by Bruce Wells | Dec 28, 2024 | Petroleum Technology
Early patent for a hollow “drill-rod” and roller bit for “making holes in hard rock.”
An “Improvement in Rock Drills” patent issued to a New Yorker after the Civil War included the basic elements of the modern petroleum industry’s rotary rig.
On January 2, 1866, Peter Sweeney of New York City was granted U.S. patent No. 51,902 for a drilling system with many innovative technologies. His rotary rig design, which improved upon an 1844 British patent by Robert Beart, applied the rotary drilling method’s “peculiar construction particularly adapted for boring deep wells.”
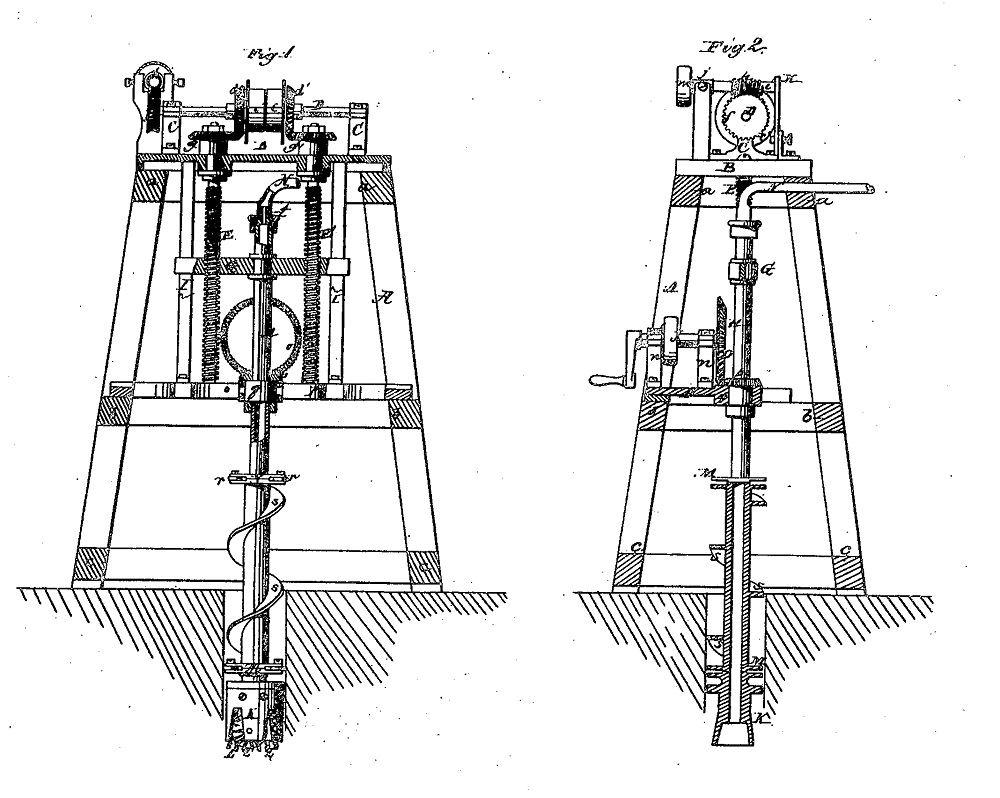
Peter Sweeney’s innovative 1866 “Stone Drill” patent included a roller bit using a “rapid rotary motion” that would evolve into modern rotary drilling technologies.
More efficient than traditional cable-tool percussion bits, Sweeney’s patent provided for a roller bit with replaceable cutting wheels such “that by giving the head a rapid rotary motion the wheels cut into the ground or rock and a clean hole is produced.”
Deeper Drilling
The Sweeney design utilized a roller bit with replaceable cutting wheels such “that by giving the head a rapid rotary motion the wheels cut into the ground or rock and a clean hole is produced.

In another innovation, the “drill-rod” was hollow and connected with a hose through which “a current of steam or water can be introduced in such a manner that the discharge of the dirt and dust from the bottom of the hole is facilitated.”
Better than commonly used steam-powered cable-tools, which used heavy rope to lift and drop iron chisel-like bits, Sweeney claimed his drilling apparatus could be used with great advantage for “making holes in hard rock in a horizontal, oblique, or vertical direction.”
Drilling operations could be continued without interruption, Sweeny explained in his patent application, “with the exception of the time required for adding new sections to the drill rod as the depth of the hole increases. The dirt is discharged during the operation of boring and a clean hole is obtained into which the tubing can be introduced without difficulty.”

A 1917 rotary rig in the Coalinga, California, oilfield. Courtesy of the Joaquin Valley Geology Organization.
Foreseeing the offshore exploration industry, Sweeney’s patent concluded with a note that “the apparatus can also be used with advantage for submarine operations.”

With the U.S. oil industry’s growth after the first commercial well in 1859, drilling contractors quickly improved upon Sweeney’s idea. A device was fitted to the rotary table that clamped around the drill pipe and turned. As this “kelly bushing” rotated, the pipe rotated and with it the bit downhole. The torque of the rotary table was transmitted to the drill stem.
Thirty-five years after Sweeney’s patent, rotary drilling revolutionized the petroleum industry after a 1901 oil discovery by Capt. Anthony Lucas launched a drilling boom at Spindletop Hill in Texas.
Learn more at Making Hole – Drilling Technology.
_______________________
Recommended Reading: History Of Oil Well Drilling (2007); The Prize: The Epic Quest for Oil, Money & Power (1991); The Extraction State, A History of Natural Gas in America (2021). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(2007); The Prize: The Epic Quest for Oil, Money & Power (1991); The Extraction State, A History of Natural Gas in America (2021). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Please become an AOGHS annual supporter and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2024 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
Citation Information – Article Title: “Sweeney’s 1866 Rotary Rig.” Authors: B.A. Wells and K.L. Wells. Website Name: American Oil & Gas Historical Society. URL: https://aoghs.org/technology/1866-patent-rotary-rig. Last Updated: December 27, 2024. Original Published Date: January 2, 2013.
by Bruce Wells | Sep 2, 2024 | This Week in Petroleum History
September 2, 1910 – Cities Service Company incorporates –
Henry Doherty organized the Cities Services Company as a public utility holding company in Bartlesville, Oklahoma. Doherty bought producing properties in Kansas and Oklahoma as he acquired distributing companies and linked them to natural gas fields.
In 1915, a Cities Service subsidiary discovered the 34-square-mile El Dorado oilfield. In 1928, another subsidiary completed the discovery well of the Oklahoma City oilfield.

Cities Service Company subsidiaries discovered major Mid-Continent oilfields.
Federal court mandates in 1940 resulted in Cities Service’s divestiture of its public utilities, and in 1959 the remaining companies were reformed as Cities Service Oil Company, which changed its marketing brand to Citgo in 1964.
After being acquired by Occidental Petroleum in 1982, Citgo was acquired by the Venezuela state-owned oil company Petróleos de Venezuela (PDVSA) in 1990.
Learn more in Cities Service Company.

September 2, 1918 – Desdemona Oilfield adds to North Texas Boom
A third oil boom arrived in Eastland County, Texas, when the Hog Creek Oil Company exploratory well at Desdemona blew in at 2,000 barrels of oil a day — thrilling the venture’s investors. Production from the new oilfield, which joined prolific fields at Breckenridge (1916) and “Roaring Ranger” (1917), would peak at more than 7.3 million barrels of oil in 1919.
“By 1919 the Desdemona field was probably the second largest in the oil belt, and the Hog Creek Oil Company’s stockholders were able to sell their $100 shares for $10,250 each,” noted Edwin Cox in his 1950 History of Eastland County, Texas.
Thanks to its oil leases, Eastland County’s Merriman Baptist Church would be declared the richest congregation in America.
September 2, 2009 – Gulf of Mexico Depth Record
BP discovered an oilfield 250 miles southeast of Houston in the Gulf of Mexico — and set a world depth record by drilling 30,923 feet into seabed from a platform floating more than 4,130 feet above.
The Tiber Prospect field — in 2009 estimated to contain more than three billion barrels of oil — was drilled by the Deepwater Horizon, which later was moved to a new site and destroyed in the deadly explosion and oil spill of April 2010. Learn about other ultra-deep wells in Anadarko Basin in Depth.
September 4, 1841 – “Rock Drill Jar” Patent for Percussion Drilling
Early drilling technology advanced when William Morris, a driller in West Virginia, patented a “Rock Drill Jar.” It was an innovation he had been experimenting with while drilling brine wells.
“The mechanical success of cable-tool drilling has greatly depended on a device called jars, invented by a spring pole driller,” according to historian Samuel Pees, who in 2004 noted Morris began using the technology as early as the 1830s.
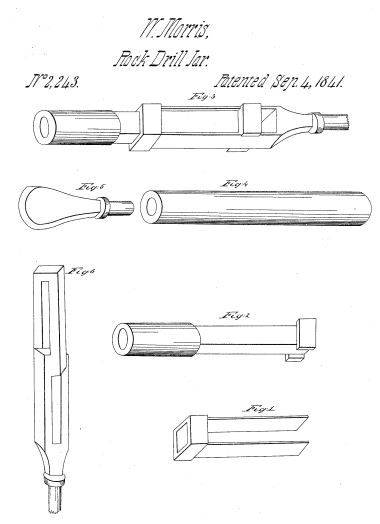
Drill jar technology improved efficiency for drilling brine wells — and later, oil wells.
For more advanced cable tools, Morris patented a “manner of uniting augers to sinkers for boring,” with the upper link of the jars helping the lower link to strike the underlying auger stem on the upstroke. This upward blow could dislodge the bit if it was stuck in the rock formation. Cable-tool drillers would soon improve upon Morris’ patented jars.
Learn more in Making Hole — Drilling Technology.

September 4, 1850 – Illuminating Chicago Streets
The Chicago Gas Light & Coke Company delivered its first commercial gas processed from coal. “The gas pipes were filled, and the humming noise made by the escaping gas at the tops of the lamp-posts indicated that everything was all right,” reported the Gem of the Prairie newspaper. “Shortly afterward the fire was applied and brilliant torches flamed on both sides of Lake Street as far as the eye could see and wherever the posts were set.”
By 1855, almost 80 miles of pipeline would be installed for about 2,000 manufactured gas consumers in Chicago. The first U.S. public street lamp fueled by manufactured gas illuminated Baltimore, Maryland, in 1817 (see Illuminating Gaslight).
September 5, 1885 – Birth of the “Filling Station” Gas Pump
Modern gasoline pump design began with inventor Sylvanus F. (Freelove) Bowser, who sold his first pump to a grocery store owner in Fort Wayne, Indiana. Designed to safely dispense kerosene as well as “burning fluid, and the light combustible products of petroleum,” Bowser’s pump included a container holding 42 gallons. The pump used marble valves, a wooden plunger, and a simple, upright faucet.

The 1916 Bowser gas pump included a “clock face” dial to measure pumped gas. Photo courtesy Smithsonian Institution.
Thanks to the pump’s success at Jake Gumper’s grocery store, Bowser formed the S.F. Bowser Company and patented his invention in 1887. Within a decade — as the automobile’s popularity grew — Bowser’s company has added new pump designs. By 1905, the S.F. Bowser “Self-Measuring Gasoline Storage Pump” became known to motorists as a “filling station.”
The Bowser gas pump included a hand-levered suction pump and a hose attachment for dispensing gas. As other pump manufacturers arrived, Fort Wayne became known as the “Gas Pump Capital of the World.”
Learn more in First Gas Pump and Service Station.
September 5, 1927 – Schlumberger Brothers test Electric Logging Tool
An electric well-logging tool was first applied at Pechelbronn, France, after brothers Conrad and Marcel Schlumberger modified their surface system to operate vertically in a well.
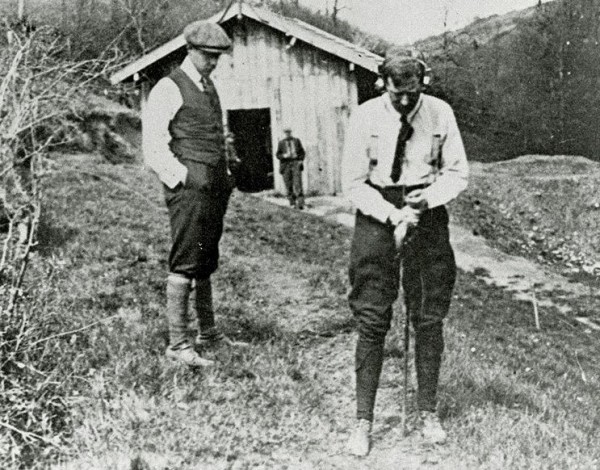

Conrad Schlumberger, using very basic equipment, in 1912 recorded the first map of equipotential curves near Caen, France.
Conrad Schlumberger had conceived the idea of using electrical measurements to map subsurface rock formations as early as 1912. After developing an electrical four-probe surface approach for mineral exploration, the brothers created the electric downhole well log.
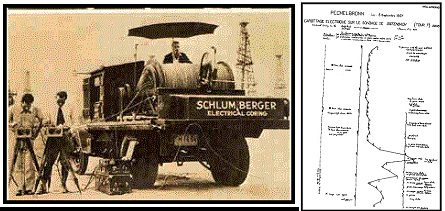
Conrad and Marcel Schlumberger tested their electronic logging tool in 1927, one year after founding the world’s first well-logging company. Photo and image courtesy Schlumberger Ltd.
Lowering their new tool into a well, they recorded a single lateral-resistivity curve at fixed points in the well’s borehole and graphically plotted the results against depth — creating a well log of geologic formations. Changes in subsurface resistance readings showed variations and possible oil and natural gas-producing areas.
The brothers’ technological breakthrough would lead to Schlumberger becoming the world’s first well-logging oilfield service company.
September 5, 1939 – Young Geologist reveals Mississippi Oilfield
Union Producing Company completed its Woodruff No. 1, the first commercial oil well in Mississippi. Drilled at Tinsley, southwest of Yazoo City, the well produced 235 barrels of oil a day from a depth of 4,560 feet in a sandstone later named the Woodruff Sand. Fieldwork by geologist Frederic Mellen led to the Tinsley oilfield discovery.
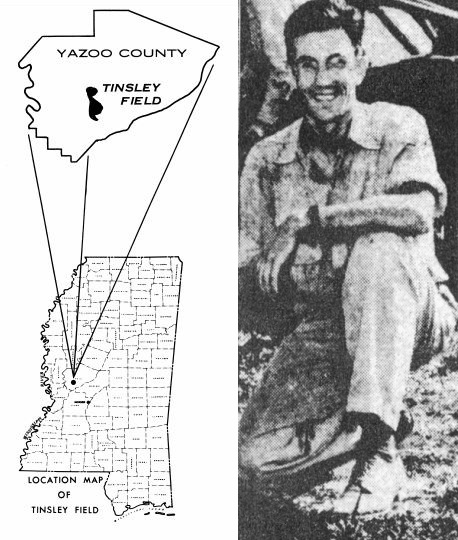
Fred Mellen was elected president of the Mississippi Geological Survey in 1946.
While working on a Works Progress Administration (WPA) project, Mellen earlier found indications of a salt dome structure similar to the giant Spindletop field of 1901 in Texas. The 28-year-old geologist urged more seismographic testing, and Houston-based Union Producing Company leased about 2,500 acres at Perry Creek.
Mellen’s original WPA project had been a clay and minerals survey, “to locate a suitable clay to mold cereal bowls and other utensils for an underprivileged children’s nursery.” Instead, he launched Mississippi’s oil industry.
Learn more in First Mississippi Oil Wells.

September 7, 1917 – Oilfield Legacy of Texas Governor Hogg
After drilling 20 dry holes, the Tyndall-Wyoming Oil Company completed the No. 1 Hogg well 50 miles south of Houston. Within four months, a second well was producing about 600 barrels a day. The discoveries ended a succession of dry holes dating back to 1901 — when former Texas Governor James “Big Jim” Hogg paid $30,000 for the lease. He also helped launch the Texas Company (Texaco).
Gov. Hogg died 11 years before the Tyndall-Wyoming Oil Company wells found oil in the giant West Columbia oilfield. Fortunately for his family, he stipulated in his will that the mineral rights should not be sold for at least 15 years after his death.
Learn more in Governor Hogg’s Texas Oil Wells.
September 7, 1923 – California Oilfield discovered at Dominguez Hills
Maj. Frederick Russell Burnham discovered oil in Dominguez Hills, an unincorporated area of Los Angeles County, California. His well produced about 1,200 barrels of oil a day from a depth of about 4,000 feet. Maj. Burnham, a decorated soldier in both the U.S. and British armies, was once known as “King of the Scouts.”
The Burnham Exploration Company and partner Union Oil Company of California opened the Dominguez Hills oilfield, “a two-square-mile, two-mile deep stack of eight producing zones.”

Maj. Frederick R. Burnham in his British Army uniform, 1901.
The region was named for a Spanish soldier who in 1784 received a land grant for grazing cattle. “But family fortunes truly took off with discovery of oil in the 1920s, first in the Torrance area and then, most resoundingly, on Dominguez Hill itself,” explained a California State University historian in 2007.
By 1933, Maj. Burnham’s petroleum exploration venture and Union Oil had paid more than $10 million to stockholders.
Learn more California history in First California Oil Wells and Discovering Los Angeles Oilfields.

September 8, 1891- Patent issued for “Flexible Driving Shafts”
The modern concept of horizontal drilling may have begun with 19th-century patents by John Smalley Campbell of London. After receiving a British patent for his “useful improvements in flexible driving shafts or cables” in 1889, Campbell received a U.S. patent (no. 459,152) for his drilling method.
While Campbell described the patent as ideal for dental engines, “the patent also carefully covered use of his flexible shafts at much larger and heavier physical scales,” reported oil historian Stephen Testa in a 2015 article for Pacific Petroleum Geology. “The modern concept of non-straight line, relatively short-radius drilling dates back at least to September 8, 1891.”
_______________________
Recommended Reading: The fire in the rock: A history of the oil and gas industry in Kansas, 1855-1976 (1976); Early Texas Oil: A Photographic History, 1866-1936
(1976); Early Texas Oil: A Photographic History, 1866-1936
 (2000); History Of Oil Well Drilling
(2000); History Of Oil Well Drilling (2007); Street Lights of the World
(2007); Street Lights of the World (2015); Vertical Reefs: Life on Oil and Gas Platforms in the Gulf of Mexico
(2015); Vertical Reefs: Life on Oil and Gas Platforms in the Gulf of Mexico (2015); Drilling Technology in Nontechnical Language
(2015); Drilling Technology in Nontechnical Language (2012); An Illustrated Guide to Gas Pumps
(2012); An Illustrated Guide to Gas Pumps (2008); Schlumberger: The History of a Technique
(2008); Schlumberger: The History of a Technique (1978); Oil in the Deep South: A History of the Oil Business in Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida, 1859-1945
(1978); Oil in the Deep South: A History of the Oil Business in Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida, 1859-1945 (1993); California State University, Dominguez Hills
(1993); California State University, Dominguez Hills (2010). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(2010). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Please become an annual AOGHS supporter today. Help us maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2024 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
by Bruce Wells | Aug 23, 2024 | Petroleum Pioneers
The U.S. petroleum industry began in 1859 to meet demand for “Coal Oil” — the popular lamp fuel kerosene.
American oil history began in a valley along a creek in remote northwestern Pennsylvania. Today’s exploration and production industry was born on August 27, 1859, near Titusville when a well specifically drilled for oil found it.
Although crude oil had been found and bottled for medicine as early as 1814 in Ohio and in Kentucky in 1818, these had been drilled seeking brine. Drillers often used an ancient technology, the “spring pole” Sometimes the salt wells produced small amounts of oil, an unwanted byproduct.

Considered America’s first petroleum exploration company – the Pennsylvania Rock Oil Company of New York – incorporated in 1854. It reorganized as Seneca Oil Company of New Haven Connecticut in 1858.
The advent of cable-tool drilling introduced the wooden derrick into the changing American landscape. The technology applied same basic idea of chiseling a hole deeper into the earth.
Using steam power, a variety of heavy bits, and improved mechanical engineering skills, cable-tool drillers became more efficient. (Learn more Making Hole – Drilling Technology.) (more…)













