by Bruce Wells | Apr 30, 2025 | Petroleum Technology
Inventing technologies for protecting oil and natural gas wells and the environment.
Erle P. Halliburton in March 1921 received a U.S. patent for his improved method for cementing oil wells, helping to bring greater production and environmental safety to America’s burgeoning oilfields.
When Halliburton patented his “Method and Means for Cementing Oil Wells,” the 29-year-old inventor changed how oil and natural gas wells were completed. His contribution to oilfield production technology was just beginning.
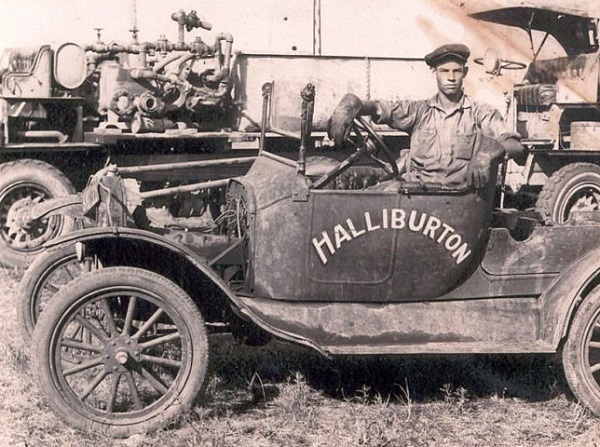

One of Erle P. Halliburton’s younger brothers, George Halliburton, posed in a Ford Model T around 1929. “George, my grandfather, and several of E.P.’s brothers were employed with the company for many years,” noted Cole Halliburton, Halliburton Operating Company president, in 2020. An early Halliburton self-propelled truck with pumps for cementing wells can be seen in background. Photo courtesy Timothy Johnson.
Halliburton was 27 years old in 1919 when he founded his oilfield equipment and service company headquartered in Duncan, Oklahoma. His New Method Oil Well Cementing Company would receive many patents on its way to becoming today’s Halliburton.

Halliburton moved to Duncan and its nearby Healdton oilfield after working in the booming fields of Burkburnett, Texas.
“It is well known to those skilled in the art of oil well drilling that one of the greatest obstacles to successful development of oil-bearing sands has been the encountering of liquid mud water and the like during and after the process of drilling the wells,” Halliburton noted in his June 1920 U.S. patent application. (more…)
by Bruce Wells | Feb 24, 2025 | This Week in Petroleum History
February 24, 1938 – First Nylon Bristle Toothbrush –
The Weco Products Company of Chicago, Illinois, “Dr. West’s Miracle-Tuft” toothbrush went on sale – the first to use synthetic nylon developed three years earlier by a former Harvard professor working at a DuPont research laboratory in New Jersey.

August 1938 Life magazine advertisement for first nylon bristle toothbrush.
“Until now, all good toothbrushes were made with animal bristles,” noted a 1938 Weco Products advertisement in Life magazine. “Today, Dr. West’s new Miracle-Tuft is a single exception. It is made with EXTON, a unique bristle-like filament developed by the great DuPont laboratories, and produced exclusively for Dr. West’s.”
Guaranteed for “no bristle shedding,” and selling for 50 cents ($10.96 in 2025 dollars), the toothbrush became the first commercial use of nylon.
February 25, 1918 – Pawnee Bill’s Oklahoma Oil Companies
As World War I neared its end, Gordon William “Pawnee Bill” Lillie entered the oil business in Yale, Oklahoma. Despite not being as famous as his Wyoming friend Col. William F. “Buffalo Bill” Cody, Lillie was a widely known showman and promoter of his state.

Although most are only family keepsakes, some old oil company certificates are valued by collectors.
During World War I, the Pawnee Bill Oil Company operated a refinery in Yale and leased 25 railroad tank cars. After the war, reduced demand for refined petroleum products, forced the company to operate at half capacity as other Oklahoma refineries began closing.
Although his oil exploration company remained, Pawnee Bill had to shut down his Yale refinery in March 1921. A decade earlier, friend and fellow western showman Col. William Cody had unsuccessfully searched for Wyoming oil (see Shoshone Oil Company).
Learn more in Pawnee Bill Oil Company.

February 25, 1919 – Oregon enacts First Gasoline Tax
Oil was selling for just $2 a barrel when Oregon enacted the one-cent gas tax to be used for road construction and maintenance. It was the first U.S. state to impose a gasoline tax. Less than two months later, Colorado and New Mexico followed Oregon’s example.

A circa 1930s service station owner explains why gas costs 20 cents a gallon in this Library of Congress photo.
By 1930, every state would add a gasoline tax of up to three cents per gallon. Faced with a $2.1 billion federal deficit, President Herbert Hoover tacked on another one-cent per gallon federal excise tax in 1932.
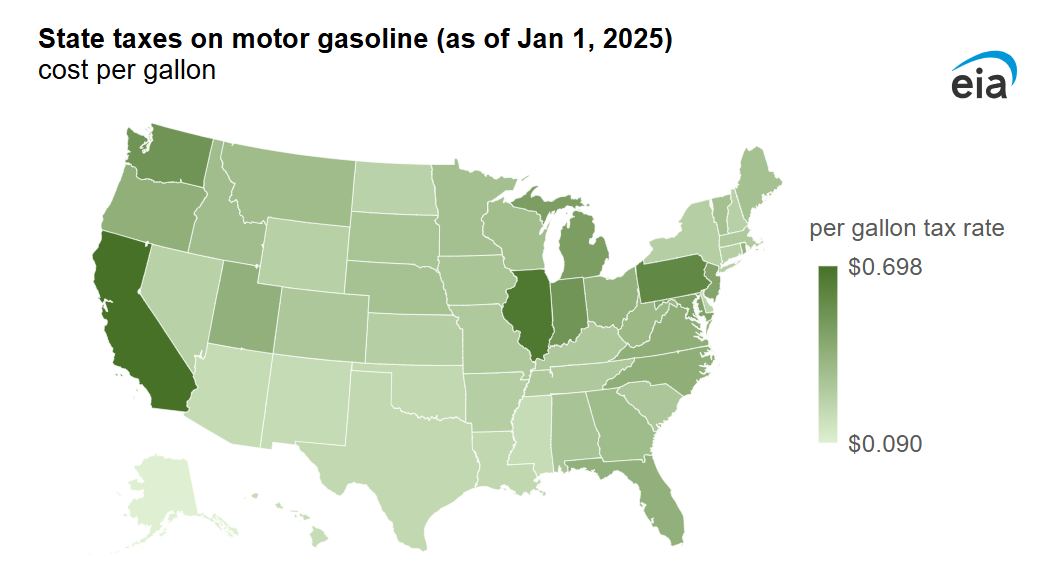
National average tax rates have remained steady with gasoline taxes increasing in seven states and decreasing in six, according to the Department of Energy.
In August 2024, federal taxes included excises taxes of 18.4 cents per gallon on gasoline and 24.3 cents per gallon on diesel fuel, according to the Energy Information Administration (EIA). State-imposed gasoline taxes have varied from a low of 8.9 cents per gallon (Alaska) to a high 69.8 cents per gallon (California). The federal tax of has not changed since 1993.
February 25, 1926 – Wyatt Earp’s California Oil Wells
A Kern County, California, oil well invested in by former lawman Wyatt Earp began producing 150 barrels of oil a day, confirming his belief in the field five miles north of Bakersfield. As early as 1901, drilling by the Shasta Oil Company had stirred local excitement, but the company went bust after three dry holes. In July 1924, Getty Oil Company began drilling on the Earp lease.
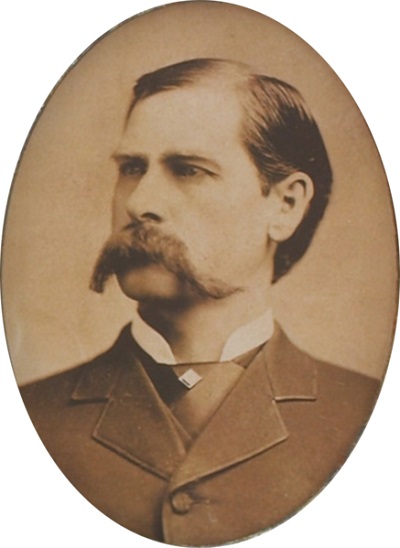

Wyatt Earp portrait, circa 1887.
“Old Property Believed Worthless for Years West of Kern Field Relocated by Old-Timer,” declared the San Francisco Examiner, describing Earp, 75, as the “pioneer mining man of Tombstone.” The newspaper also reported, “Indications are that a great lake of oil lies beneath the surface in this territory.”
Working on his memoirs, Earp turned over management of his oil properties to his sister-in-law, and his wife noted, “I was in hopes they would bring in a two or three hundred barrel well. But I must be satisfied as it could have been a duster, too.”
Learn more in Wyatt Earp’s California Oil Wells.
February 27, 1925 – Congress passes Osage Indians Act
As a result of murders and a “reign of terror” in the Osage Nation, the U.S. Congress passed the Osage Indians Act of 1925, prohibiting non-Osages from inheriting headrights of tribal members possessing more than one-half Osage blood. The Osage people’s sudden wealth from oil royalties (see Million Dollar Auctioneer) had brought criminal conspiracies to the Oklahoma Indian Reservation with dozens of Osage killed for the headrights to their land.
February 27, 1962 – California Voters approve Offshore Drilling
Voters in Long Beach, California, approved the “controlled exploration and exploitation of the oil and gas reserves” underlying their harbor south of Los Angeles. The city’s charter had prohibited drilling there since a 1956 referendum, but advances in technology offered new and environmentally sensitive opportunities to exploit an additional 6,500 acres of the Wilmington oilfield.

Los Angeles Association of Professional Landmen members toured THUMS in 2017. Photo courtesy LAAPL.
Four artificial islands were soon constructed at a cost of $22 million by a consortium of companies called THUMS: Texaco (now Chevron), Humble (now ExxonMobil), Union Oil (now Chevron), Mobil (now ExxonMobil) and Shell Oil. The islands in 1967 were named Grissom, White, Chaffee, and Freemen in honor of lost NASA astronauts. Occidental Petroleum purchased THUMS in 2000.
Eventually operated by the California Resources Corporation, the four “Astronaut Islands” are designed to appear to be occupied by upscale condominiums, thanks to Disneyland architect Joseph Linesch, whose integration of oil production structures the Los Angeles Times described as “part Disney, part Jetsons, part Swiss Family Robinson.”
Learn more in THUMS – California’s Hidden Oil Islands.

February 28, 1935 – DuPont Chemist invents Nylon
A former Harvard professor working in a DuPont research laboratory discovered the world’s first synthetic fiber, the petroleum product nylon. After experimenting with artificial materials for more than six years, professor Wallace Carothers created a long molecule chain — a stretching plastic. The inventor earlier discovered neoprene (commonly used in wetsuits).
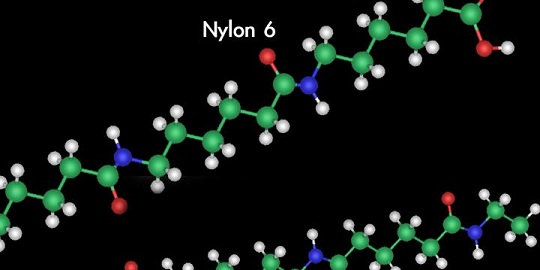
Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms strung in a chain create manmade fibers used for textiles and plastics. Each molecule contains six carbon atoms.
Carothers produced the fibers when he formed a polymer chain using a process to join individual molecules. Each molecule consisted of 100 or more repeating units of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms, strung in a chain. DuPont patented nylon in 1935, but it was not revealed until 1938.
Originally called “Fiber 66,” the polyamide resulted from 12 years and $27 million in research. Several marketing names were considered for the “artificial silk,” before nylon was chosen. The first commercial use was for toothbrush bristles. After World War II, nylon hosiery for women would make a fortune for the Delaware chemical company.
Learn more in Nylon, a Petroleum Polymer.
February 28, 1982 – Getty Museum becomes Richest in World
Following years of legal battle by his relatives, the J. Paul Getty Museum in Los Angeles became the most richly endowed museum in the world after receiving a $1.2 billion bequest left to it by oil billionaire J. Paul Getty, who died in 1976.
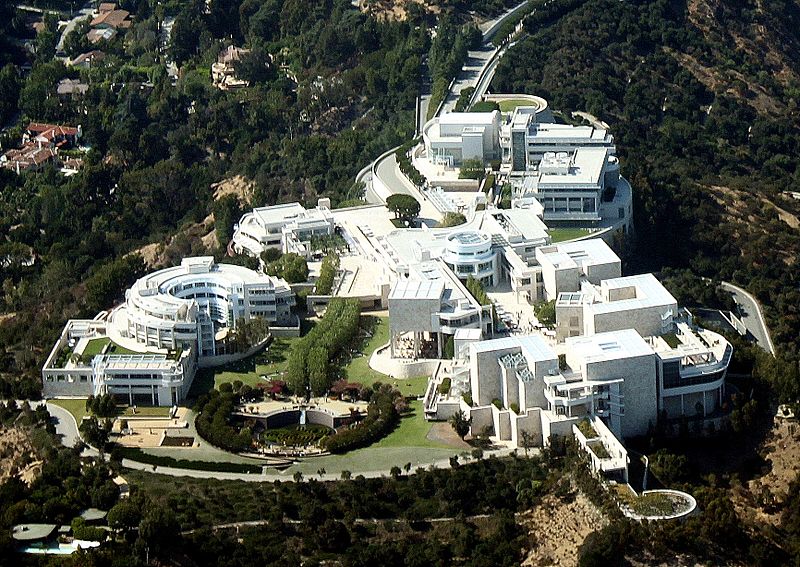

The J. Paul Getty Museum opened in Los Angeles in 1954. The museum’s art collection today is housed at the Getty Center (above in 2009) and the Getty Villa on the Malibu coast.
After working in his father’s oilfields in Oklahoma, Getty founded his first oil company in Tulsa and drilled the Nancy Taylor No. 1 well near Haskell, where oil and natural gas production began in 1910. Getty’s oil wealth philanthropy also established the Getty Conservation Institute and the Getty Research Institute, according to the J. Paul Getty Trust.
March 1, 1921 – Halliburton improves Well Cementing
Erle P. Halliburton patented his “Method and Means for Cementing Oil Wells,” improving a key oilfield technology. “It is well known to those skilled in the art of oil well drilling that one of the greatest obstacles to successful development of oil bearing sands has been the encountering of liquid mud water and the like during and after the process of drilling the wells,” he noted in his patent application.
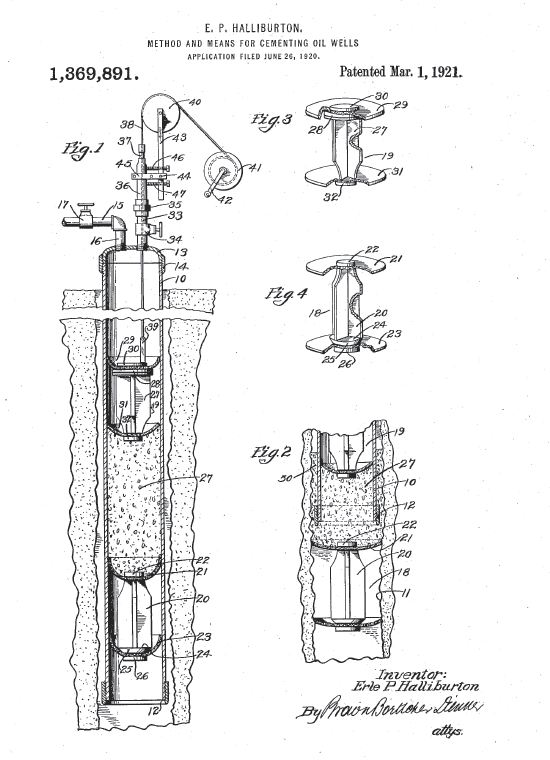
The Halliburton 1921 cementing process isolated geologic zones while protecting casing integrity.
Halliburton’s well cementing process isolated downhole zones, guarded against collapse of the casing, and allowed control of the well, helping to protect the environment. His patent application noted that typical oil production, “hampered by water intrusion that required time and expense for pumping out…has caused the abandonment of many wells which would have developed a profitable output.”
In March 1949, Halliburton Oil Well Cementing Company and Stanolind Oil completed the first commercial application of hydraulic fracturing at a well near Duncan.
Learn more in Halliburton cements Wells.

March 2, 1922 – Lease sells for $1 Million in Osage Nation
Under the broad crown of a giant elm next to the Osage Council House in Pawhuska, Oklahoma, Skelly Oil and Phillips Petroleum Company jointly bid more than one million dollars for a 160-acre tract of land.

Colonel Elmer Ellsworth Walters (in the striped shirt) was famous as “auctioneer of the Osage Nation.”
The 1922 auction — Oklahoma’s first million dollar mineral lease — took place in the shade of what became known as the “Million Dollar Elm.” Independent producers such as Frank Phillips, Harry Sinclair, Bill Skelly, J. Paul Getty and E.W. Marland were frequent bidders for promising leases. The Osage would erect a statue of their auctioneer, Colonel Elmer Ellsworth Walters, in his hometown of Skedee.
Learn more in Million Dollar Elm.
_______________________
Recommended Reading: Enough for One Lifetime: Wallace Carothers, Inventor of Nylon (2005); Pawnee Bill: A Biography of Major Gordon W. Lillie (1958); Wyatt Earp: The Life Behind the Legend
(1958); Wyatt Earp: The Life Behind the Legend (2012); Black Gold in California: The Story of California Petroleum Industry
(2012); Black Gold in California: The Story of California Petroleum Industry  (2016); Du Pont Dynasty: Behind the Nylon Curtain
(2016); Du Pont Dynasty: Behind the Nylon Curtain (1984); The Great Getty: The Life and Loves of J. Paul Getty – Richest Man in the World
(1984); The Great Getty: The Life and Loves of J. Paul Getty – Richest Man in the World (1986); Erle P. Halliburton, Genius with Cement
(1986); Erle P. Halliburton, Genius with Cement (1959); The Osage Oil Boom
(1959); The Osage Oil Boom (1989). Your Amazon purchases benefit the American Oil & Gas Historical Society; as an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(1989). Your Amazon purchases benefit the American Oil & Gas Historical Society; as an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Please become an AOGHS annual supporter and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2025 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
by Bruce Wells | May 25, 2024 | Petroleum Pioneers
Shallow Oklahoma oilfield launched many petroleum giants.
When an Oklahoma drilling boom arrived in 1919 thanks to shallow wells in the Healdton oilfield, a 27-year-oid inventor applied his new method for cementing oil wells. His service company would become one of the largest in the world.
Erle Palmer Halliburton (1892-1957) received a U.S. patent for his “Method and Means for Cementing an Oil Well in 1921 during Oklahoma drilling booms in and around the Healdton oilfield. He had arrived in Duncan after working for service companies in North Texas towns, including boom town Burkburnett.

The Healdton Oil Museum includes IPAA founder Wirt Franklin’s Pierce-Arrow. The museum hosts annual oil history events.
Halliburton’s New Method Oil Well Cementing Company would receive many patents on its way to becoming Halliburton Corporation, which in 2022 employed 42,000 worldwide specializing in “locating hydrocarbons and managing geological data, to drilling and formation evaluation, well construction and completion, and optimizing production through the life of the field.”
The Healdton field was first revealed in August 1913 by the Wirt Franklin No. 1 well about 20 miles northwest of Ardmore. The wildcat well discovered what soon became known as the “poor man’s field,” because of its shallow depth and low cost of drilling.

The Carter County oilfield, about 70 miles east of Burkburnett, quickly attracted independent producers with limited financial backing — often edging out major oil company competitors.
“Within a 22-mile swath across Carter County, one of the nation’s greatest oil discoveries was made — the Greater Healdton-Hewitt Field,” reported Kenny Arthur Franks in his 1989 history of the oilfield.
“Encompassing some of the richest oil-producing land in America, Healdton and Hewitt, discovered in 1913 and 1919 respectively, produced an astounding 320,753,000 barrels of crude by the close of the first half of the 20th century,” Franks explained.
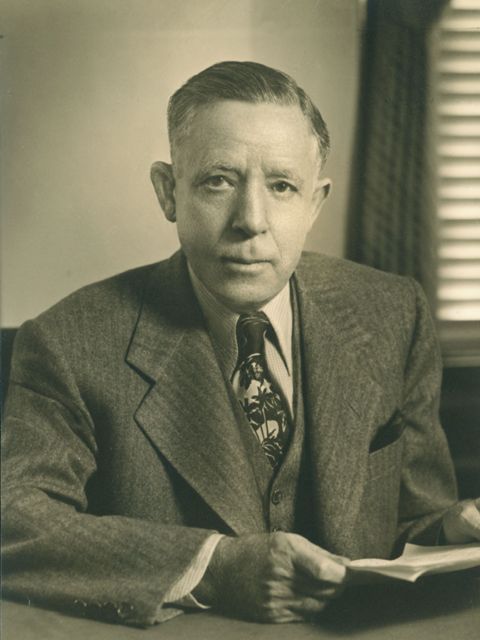

Erle P. Halliburton Halliburton in 1957. Photo courtesy Oklahoma Hall of Fame.
In addition to launching Halliburton’s petroleum career, the shallow field also helped independent producer Wirt Franklin in 1929 become the first president of the then Tulsa-based Independent Petroleum Association of America (IPAA).
The Healdton Oil Museum preserves Franklin’s and other independent producers’ exploration heritage — and many who got their start in the Healdton field. Among them were former Oklahoma Governor Charles Haskell and Roy Johnson, president of the Healdton Petroleum Company.
According to the Oklahoma Historical Society (OHS), the towns of Wilson, Ringling, and New Healdton (now Healdton) came into existence during the oilfield’s development. Just a few who began their careers there were Robert Hefner Sr. and Lloyd Noble.

“Hefner, a lawyer, introduced the concept of subsurface leasing into mineral rights law,” OHS notes. “Noble developed an international oil business and established the Samuel Roberts Noble Foundation, a nonprofit biotechnology research foundation that helps farmers.”
Born in Ardmore in 1896, Noble found early success at Healdton — and at the Seminole oil boom in 1926.
Noble also was instrumental in the success of a top-secret drilling project during World War II (see Roughnecks of Sherwood Forest).
Cement Well Control
Healdton drilling boom and its many shallow wells, Halliburton established his New Method Oil Well Cementing in Duncan. He was soon experimenting with technologies to improve oil well production. Water intrusion hampered many wells, requiring time and expense for pumping out.
Halliburton noted in his 1920 patent application, “Water has caused the abandonment of many wells which would have developed a profitable output.”
The oilfield cementing innovation — at first resisted by some skeptics — isolated the various down-hole zones, guarded against collapse of the casing and permitted control of the well throughout its producing life.

The city of Duncan, Oklahoma, dedicated a Halliburton statue in 1993.
According to William Pike, former editor-in-chief of E&P magazine, Halliburton’s well cementing process revolutionized how oil and natural gas wells were completed.
Halliburton also patented other modern cementing technologies, including the jet mixer, the remixer and the float collar, guide shoe and plug system, bulk cementing, multiple-stage cementing, advanced pump technology and offshore cementing technology.

Halliburton’s only real service company competitor for decades was Carl Baker of Baker Oil Tools. Halliburton Oil Well Cementing Company in 1938 expanded into offshore work with a barge-mounted unit cementing a well off the Louisiana coast.
Meanwhile, another Oklahoma oilfield service company, the Reda Pump Company, had been founded by Armais Arutunoff, thanks to help from his close friend Frank Phllips and Phillips Petroleum of Bartlesville, Oklahoma.
Arutunoff invented a practical electric submersible pump). As Phillips foresaw, use of the Arutunoff artificial lift pump would dominate U.S. oilfields by 1938 — and oilfields worldwide after World War II.
Hydraulic Fracking
A major petroleum industry milestone came in 1949, when Halliburton and Stanolind Oil Company completed a well near Duncan, Oklahoma – the first commercial application of hydraulic fracturing (see Shooters – A “Fracking” History).
“Halliburton was ever the tinkerer. He owned nearly 50 patents,” noted Pike. “Most are oilfield, and specifically cementing related, but the number includes patents for an airplane control, an opposed piston pump, a respirator, an airplane tire and a metallic suitcase.”

Thanks in part to his prospering oilfield service company, Halliburton in 1931 started his own airline in Tulsa, the Southwest Air Fast Express — Safeway Airlines — that later merged with American Airlines.
As U.S. production from oil and natural gas shale formations grew in 2018, Halliburton Corporation’s worldwide operations employed 80,000 people.
Learn more about Halliburton’s oilfield inventiveness in Halliburton cements Wells.
_______________________
Recommended Reading: Ragtown: A History of the Greater Healdton-Hewitt Oil Field (1989); Erle P. Halliburton: Genius with Cement (1959). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(1959). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Please become an AOGHS supporter and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. © 2024 Bruce A. Wells.
Citation Information – Article Title: “Halliburton and the Healdton Oilfield.” Authors: B.A. Wells and K.L. Wells. Website Name: American Oil & Gas Historical Society. URL: https://aoghs.org/petroleum-pioneers/halliburton-and-healdton-oilfield. Last Updated: June 3, 2024. Original Published Date: July 14, 2015.

















