determined it could accurately map subsurface structures. Led by Prof. John C. Karcher and W.P. Haseman, the team from the University of Oklahoma found that seismology could be useful for oil and natural gas exploration and production. Further seismic reflection tests, including one in the Arbuckle formation in August, confirmed their results.

June 6, 1932 – First Federal Gasoline Tax
The federal government taxed gasoline for the first time when the Revenue Act of 1932 added a one-cent per gallon excise tax to U.S. gasoline sales. The first state to tax gasoline was Oregon, which imposed a one-cent per gallon tax in 1919. Colorado, New Mexico, and other states followed. The federal tax, last raised on October 1, 1993, has remained at 18.4 cents per gallon (24.4 cents per gallon for diesel). About 60 percent of federal gasoline taxes are used for highway and bridge construction.
June 6, 1944 – English Channel Pipelines fuel WWII Victory
As the D-Day invasion began along 50 miles of fortified French coastline in Normandy, logistics for supplying the effort would include two top-secret engineering feats — the construction of artificial harbors followed by the laying of pipelines across the English Channel.

Operation PLUTO (Pipe Line Under The Ocean) unspooled flexible steel pipelines across the English Channel, but the channel was deep, the French ports distant.
Code-named “Mulberrys” and using a design similar to modern jack-up offshore rigs, the artificial harbors used barges with retractable pylons to provide platforms to support floating causeways extending to the beaches.
To fuel the Allied advance into Nazi Germany, Operation PLUTO (Pipe Line Under The Ocean) used flexible steel pipelines wound onto giant “conundrums” designed to spool off when towed. Gen. Dwight Eisenhower later acknowledged the vital importance of the oil pipelines.
Learn more in PLUTO, Secret Pipelines of WW II.
June 6, 1976 – Oil Billionaire J. Paul Getty dies
With a fortune reaching $6 billion (about $32 billion in 2023), J. Paul Getty died at 83 at his estate near London. Born into his father’s petroleum wealth from the Oil Company of Tulsa, Getty made his first million by age 23 from buying and selling oil leases.

The J. Paul Getty Museum art collection is housed in the Getty Center (above) and the Getty Villa on the California Malibu coast.
“I started in September 1914, to buy leases in the so-called red-beds area of Oklahoma,” Getty once told the New York Times. “The surface was red dirt and it was considered impossible there was any oil there. My father and I did not agree and we got many leases for very little money which later turned out to be rich leases.”
Getty, who incorporated Getty Oil in 1942, gave more than $660 million from his estate to the J. Paul Getty Museum.
______________________
Recommended Reading: History Of Oil Well Drilling (2007); Western Pennsylvania’s Oil Heritage
(2007); Western Pennsylvania’s Oil Heritage (2008); The Maybelline Story: And the Spirited Family Dynasty Behind It
(2008); The Maybelline Story: And the Spirited Family Dynasty Behind It (2010); Around Titusville, Pennsylvania, Images of America
(2010); Around Titusville, Pennsylvania, Images of America (2004); I Invented the Modern Age: The Rise of Henry Ford
(2004); I Invented the Modern Age: The Rise of Henry Ford (2014); Trek of the Oil Finders: A History of Exploration for Petroleum (1975); Code Name MULBERRY: The Planning Building and Operation of the Normandy Harbours
(2014); Trek of the Oil Finders: A History of Exploration for Petroleum (1975); Code Name MULBERRY: The Planning Building and Operation of the Normandy Harbours (1977); The Great Getty (1986). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(1977); The Great Getty (1986). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Please become an AOGHS annual supporter and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. © 2025 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
by Bruce Wells | May 26, 2025 | This Week in Petroleum History
May 26, 1891 – Carbon Black Patent leads to Crayola –
Edwin Binney and C. Harold Smith received a patent for an “Apparatus for the Manufacture of Carbon Black.” The Binney & Smith process created a fine, intensely black soot-like substance — a pigment blacker than any other. Its success would lead to another petroleum product, Crayola crayons.
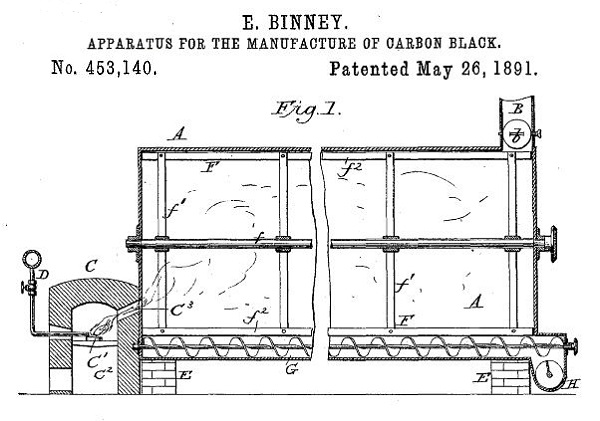
Edwin Binney in 1891 patented a petroleum-burning “Apparatus for the Manufacture of Carbon Black.” Twelve years later, Binney & Smith produced another oilfield product, Crayola, named by his wife Alice.
After introducing a popular black crayon called Staonal (stay-on-all) the Pennsylvania company began manufacturing Crayola crayons in 1903 using paraffin hand-mixed pigments. Each box contained eight colors: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, violet, brown and black.
Learn more in Carbon Black and Oilfield Crayons. (more…)






(2000); The Discovery of Oil in South Arkansas, 1920-1924 (1974); Historic Battleship Texas: The Last Dreadnought
(2007); Evolution of the American Diesel Locomotive, Railroads Past and Present
(2007); Early Texas Oil: A Photographic History, 1866-1936
(2000) Death and Oil: A True Story of the Piper Alpha Disaster on the North Sea
(2011). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
































