Inventing the Electric Submersible Pump
Armais Arutunoff designed a downhole centrifugal pump and founded an oilfield service company.
The modern petroleum industry owes a lot to the son of an Armenian soap maker who invented an artificial lift system using an electric motor to drive a centrifugal pump at the well.
With the help of the Phillips Petroleum Company in the 1930s, Armais Sergeevich Arutunoff moved to Bartlesville, Oklahoma, and built the earliest practical downhole electric submersible pump. His invention would enhance oilfield production in wells worldwide.
A 1936 Tulsa World article described the Arutunoff electric submersible pump (ESP) as “an electric motor with the proportions of a slim fence post which stands on its head at the bottom of a well and kicks oil to the surface with its feet.”
By 1938, an estimated two percent of all oil produced in the United States with artificial lift used an Arutunoff pump (see All Pumped Up – Oilfield Technology).
Early Downhole Patents
The first U.S. patent for an oil-related electric pump arrived in the late 19th century during the growth of electrical power generation, according to a 2014 article in the Journal of Petroleum Technology (JPT).
In 1894, a design by Harry Pickett (patent no. 529,804) used a downhole rotary electric motor with “a Yankee screwdriver device to drive a plunger pump.” Expanding Picket’s concept, Robert Newcomb in 1918 received a patent for his “electro-magnetic engine” driving a reciprocating plunger.
“Heretofore, in very deep wells the rod that is connected to the piston, and generally known as the ‘sucker’ rod, very often breaks on account of its great length and strains imposed thereon in operating the piston,” noted Newcomb in his patent application.
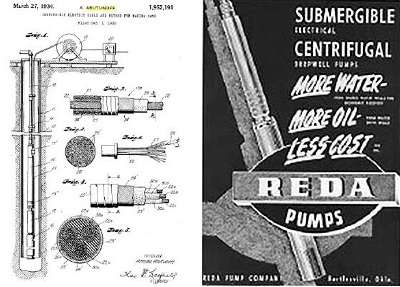
Armais Arutunoff obtained 90 patents, including one in 1934 for an improved well pump and electric cable. At right is a 1951 “submergible” Reda advertisement.
Although several patents followed those of Picket and Newcomb, the Journal reports, “It was not until 1926 that the first patent for a commercial, operatable ESP was issued — to ESP pioneer Armais Arutunoff. The cable used to supply power to the bottomhole unit was also invented by Arutunoff.”
Reda: Russian Electrical Dynamo of Arutunoff
Arutunoff built his first ESP in 1916 in Germany, according to the Oklahoma Historical Society. “Suspended by steel cables, it was dropped down the well casing into oil or water and turned on, creating a suction that would lift the liquid to the surface formation through pipes,” reported OHS historian Dianna Everett.
After immigrating to the United States in 1923, in California Arutunoff could not find financial support for manufacturing his pump design. He moved to Bartlesville, Oklahoma, in 1928 at the urging of a new friend — Frank Phillips, head of Phillips Petroleum Company.
“With Phillips’s backing, he refined his pump for use in oil wells and first successfully demonstrated it in a well in Kansas,” noted Everett. The small company that became Reda Pump manufactured the device.
The name Reda – Russian Electrical Dynamo of Arutunoff – derived from the cable address of the company that Arutunoff originally started in Germany. The inventor would move his family into a Bartlesville home just across the street from Frank Phillips’ mansion.

The founder of Reda Pump once lived in this Bartlesville, Oklahoma, home across from Frank Phillips, whose home today is a museum. Photo courtesy Kathryn Mann, Only in Bartlesville.
A holder of more than 90 patents in the United States, Arutunoff was elected to the Oklahoma Hall of Fame in 1974. “Try as I may, I cannot perform services of such value to repay this wonderful country for granting me sanctuary and the blessings of freedom and citizenship,” Arutunoff said at the time.
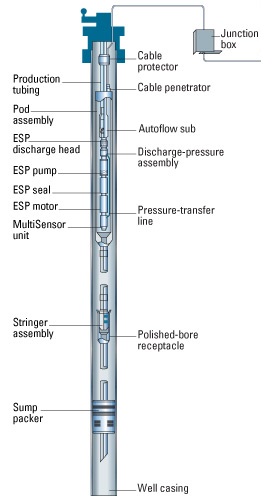
Artificial lift spins the impellers on the pump shaft, putting pressure on the surrounding fluids and forcing them to the surface. Image courtesy Schlumberger.
Arutunoff died in February 1978 in Bartlesville. At the end of the 20th century, Reda ranked as the world’s largest manufacturer of ESP systems. It is now part of Schlumberger.
Armais Sergeevich Arutunoff was born to Armenian parents in Tiflis, part of the Russian Empire, on June 21, 1893. His hometown in the Caucasus Mountains dates back to the 5th Century. His father manufactured soap; his grandfather earned a living as a fur trader.
Centrifugal Pumps
As a young scientist, Arutunoff’s research convinced him that electrical transmission of power could be efficiently applied to oil drilling and improve the production methods he saw in use in the early 1900s in Russia.
Downhole production would require a powerful electric motor, but limitations imposed by the available casing sizes required a new kind of motor.
A small-diameter motor had too little horsepower for the job, Arutunoff discovered. He studied the fundamental laws of electricity seeking answers to how to build a higher horsepower motor exceedingly small in diameter.
By 1916, Arutunoff designed a centrifugal pump to be coupled to the motor for de-watering mines and ships. To develop enough power, the motor needed to run at very high speeds. He successfully designed a centrifugal pump, small in diameter and with stages to achieve high discharge pressure.
Arutunoff designed a motor ingeniously installed below the pump to cool the motor with flow moving up the oil well casing. The entire unit could be suspended in the well on the discharge pipe. The motor, sealed from the well fluid, operated at high speed in the oil.
Although Arutunoff built the first centrifugal pump while living in Germany, he built the first submersible pump and motor in the United States while living in southern California.
Friend of Frank
Arutunoff already had formed Reda to manufacture his idea for electric submersible motors, and after living in Germany, Arutunoff came to the United States with his wife and one-year-old daughter to settle in Michigan, and then Los Angeles.
However, after emigrating to America in 1923, Arutunoff could not find financial support for his downhole production technology. Everyone he approached turned him down, believing his downhole concept impossible under the “laws of electronics.”
No one would consider his inventions until a friend at Phillips Petroleum Company — Frank Phillips — encouraged him to form his own company in Bartlesville. The Arutunoff family moved into a house on the same street as the Phillips home.

Arutunoff’s manufacturing plant in Bartlesville spread over nine acres, employing hundreds during the Great Depression.
In 1928 Arutunoff moved to Bartlesville, where he formed Bart Manufacturing Company, which changed its name to Reda Pump Company in 1930. He soon demonstrated a working model of an oilfield electric submersible pump.
Upside down Motors
One of his pump-and-motor devices produced oil at well in the El Dorado field near Burns, Kansas — the first equipment of its kind to be used downhole. One reporter telegraphed his editor, “Please rush good pictures showing oil well motors that are upside down.”
By the end of the 1930s, Arutunoff’s company held dozens of patents for industrial equipment, leading to decades of success — and still more patents. His “Electrodrill” aided scientists in penetrating the Antarctic ice cap for the first time in 1967.
Arutunoff oilfield technologies had a significant impact on the petroleum industry — quickly proving crucial to successful production for hundreds of thousands of U.S. oil wells.
Also see Conoco & Phillips Petroleum Museums.
_______________________
Recommended Reading: Artificial Lift-down Hole Pumping Systems (1984); Oil Man: The Story of Frank Phillips and the Birth of Phillips Petroleum
(2016). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Please become an AOGHS annual supporter and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. © 2025 Bruce A. Wells.
Citation Information – Article Title: “Inventing the Electric Submersible Pump.” Author: Aoghs.org Editors. Website Name: American Oil & Gas Historical Society. URL: https://aoghs.org/technology/electric-submersible-pump-inventor. Last Updated: June 12, 2025. Original Published Date: April 29, 2014.




