by Bruce Wells | Apr 8, 2024 | This Week in Petroleum History
April 9, 1914 – Ohio Cities Gas Company founded –
Beman Dawes and Fletcher Heath organized the Ohio Cities Gas Company in Columbus, Ohio, before building an oil refinery in West Virginia. Ohio Cities Gas acquired Pennsylvania-based Pure Oil Company in 1917 and adopted that name three years later. Pure Oil had been founded in Pittsburgh in 1895 by independent oil producers, refiners, and pipeline operators to counter the market dominance of Standard Oil Company.

Ohio Cities Gas Company became Pure Oil in 1917.
By producing, refining and selling its products, Pure Oil became the second vertically integrated petroleum company after Standard Oil. Headquartered in a now iconic Chicago skyscraper it built in 1926, the company joined the 100 largest U.S. industrial corporations. It was acquired in 1965 by Union Oil Company of California, now a division of Chevron.

April 9, 1966 – Birthday of Tula’s Golden Driller
A 76-foot statue of an oilfield worker today known as “The Golden Driller” made its debut at the International Petroleum Exposition in Tulsa, Oklahoma. After several refurbishments, the 22-ton statue would contain 2.5 miles of rods and mesh with tons of plaster and concrete — withstanding winds up to 200 mph. A smaller version of Tulsa’s iconic roughneck originally appeared at the 1953 petroleum exposition as a promotion for the Mid-Continent Supply Company of Fort Worth, Texas.
April 10, 1866 – Densmore Brothers patent Railroad Oil Tank Car
James and Amos Densmore of Meadville, Pennsylvania, received a patent for their “Improved Car for Transporting Petroleum,” developed a year earlier in the northwestern Pennsylvania oil regions. Their patent illustrated a simple but sturdy design for securing two re-enforced containers on a typical railroad car.
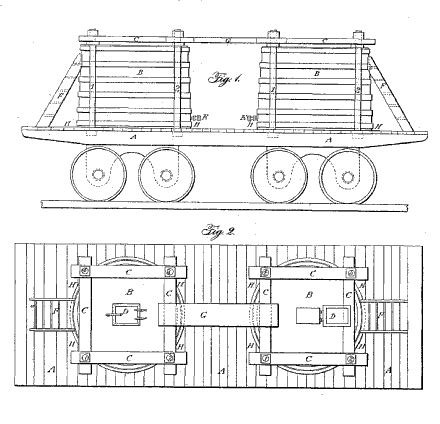
The Densmore oil tank car briefly revolutionized the bulk transportation of oil to market. Hundreds of the twin tank railroad cars were in use by 1866.
Although the Densmore cars were an improvement, they would be replaced by the more practical single, horizontal tank. After leaving the business, Amos Densmore in 1875 invented a new way for arranging “type writing machines” so commonly used letters would no longer collide — the “Q-W-E-R-T-Y” keyboard. James Densmore’s continued success in oilfields helped finance the start of the Densmore Typewriter Company.
Learn more in Densmore Brothers invent First Oil Tank Car.
April 11, 1957 – Oklahoma Independent William Skelly dies
William Grove Skelly (1878 -1957) died in Tulsa after a long career as an independent producer that he began as a 15-year-old tool dresser in early Pennsylvania oilfields. Prior to World War I, he found success in the El Dorado field outside Wichita, Kansas. Skelly incorporated Skelly Oil Company in Tulsa in 1919. Four years later, he established the International Petroleum Exposition while serving as president of the Tulsa Chamber of Commerce. Skelly also helped establish the first FM radio station in Oklahoma, KWGS, in 1947.

April 13, 1974 – Depth Record set in Oklahoma Anadarko Basin
After drilling for 504 days and costing about $7 million, the Bertha Rogers No. 1 well reached a total depth of 31,441 feet (5.95 miles) before being stopped by liquid sulfur. Drilled in the heart of Oklahoma’s Anadarko Basin, it was the deepest well in the world for more than a decade.
Robert Hefner III’s GHK Company and partner Lone Star Producing Company believed natural gas reserves resided deep in the basin, which extends across West-Central Oklahoma and the Texas Panhandle. Their first attempt began in 1967 and took two years to reach what at the time was a record depth of 24,473 feet.

A 1974 souvenir plaque of the Bertha Rogers No. 1 well, which reached almost six miles deep in Oklahoma’s Anadarko Basin.
The high-tech well found plenty of natural gas, according to historian Robert Dorman, but because of federal price controls at the time, “the sale of the gas could not cover the high cost of drilling so deeply – $6.5 million, as opposed to a few hundred thousand dollars for a conventional well.”
Drilling began in November 1972 and averaged about 60 feet per day. By April 1974, bottom-hole pressure reached almost 25,000 pounds per square inch with a temperature of 475 degrees. It took eight hours for cuttings to reach the surface. The well’s 1.5 million pounds of casing was the heaviest ever handled by any drilling rig.
Learn more in Anadarko Basin in Depth.
April 14, 1865 – Dramatic Oil Company’s Failed Oilman turns Assassin
After failing to make his fortune in Pennsylvania oilfields, John Wilkes Booth assassinated President Abraham Lincoln in Washington, D.C. One year earlier, Booth had left his acting career to drill an oil well in booming Venango County.
In January 1864, Booth visited Franklin, Pennsylvania, where he leased 3.5 acres on a farm, about one mile south of the village of Franklin and on the east side of the Allegheny River. With several partners, including his friends from the stage, Booth formed the Dramatic Oil Company and raised money to drill a well.
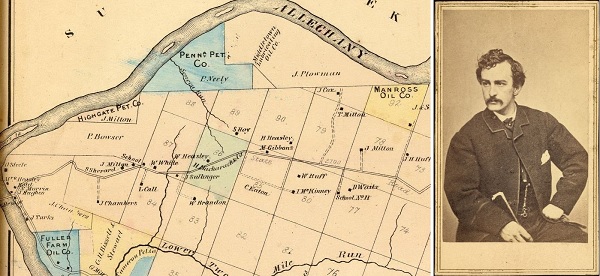
John Wilkes Booth made his first trip to the oil boom town of Franklin, Pennsylvania, in January 1864. He purchased a 3.5-acre lease on the Fuller farm (lower left). Circa 1865 photo of Booth by Alexander Gardner, courtesy Library of Congress.
Although the Dramatic Oil Company’s well found oil and began producing about 25 barrels a day, Booth and his partners wanted more and tried “shooting” the well to increase production. When the well was ruined, the failed oilman left the Pennsylvania oil region for good in July 1864.
Learn more in Dramatic Oil Company.

_______________________
Recommended Reading: The American Railroad Freight Car (1995); Story of the Typewriter, 1873-1923 (2019); Tulsa Oil Capital of the World, Images of America (2004); Oil in Oklahoma
(2004); Oil in Oklahoma (1976); Myth, Legend, Reality: Edwin Laurentine Drake and the Early Oil Industry
(1976); Myth, Legend, Reality: Edwin Laurentine Drake and the Early Oil Industry (2009). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(2009). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Become an AOGHS annual supporting member and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2024 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
by Bruce Wells | Apr 5, 2024 | Petroleum Transportation
Pennsylvanians advance oil industry infrastructure and later help invent “QWERTY” typewriter keyboard.
As Northwestern Pennsylvania oil production skyrocketed following the Civil War, railroad oil tank cars fabricated by two brothers improved shipment volumes from oilfields to kerosene refineries. The tank car designed by James and Amos Densmore would not last long, but more success followed when Amos came up with an innovative keyboard arrangement for typewriters.
Flatbed railroad cars with two wooded oil tank cars became the latest advancement in oilfield infrastructure after the Densmore brothers patented their design on April 10, 1866.
The inventors from Meadville, Pennsylvania, had developed an “Improved Car for Transporting Petroleum” one year earlier in America’s booming oil regions. The first U.S. oil well had been drilled just seven years earlier along Oil Creek in Titusville.

The first functional railway oil tank car was invented and constructed in 1865 by James and Amos Densmore at the Miller Farm along Oil Creek, Titusville, Pennsylvania. Photo courtesy Drake Well Museum and Park.
Using an Atlantic & Great Western Railroad flatcar, the brothers secured two tanks in order to ship oil in bulk. The patent (no. 53,794) described and illustrated the railroad car’s design.
The nature of our invention consists in combining two large, light tanks of iron or wood or other material with the platform of a common railway flat freight-car, making them practically part of the car, so as they carry the desired substance in bulk instead of in barrels, casks, or other vessels or packages, as is now universally done on railway cars.

Development of railroad tank cars came when traditional designs, including the flatcar, hopper, and boxcar, proved inadequate for large amounts of oil — often shipped in 42-gallon barrels.
New designs were born out of necessity, as the fledgling oil industry demanded a better car for the movement of its product, according to American-Rails.com.
“Before the car was developed, railroads used a combination of boxcars, flatcars, and gondolas to haul everything from lumber and coal to crude oil, molasses, and water (by use of barrels),” noted Adam Burns in 2022. “One of the most prolific car types you will find moving within a freight train today is the tank car.”
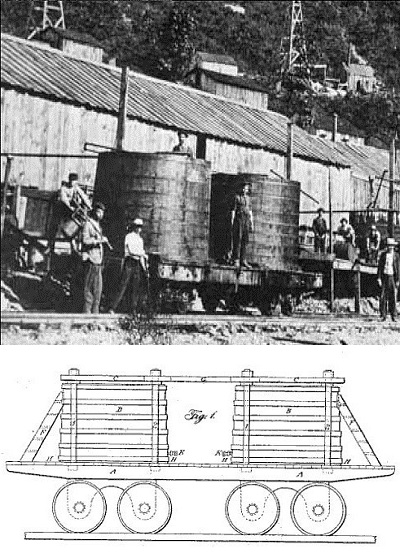
Prone to leaks and top heavy, Densmore tank cars provided a vital service, if only for a few years before single, horizontal tanks replaced them.
According to transportation historian John White Jr., the Densmore brothers’ oil tank design essentially consisted of a flat car with wooden vats attached. “The Central Pacific is known to have used such specialized cars to transport water, he noted in his 1995 book, The American Railroad Freight Car.
“However, prior to the discovery of oil by Colonel Edward (sic) Drake near Titusville, Pennsylvania, on August 27, 1859, the tank car was virtually non-existent,” added White, a former curator of Transportation at the Smithsonian Institution.
Dual Tank Design
The brothers further described the use of special bolts at the top and bottom of their tanks to act as braces and “to prevent any shock or jar to the tank from the swaying of the car while in motion.”

A Pennsylvania historical marker on U.S. 8 south of Titusville commemorates the Densmore brothers’ significant contribution to petroleum transportation technology. Dedicated in 2004, the marker notes:
The first functional railway oil tank car was invented and constructed in 1865 by James and Amos Densmore at nearby Miller Farm along Oil Creek. It consisted of two wooden tanks placed on a flat railway car; each tank held 40-45 barrels of oil. A successful test shipment was sent in September 1865 to New York City. By 1866, hundreds of tank cars were in use. The Densmore Tank Car revolutionized the bulk transportation of crude oil to market.
The benefit of such railroad cars to the early petroleum industry’s infrastructure was immense, especially as more Americans eagerly sought oil-refined kerosene for lamps.
Despite design limitations that would prove difficult to overcome, independent producers took advantage of the opportunity to transport large amounts of petroleum. Other transportation methods required teamsters taking barrels to barges on Oil Creek and the Allegheny River to get to kerosene refineries in Pittsburgh.
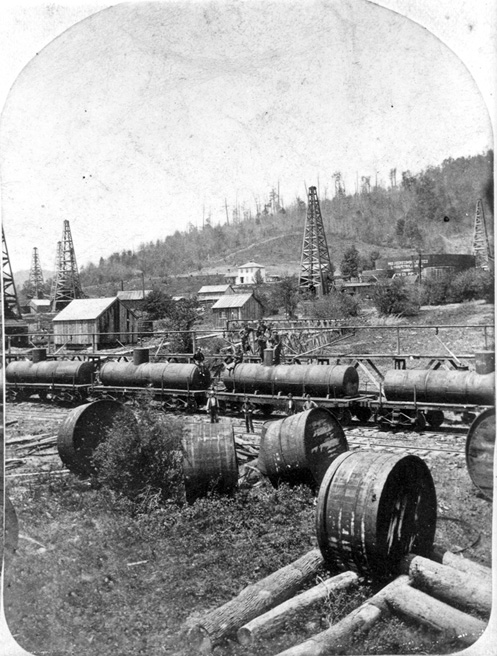

Riveted cylindrical iron tank cars replaced Densmore brothers’ wooden vat cars. Discarded Densmore tanks can be seen. Photo courtesy Drake Well Museum.
As larger refineries were constructed, it was found that it cost $170 less to ship 80 barrels of oil from Titusville to New York in a tank car instead of individual barrels. But the Densmore cars had flaws.
They were unstable, top heavy, prone to leaks, and limited in capacity by the eight-foot width of the flatcar. Within a year, oil haulers shifted from the Densmore vertical vats to larger, horizontal riveted iron cylindrical tanks, which also demonstrated greater structural integrity during derailments or collisions.

The same basic cylindrical design for transporting petroleum can be seen as modern railroads load products from corn syrup to chemicals — all in a versatile tank car that got its start in the Pennsylvania oil industry.
Oil Tanks to Typewriters
Although the Densmore brothers left the oil region by 1867 — their inventiveness was far from over. In 1875, Amos Densmore assisted Christopher Sholes to rearrange the “type writing machine” keyboard so that commonly used letters no longer collided and got stuck. The “QWERTY” arrangement vastly improved Shole’s original 1868 invention.

Amos Densmore helped invent one of the first practical typewriters.
Following his brother’s work with Sholes, inventor of the first practical typewriter, James Densmore’s oilfield financial success helped the brothers establish the Densmore Typewriter Company, which produced its first model in 1891. Few historians have made the oil patch to typewriter keyboard connection — including Densmore biographers.

“Biographies of the Densmores — and even their personal papers now residing at the Milwaukee Public Museum — all refer to their work on typewriters, but make no mention of their pioneering work in railroad tank car design,” notes the Pennsylvania Historical Commission.
_______________________
Recommended Reading: The American Railroad Freight Car (1995); Early Days of Oil: A Pictorial History of the Beginnings of the Industry in Pennsylvania (2000); Story of the Typewriter, 1873-1923 (2019); Myth, Legend, Reality: Edwin Laurentine Drake and the Early Oil Industry
(2000); Story of the Typewriter, 1873-1923 (2019); Myth, Legend, Reality: Edwin Laurentine Drake and the Early Oil Industry (2009). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(2009). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Become an AOGHS annual supporting member and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. © 2024 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
Citation Information – Article Title: “Densmore Oil Tank Cars.” Authors: B.A. Wells and K.L. Wells. Website Name: American Oil & Gas Historical Society. URL: https://aoghs.org/transportation/densmore-oil-tank-car. Last Updated: April 5, 2024. Original Published Date: April 7, 2013.




(2004); Oil in Oklahoma
(1976); Myth, Legend, Reality: Edwin Laurentine Drake and the Early Oil Industry
(2009). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.






