by Bruce Wells | Apr 22, 2024 | This Week in Petroleum History
April 22, 1920 – Natural Gas Well leads Arkansas Discoveries –
Although natural gas was first discovered in 1887 at Fort Smith, the first commercial production began in southern Arkansas with a well completed southeast of El Dorado. Drilled to a depth of almost 2,250 feet, the well produced up to 60 million cubic feet of natural gas a day and showed signs of oil from the Nacatoch formation sandstone. The first Arkansas oil wells arrived one year later at El Dorado and at Smackover in 1922.
April 22, 1926 – Osage Oil Lease Auctioneer Statue dedicated
A statue commemorating the friendship between oil and gas lease auctioneer Colonel E.E. Walters and Osage Indian Chief Baconrind (phonetically, Wah-she-hah) was dedicated in Walters’ hometown of Skedee, Oklahoma. Beginning in 1912, Colonel Elmer Ellsworth Walters (his real name) and the popular Chief of the Osage Nation raised millions of dollars for the tribe from mineral lease sales.
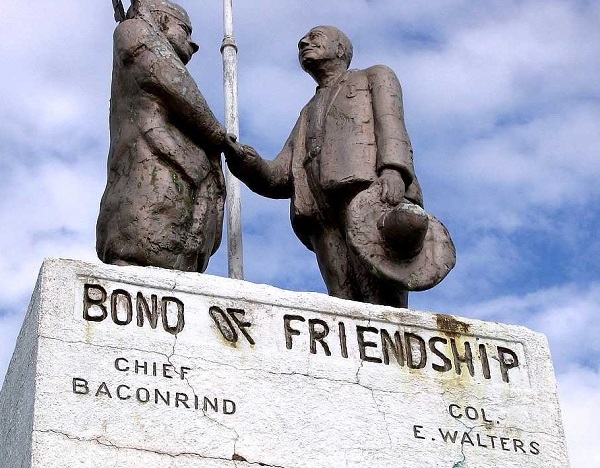

The town of Skedee, Oklahoma, has declined in population, but its 1926 statue of a famed auctioneer and Osage chief remains. Photo by Bruce Wells.
The auctions took place beneath an elm tree at the Tribal Council House in Pawhuska, where crowds gathering to witness bidding from Frank Phillips, E.W. Marland and William Skelly. The Skedee unveiling revealed “painted bronze” statues of Walters and the Chief Baconrind shaking hands on a sandstone base.
Learn more in Million Dollar Auctioneer.

April 22, 1930 – Marland unveils Pioneer Woman
One block from his mansion in Ponca City, Ernest Whitworth “E.W.” Marland unveiled The Pioneer Woman statue, his gift to the state to honor the role of women who settled there. A Pioneer Woman Museum opened nearby in 1958.
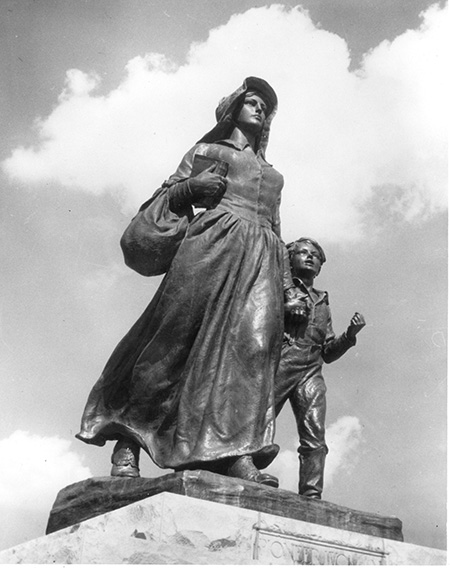

More than 40,000 gathered in Ponca City for the unveiling of The Pioneer Woman, a 17-foot bronze statue. Photo courtesy Oklahoma Historical Society.
“Marland invited sculptors to submit competitive designs in the form of small models,” notes the Oklahoma Historical Society (OHS). “The models were exhibited across the nation and 750,000 people cast their vote.” The 17-foot bronze cast was erected at a cost of $300,000.
Marland had lost a fortune in the Pennsylvania oilfields during the panic of 1907 before founding Marland Oil in Ponca City in 1917. An early advocate of using seismography and core drilling for finding oil, by 1920 Marland’s company controlled an estimated 10 percent of the world’s oil production.
April 22, 1964 – Sinclair Dinoland returns to New York World’s Fair
Continuing its successful marketing campaign begun in the 1930s, Sinclair Oil opened a Dinoland pavilion at the 1964-1965 New York World’s Fair. The exhibition of giant, fiberglass dinosaurs proved a hit with the 50 million people attending the fair. The first Sinclair Oil Dinoland, which attracted crowds to the Texas Centennial Exposition in 1936, had been expanded for the 1939-1940 New York World’s Fair. Following the latest New York exhibition, the 70-foot green “Dino” and eight other dinosaurs traveled to make stops at shopping centers, delighting children in 25 states.
April 23, 1878 – Oil Exchange Building opened in Pennsylvania
The Oil Exchange of Oil City, Pennsylvania, opened a new, $100,000 brick building on Seneca Street. Independent producers began meeting there to trade oil and pipeline certificates. They had earlier gathered at local hotels or along Oil City’s Centre Street, then known as the “Curbside Exchange.”

By 1877, Pennsylvania oil companies had created the third largest financial exchange of any kind in America, behind only New York and San Francisco.
Before the 1870s, most Pennsylvania oil buyers had taken on-site delivery of oil in wooden barrels they provided themselves. A rapidly growing oil pipeline infrastructure created the need for a place to trade certificates as oil commerce expanded. The Standard Oil Company of New Jersey would bring an end to Pennsylvania’s highly speculative oil-trading markets.
Learn more in End of Oil Exchanges.

April 24, 1911 – Magnolia Petroleum founded
The Magnolia Petroleum Company was founded as an unincorporated joint-stock association — a consolidation of several companies, the first of which began in 1898 as a small refinery in Corsicana during the first Texas oil boom.

Magnolia Petroleum would merge with Socony Mobil Oil in the 1930s and replace its flower with the “Flying Pegasus” logo.
As Magnolia Petroleum established service stations in southwestern states, Standard Oil Company of New York (Socony) began acquiring the company in 1925 before merging with the Vacuum Oil Company in 1931. The new company, Socony-Vacuum Oil — the future Mobil Oil — included stations in 20 states operated by Magnolia Petroleum, headquartered in a Dallas skyscraper. Magnolia adopted the Socony-Vacuum Oil Pegasus logo, which began rotating atop the building in 1934.
Learn more in Mobil’s High-Flying Trademark.
April 24, 1917 – Petroleum Product for Eyelashes trademarked
Tom Lyle Williams, doing business in Chicago as Maybell Laboratories, trademarked the name Lash-Brow-Ine as a mascara and “preparation for stimulating the growth of eyebrows and eyelashes.” Two years earlier, Williams had watched his sister Mabel perform what she called “a secret of the harem,” mixing petroleum jelly with coal dust and applying it to her eyelashes.

Women once used toothpicks to mix lamp black with Vaseline. By the 1930s, Maybelline mascara was available at local five-and-dime stores. Photo courtesy Sharrie Williams.
The mascara’s key ingredient, Vaseline, had been patented in 1872 by Robert Chesebrough, a young chemist in Brooklyn, New York. Williams began selling tins of Mabel’s mixture by mail-order catalog, calling it “lash-brow-ine.” With sales exceeding $100,000 by 1920, Williams renamed the mascara Maybelline in honor of his sister, who worked with him in his Chicago office.
Learn more in The Crude Story of Mabel’s Eyelashes.

April 25, 1865 – Civil War Veteran patents Well Torpedo
Civil War veteran Col. Edward A.L. Roberts of New York City received the first of his many patents for an “Improvement in Exploding Torpedoes in Artesian Wells.” The invention used controlled downhole explosions “to fracture oil-bearing formations and increase oil production.”

A Pennsylvania historical marker notes the 1865 first demonstration of the invention of Union Col. E.A.L. Roberts.
Roberts torpedoes were filled with gunpowder, lowered into wells, and ignited by a weight dropped along a suspension wire to percussion caps. In later models, nitroglycerin replaced gunpowder. Before the well torpedo’s invention, many early wells in the new oil regions of Pennsylvania, New York, and West Virginia often produced limited amounts of oil.
With its exclusive patent licenses, the Roberts Petroleum Torpedo Company charged up to $200 per torpedo “shoot” and a one-fifteenth royalty. Seeking to avoid the expense, unlicensed practitioners operated at night with their own explosive devices, reportedly leading to the term “moonlighter.”
Learn more in Shooters – A “Fracking” History.
April 26, 1947 – Oil Industry promoted on Radio
For the first time since its establishment in 1919, the American Petroleum Institute launched a national advertising campaign. “The theme of the drive is that the petroleum industry is a modern and progressive one, and is now turning out the best products in its history,” noted The Billboard.

Founded in 1919 in New York City, API moved its headquarters to the nation’s capital in 1929.
“Radio this week struck real pay dirt as a ‘Gusher’ will come mainly from expansion of current air time on spot local or regional levels by the thousands of petroleum and related corporations,” proclaimed the weekly publication. API today is a Washington, D.C.-based lobbying organization representing major U.S. petroleum companies. It issues industrywide recommended practices, “to promote the use of safe equipment and proven engineering.”

April 27, 1966 – Ariel Corporation founded
After receiving a degree in mechanical engineering in 1954, former eighth-grade teacher Jim Buchwald founded Ariel Corporation in Mount Vernon, Ohio. “With little money to pay for a facility to house the tools, a room in the basement of the Buchwald family home is cleaned up,” according to the Ariel website.
Buchwald bought a lathe, a small hand-cranked rotary table and a vertical drill for manufacturing valves. “This room becomes the first Ariel machine shop, with an adjoining room functioning as Ariel’s first official engineering department.”
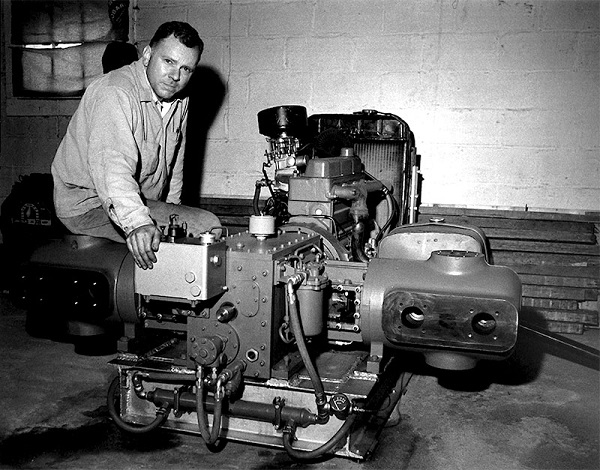
Jim Buchwald with Ariel’s prototype compressor after it has completed a 10-hour run test. Photo courtesy Ariel.
By 1968, Buchwald had built a prototype gas compressor that ran at the unprecedented speed of 1,800 RPM. His Ohio machine shop soon transitioned into a manufacturing facility, and Buchwald named the company after his favorite 1948 Ariel motorcycle. His company has become one of the world’s largest manufacturers of reciprocating gas compressors.
_______________________
Recommended Reading: The Osage Oil Boom (1989); The Prize: The Epic Quest for Oil, Money & Power (1991); Historic Photos of Texas Oil
(1989); The Prize: The Epic Quest for Oil, Money & Power (1991); Historic Photos of Texas Oil (2012); The Maybelline Story: And the Spirited Family Dynasty Behind It
(2012); The Maybelline Story: And the Spirited Family Dynasty Behind It (2010); The Boom: How Fracking Ignited the American Energy Revolution and Changed the World
(2010); The Boom: How Fracking Ignited the American Energy Revolution and Changed the World (2015); Michigan Yesterday & Today (2009); The Seven Sisters: The great oil companies & the world
(2015); Michigan Yesterday & Today (2009); The Seven Sisters: The great oil companies & the world (1975). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(1975). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Become an AOGHS annual supporting member and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2024 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
by Bruce Wells | Mar 25, 2024 | This Week in Petroleum History
March 26, 1930 – Oklahoma City’s “Wild Mary Sudik” makes Headlines –
What would become one of Oklahoma’s most famous wells struck a high-pressure formation about 6,500 feet beneath Oklahoma City and oil erupted skyward. The Indian Territory Illuminating Oil Company’s Mary Sudik No. 1 flowed for 11 days before being brought under control. It produced about 20,000 barrels of oil and 200 million cubic feet of natural gas daily, becoming a worldwide sensation.

Highly pressured natural gas from the Wilcox formation proved difficult to control in the prolific Oklahoma City oilfield. Within a week of a 1930 gusher, Hollywood newsreels of it appeared in theaters across America. Photo courtesy Oklahoma History Center.
Efforts to control the well in Oklahoma City’s prolific oilfield (discovered in 1928) were featured in movie newsreels and on radio broadcasts. It was later learned that after drilling more than a mile deep, the exhausted crew did not know the Wilcox Sand oil formation was permeated with highly pressurized natural gas, according to the Oklahoma History Center in Oklahoma City.
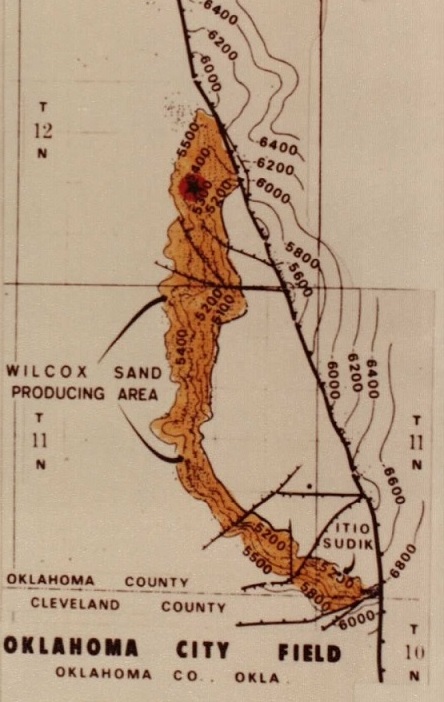
Map of the Wilcox sands formation of the Oklahoma City oilfield in the 1940s.
Although the first ram-type blowout preventer (BOP) had been patented in 1926, many high-pressure oilfields would take time to tame.
Learn more about the well that became known as “Wild Mary Sudik.”
March 27, 1855 – Canadian Chemist trademarks Kerosene
Canadian physician and chemist Abraham Gesner (1797-1864) patented a process to distill coal into kerosene. “I have invented and discovered a new and useful manufacture or composition of matter, being a new liquid hydrocarbon, which I denominate Kerosene,” he proclaimed. Because his new illuminating fluid was extracted from coal, consumers called it “coal oil” as often as kerosene.

On March 17, 2000, Canada issued one million commemorative stamps featuring kerosene inventor Abraham Gesner.
Gesner, considered the father of Canada’s petroleum industry, in 1842 established the country’s first natural history museums, the New Brunswick Museum, which today houses one of Canada’s oldest geological collections.
The U.S. petroleum industry began when it was learned that oil could be distilled into a lamp fuel (and much later, a rocket fuel). With new oilfields discovered in Pennsylvania, West Virginia, and Ohio, inexpensive kerosene became America’s main source of light.
Learn more in Camphene to Kerosene Lamps.

March 27, 1975 – First Pipe laid for Trans-Alaskan Pipeline
With the laying of the first section of pipe in Alaska, construction began on the largest private construction project in American history at the time. Recognized as a landmark of engineering, the 800-mile Trans-Alaska Pipeline system, including pumping stations and the Valdez Marine Terminal, would cost $8 billion by the time it was completed in 1977.
Learn more in Trans-Alaska Pipeline History.
March 27, 1999 – Offshore Platform Rocket Launch Test
The Ocean Odyssey, a converted semi-submersible drilling platform, launched a Russian rocket that placed a demonstration satellite into geostationary orbit.
The Zenit-3SL rocket, fueled by liquid oxygen and kerosene rocket fuel, was part of Sea Launch, a Boeing-led consortium of companies from the United States, Russia, Ukraine, and Norway. The platform had once been used by Atlantic Richfield Company (ARCO) for North Sea exploration.
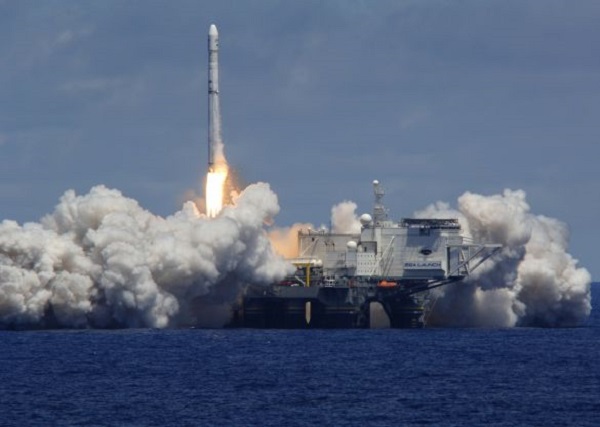

With an orbital test on March 27, 1999, the Ocean Odyssey, a converted semi-submersible drilling platform, became the world’s first floating equatorial launch pad. Photo courtesy Sea Launch.
“The Sea Launch rocket successfully completed its maiden flight today,” Boeing announced. “The event, which placed a demonstration payload into geostationary transfer orbit, marked the first commercial launch from a floating platform at sea.”
The Sea Launch consortium provided orbital launch services until 2014, when Russia invaded and annexed the Crimean Peninsula of Ukraine.
Learn more in Offshore Rocket launcher.
March 28, 1886 – Discovery launches Indiana Natural Gas Boom
A drilling boom began at Portland, Indiana, after the Eureka Gas and Oil Company found a natural gas field at a depth of only 700 feet. The discovery arrived just two months after a spectacular natural gas well about 100 miles to the northeast — the “Great Karg Well” of Findlay, Ohio.
According to industrialist Andrew Carnegie, natural gas daily replaced 10,000 tons of coal for making steel.
Portland foundry owner Henry Sees had followed the news from Findlay. He persuaded local investors to drill for Indiana natural gas. In western Pennsylvania, reserves found near Pittsburg had encouraged industrialists there to replace their coal-fired steel and glass foundries with the first large-scale industrial use of natural gas.
Indiana would become the world’s largest natural gas producer, thanks to its Trenton limestone stretching more than 5,100 square miles across 17 counties. Within three years, more than 200 companies were drilling, distributing, and selling natural gas.
Learn more in Indiana Natural Gas Boom.
March 28, 1905 – Oil Boom begins in North Louisiana
An oilfield discovery in Caddo Parish, Louisiana, created a classic boom town in Oil City and brought economic prosperity to northern Louisiana. The Offenhauser No. 1 well was completed at a depth of 1,556 feet, but the well yielded only five barrels a day and was abandoned. More productive wells soon followed, and the Caddo-Pine Island oilfield, about 20 miles northwest of Shreveport, expanded to include more than 80,000 acres.

The Shreveport Chamber of Commerce in 1955 dedicated a 40-foot monument commemorating the 50th anniversary of oil in Caddo Parish. Photo by Bruce Wells.
“This part of Louisiana, of course, was built on the oil and gas industry, and those visitors interested in the technical aspects of oilfield work will find the museum particularly appealing,” notes the Louisiana State Oil and Gas Museum (formerly the Caddo-Pine Island Oil and Historical Museum). More oilfield history can be found at Shreveport, where natural gas was discovered in 1870, thanks to an ice plant’s water well. To prevent the waste of natural gas through flaring, Louisiana passed its first conservation law in 1906.
Learn more in Louisiana Oil City Museum.
March 28, 1918 – Oil Research Center Opens in Oklahoma
The U.S. Bureau of Mines established the first U.S. oil and natural gas research and development center in Bartlesville, Oklahoma. Two years earlier, independent producers had pledged $50,000 to help build the bureau’s Bartlesville Experiment Station. Discoveries in the Osage Nation had “catapulted Oklahoma to the forefront of the burgeoning mid-continent oil industry,” according to the U.S. Office of Fossil Energy.

March 29, 1819 – Birthday of Father of the Petroleum Industry
Edwin Laurentine Drake (1819-1880) was born in Greenville, New York. Forty years later, he used a steam-powered cable-tool rig to drill the first commercial U.S. oil well at Titusville, Pennsylvania. The former railroad conductor overcame many financial and technical obstacles to make “Drake’s Folly” a milestone in energy history.
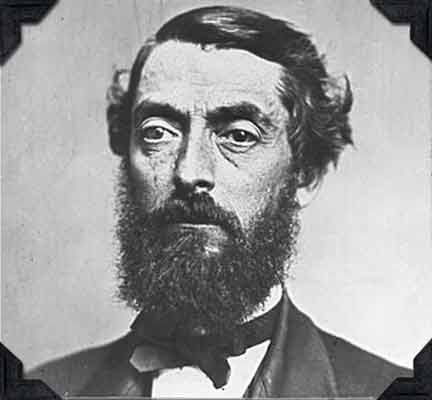

Edwin L. Drake (1819-1880) invented a method of driving a pipe down to protect the integrity of America’s first oil well. Photo courtesy Drake Well Museum.
Drake pioneered using iron casing to isolate his well from nearby Oil Creek. “In order to overcome the hurdles before him, he invented a ‘drive pipe’ or ‘conductor,’ an invention he unfortunately did not patent,” noted historian Urja Davé in 2008. “Mr. Drake conceived the idea of driving a pipe down to the rock through which to start the drill.”
Determined to find oil for refining into the popular lamp fuel kerosene, Drake created the American petroleum industry on August 27, 1859, at a depth of 69.5 feet.
Visit the Drake Well Museum in Titusville.
March 29, 1938 – Magnolia Oilfield Discovery in Arkansas
A well drilled by Kerlyn Oil Company (predecessor to the Kerr-McGee company) revealed the 100-million-barrel Magnolia oilfield in Arkansas, adding to 1920s giant oilfield discoveries at El Dorado and Smackover. “Wildcat Strike In Southern Arkansas is Sensation of the Oil Country” proclaimed the local newspaper.
Drilling on the Barnett No. 1 well had been suspended by a lack of funds, but Kerlyn Oil Company Vice President Dean McGee persevered. An experienced geologist, McGee was rewarded with the giant oilfield discovery at a depth of 7,650 feet. He would later lead efforts in early offshore exploration in the Gulf of Mexico.

March 30, 1980 – Deadly North Sea Gale
Massive waves during a North Sea gale capsized a floating apartment for Phillips Petroleum Company workers, killing 123 people. The Alexander Kielland platform, 235 miles east of Dundee, Scotland, housed 208 men who worked on a nearby rig in the Ekofisk field. Most of the Phillips workers were from Norway. The platform, converted from a semi-submersible drilling rig, served as overflow accommodation for the Phillips production platform 300 yards away.
_______________________
Recommended Reading: The Oklahoma Petroleum Industry (1980); Oil Lamps The Kerosene Era In North America
(1980); Oil Lamps The Kerosene Era In North America (1978); Amazing Pipeline Stories: How Building the Trans-Alaska Pipeline Transformed Life in America’s Last Frontier
(1978); Amazing Pipeline Stories: How Building the Trans-Alaska Pipeline Transformed Life in America’s Last Frontier (1997); The Extraction State, A History of Natural Gas in America (2021); Myth, Legend, Reality: Edwin Laurentine Drake and the Early Oil Industry
(1997); The Extraction State, A History of Natural Gas in America (2021); Myth, Legend, Reality: Edwin Laurentine Drake and the Early Oil Industry (2009); Texas Oil and Gas, Postcard History
(2009); Texas Oil and Gas, Postcard History (2013); Early Louisiana and Arkansas Oil: A Photographic History, 1901-1946
(2013); Early Louisiana and Arkansas Oil: A Photographic History, 1901-1946 (1982). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(1982). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Become an AOGHS annual supporting member and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2024 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
by Bruce Wells | Nov 20, 2023 | This Week in Petroleum History
November 20, 1866 – Improved Well Torpedo patented –
Col. Edward A.L. Roberts of New York City patented improvements to his Roberts Torpedo, an oilfield technology for increasing production by fracturing oil-bearing formations.
“Our attention has been called to a series of experiments that have been made in the wells of various localities by Col. Roberts, with his newly patented torpedo,” noted the Titusville Morning Herald newspaper in 1865. “The results have in many cases been astonishing.”
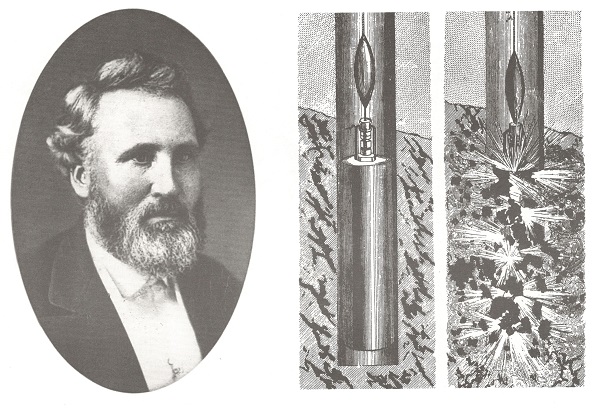
Portrait of Edward Roberts, a Civil War veteran who patented well “torpedo” technologies that improved oilfield production.
The Civil War Union Army veteran would receive many patents for his “Exploding Torpedoes in Artesian Wells” method to increase petroleum production (see Shooters – A “Fracking” History).
November 20, 1930 – Oil Booms help Hilton expand in Texas
After buying his first hotel in the booming oil town of Cisco, Texas, Conrad Hilton opened a high-rise in El Paso. While visiting Cisco in 1919, Hilton had witnessed roughnecks from the Ranger oilfield waiting for rooms. Hilton’s first hotel, the Mobley, offered 40 rooms for eight-hour periods to coincide with workers’ shifts.
Thanks to booming oilfields, Hilton was firmly established in the Texas hotel business. His El Paso Hilton (now the Plaza Hotel) was placed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1980.

November 20, 1980 – Texaco Well drains Louisiana Lake
Minutes after its drilling crew evacuated, a Texaco drilling platform overturned and disappeared into a whirlpool that drained Lake Peigneur, Louisiana, over the next three hours. The crew had accidently penetrated a salt dome containing the mining operations of Diamond Crystal Salt Company.
All 50 miners working as deep as 1,500 feet below the surface escaped with no serious injuries as a maelstrom swallowed the $5 million Texaco platform — and 11 barges holding drilling supplies.
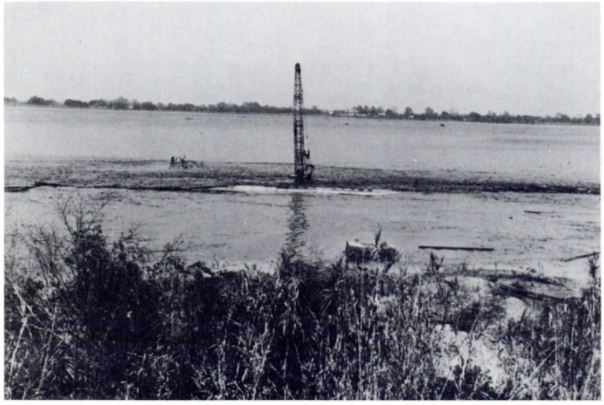

Photo from a 1981 government report on Texaco’s accidental “Jefferson Island Mine Inundation” of one year earlier.
“Texaco, who had ordered the oil probe, was aware of the salt mine’s presence and had planned accordingly; but somewhere a miscalculation had been made, which placed the drill site directly above one of the salt mine’s 80-foot-high, 50-foot-wide upper shafts,” noted a 2005 article.
According to a 1981 government report, “Jefferson Island Mine Inundation,“ evidence for identifying the exact cause was washed away, but Texaco and Wilson Drilling paid $32 million to Diamond Crystal Salt Company and another $12.8 million to a nearby botanical garden. Changed from freshwater to saltwater with a depth reaching 200 feet, Lake Peigneur became the deepest lake in Louisiana.
November 21, 1925 – Magnolia Petroleum incorporates –
Formerly an unincorporated joint-stock association with roots dating to an 1889 refinery in Corsicana, Texas, Magnolia Petroleum Company incorporated. The original association had sold many grades of refined petroleum products through more than 500 service stations in Texas, Oklahoma, and Arkansas.

Magnolia Petroleum operated gas stations throughout the Southeast.
Within a month of the new company’s founding, John D. Rockefeller’s Standard Oil of New York (Socony) purchased most Magnolia Petroleum assets and operated it as a subsidiary. Magnolia merged with the Socony Mobile Oil Company in 1959 and adopted the red Pegasus logo, replacing the magnolia logo at gas stations (see Mobil’s High-Flying Trademark). Magnolia Petroleum assets were part of 1999 merger that created today’s ExxonMobil.

November 21, 1980 – Millions watch “Dallas” Episode Who shot J.R
The cliffhanger episode “Who shot J.R.?” on the prime-time soap opera “Dallas” was watched by 83 million people in the United States and 350 million worldwide, according to History.com. The CBS show, which debuted in 1978, revolved around two Texas oil families and featured Larry Hagman as J.R. Ewing, “the character fans loved to hate.” His portrayal of a “greedy, conniving, womanizing scoundrel” and the business dealings of Ewing Oil Company would stereotype the Texas petroleum industry for 14 seasons.
November 22, 1878 – Tidewater Pipe Company established
Byron Benson organized the Tidewater Pipe Company in Pennsylvania. In 1879 his company would build the first oil pipeline to cross the Alleghenies from Coryville to the Philadelphia Reading Railroad 109 miles away in Williamsport. This technological achievement was considered by many as the first true oil pipeline in America, if not the world.

Despite protests from teamsters, a 109-mile oil pipeline revolutionized oil transportation. Photo courtesy explorepahistory.com.
The difficult work — much of it done in winter using sleds to move pipe sections — bypassed Standard Oil Company’s dominance in transporting petroleum. Tidewater made an arrangement with Reading Railroad to haul the oil in tank cars to Philadelphia and New York. In 1879, about 250 barrels of oil from the Bradford field was pumped across the mountains and into Williamsport.
More than 80 percent of America’s oil soon would come from Pennsylvania oilfields, according to Floyd Hartman Jr. in a 2009 article, “Birth of Coryville’s Tidewater Pipe Line.”

November 22, 1905 – Glenn Pool Field discovered in Indian Territory
Two years before Oklahoma statehood, the Glenn Pool (or Glenpool) oilfield was discovered in the Creek Indian Reservation south of Tulsa. The greatest oilfield in America at the time, it would help make Tulsa the “Oil Capital of the World.” Many independent oil producers, including Harry Sinclair and J. Paul Getty, got their start during the Glenn Pool boom.

An oilfield pioneers monument was dedicated in April 2008 at Glenpool, Oklahoma. Photo by Bruce Wells.
With production exceeding 120,000 barrels of oil a day, Glenn Pool exceeded Tulsa County’s earlier Red Fork Gusher. The giant oilfield even exceeded production from Spindletop Hill in Texas four years earlier. The Ida Glenn No. 1 well, drilled to about 1,500 feet deep, led to more prolific wells in the 12-square-mile Glenn Pool.
By the time of statehood in 1907, Tulsa area oilfields made Oklahoma the biggest U.S. oil producing state. Advances in enhanced recovery technologies later added to the region’s productivity. Glenpool residents celebrate their “Black Gold Days,” and the 46th annual festival took place September 26-29, 2023, in Black Gold Park.
Learn more in Making Tulsa “Oil Capital of the World.”
November 22, 2003 – Smithsonian Museum opens Transportation Hall
A permanent exhibit about U.S. transportation history opened at the Smithsonian’s National Museum of American History in Washington, D.C. “Get your kicks on 40 feet of Route 66,” the Smithsonian exhibit noted on opening day of the $22 million renovation of the museum’s Hall of Transportation.

Opened in 2003 after a $22 million renovation, the Transportation Hall of the National Museum of American History exhibits 340 historic objects in 26,000 square feet. Photo by Bruce Wells.
The hall was designed to let visitors “travel back in time and experience transportation as it changed America.” Opening day exhibits included 340 objects and 19 historic settings in chronological order. At the same museum in 1967, the Smithsonian’s “Hall of Petroleum” devoted an entire wing to drilling rigs, pipelines, and pump jacks.
Learn more in America on the Move.
November 23, 1951 – Superman and the World’s Deepest Oil Well
Public fear of the risk of drilling wells too deep highlighted the theatrical release of Superman’s first feature length movie, “Superman and the Mole Men.” The 1951 plot unfolded in the fictional town of Silsbey, “Home of the World’s Deepest Oil Well,” after an experimental well’s drill bit had “broken into clear air” at a depth of 32,742 feet.

Mole men emerge from an experimental oil well drilled more than six miles deep.
“Good heavens, that’s practically to the center of the earth!” exclaimed Lois Lane (in fact, the deepest U.S. well in 1951 reached 20,521 feet). When mole-men emerged from the well, townspeople feared an invasion. In the end, Superman calmed an angry mob and the well ignited in flames, forever closing the connection between the two worlds.
Learn about a real six-mile-deep well in Anadarko Basin in Depth.

November 23, 1947 – World’s First LPG Ship
The first U.S. seagoing Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) ship went into service as Warren Petroleum Corporation of Tulsa, Oklahoma, sent the Natalie O. Warren from the Houston Ship Channel to Newark, New Jersey. The vessel had an LPG capacity of 38,053 barrels in 68 vertical pressure tanks.

The first vessel had an LPG capacity of 38,053 barrels in 68 vertical pressure tanks.
The one-of-a-kind ship was the former Cape Diamond dry-cargo freighter, converted by the Bethlehem Steelyard in Beaumont, Texas. The experimental design would lead to new maritime construction standards for such vessels. Warren Petroleum was the largest producer and marketer of natural gasoline and propane in the world by the early 1950s, according to an exhibit at the Tulsa Historical Society and Museum. LPG tankers today carry 20 times the capacity of the early vessels.
November 25, 1875 – Continental Oil brings Kerosene to the West
Convinced that he could profit by purchasing bulk kerosene in cheaper eastern markets, Isaac Blake formed the Continental Oil and Transportation Company. He soon transported Ohio kerosene to Ogden, Utah, for distribution.

Conoco began in 1875 as Continental Oil, delivering kerosene to retail stores in Ogden, Utah.
Continental purchased two railroad tank cars — the first to be used west of the Mississippi River — and began shipping kerosene from a Cleveland refinery. The company grew, expanding into Colorado in 1876 and California in 1877. Standard Oil Company absorbed Continental Oil in 1885.
Following the 1911 breakup of Standard, Continental Oil reemerged as Conoco, becoming ConocoPhillips in 2002 (see ConocoPhillips Petroleum Museums).
_______________________
Recommended Reading: History Of Oil Well Drilling (2007); Be My Guest
(2007); Be My Guest (1957); Magnolia Oil News Magazine
(1957); Magnolia Oil News Magazine (January 1930); Oil and Gas Pipeline Fundamentals
(January 1930); Oil and Gas Pipeline Fundamentals (1993); Glenn Pool…and a little oil town of yesteryear
(1993); Glenn Pool…and a little oil town of yesteryear (1978); The American Highway: The History and Culture of Roads in the United States
(1978); The American Highway: The History and Culture of Roads in the United States (2000); CONOCO: The First One Hundred Years Building on the Past for the Future
(2000); CONOCO: The First One Hundred Years Building on the Past for the Future (1975). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(1975). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
he American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Become an AOGHS annual supporting member and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2023 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
by Bruce Wells | May 17, 2023 | AOGHS Newsletter








(1989); The Prize: The Epic Quest for Oil, Money & Power (1991); Historic Photos of Texas Oil
(2012); The Maybelline Story: And the Spirited Family Dynasty Behind It
(2010); The Boom: How Fracking Ignited the American Energy Revolution and Changed the World
(2015); Michigan Yesterday & Today (2009); The Seven Sisters: The great oil companies & the world
(1975). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.


















