by Bruce Wells | Nov 17, 2025 | This Week in Petroleum History
November 18, 1847 – Manufactured Gas illuminates U.S. Capitol –
Lamps fueled by “coal gas” began replacing whale oil lamps in the U.S. Capitol. Manufactured gas distilled beneath the Capitol flowed through newly installed pipes into light fixtures, including chandeliers in both House chambers. James Crutchett had invented the lighting system and convinced Congress to appropriate $17,500 to fund his plan, which included a lantern atop the dome.
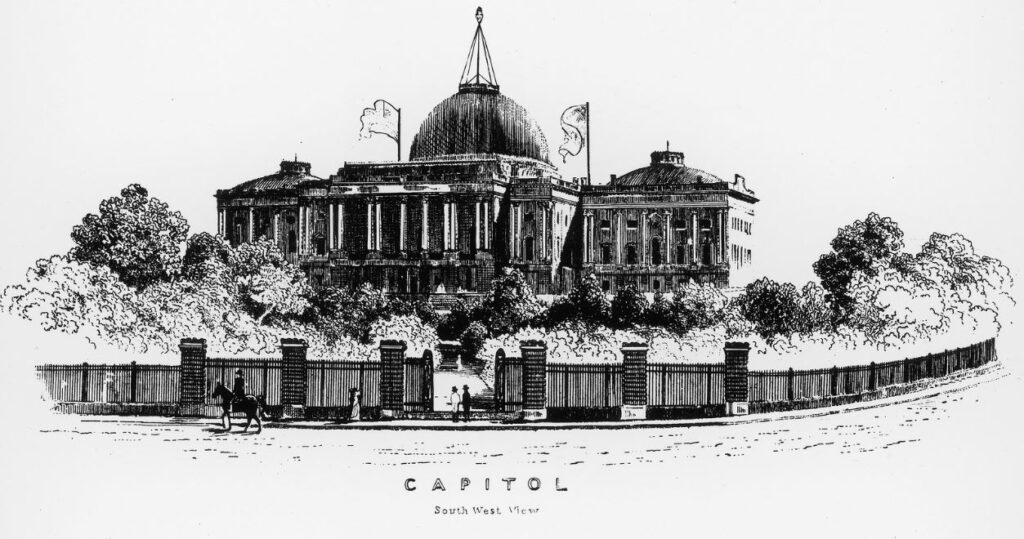

A mast with a gas lantern was erected on the U.S. Capitol dome in 1847. The rotunda interior used 1,083 gas jets by 1865. Incandescent lighting began in 1885. Image courtesy Architect of the Capitol.
Onlookers witnessed “one of the most splendid and beautiful spectacles we ever beheld,” according to David Rotenstein in History Sidebar. Crutchett built a gas plant in the Capitol’s northwest quadrant, placing lighting fixtures throughout the building.
Although the dome’s 80-foot mast and lantern would be removed within a year, a citywide manufactured gas system followed — similar to ones established in Philadelphia and Baltimore (see Illuminating Gaslight).
November 19, 1861 – America exports Oil for First Time
America exported petroleum for the first time when the merchant brig Elizabeth Watts departed the Port of Philadelphia for Great Britain. The Union vessel arrived in London 45 days later carrying a cargo of 901 barrels of Pennsylvania oil and 428 barrels of refined kerosene.
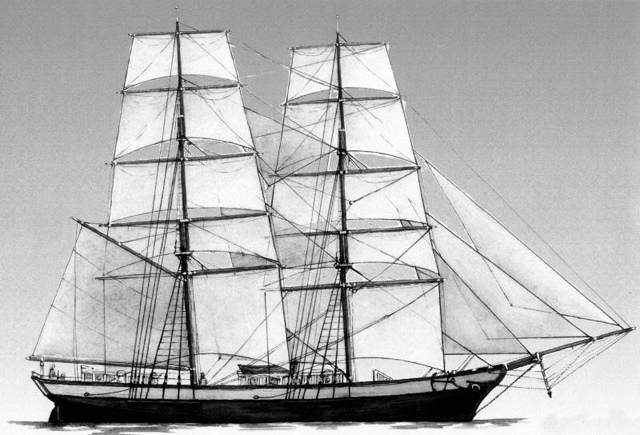

Launched in 1847 by the shipbuilding firm of J. & C.C. Morton of Thomaston, Maine, the Elizabeth Watts was about 96 feet long with a draft of 11 feet.
The shippers were the successful Philadelphia import-export firm of Peter Wright & Sons, which since its founding in 1818 had prospered transporting glass, porcelain, and queensware china. The company hired the brig Elizabeth Watts to ship the petroleum to three British companies. On January 9, 1862, the brig sailed down the Thames River to arrive at London, where it took 12 days to unload the 1,329 barrels of oil and kerosene.
Learn more in America exports Oil.
November 19, 1927 – Phillips Petroleum introduces “Phillips 66” Gasoline
After a decade as an exploration and production company, Phillips Petroleum entered the business of refining and retail gasoline distribution. The Bartlesville, Oklahoma, company introduced a new line of gasoline — “Phillips 66” — at its first service station, which opened in Wichita, Kansas.

Originally promoted as a dependable “winter gasoline,” by 1930 “Phillips 66” gasoline was marketed in 12 states.
The gasoline was named “Phillips 66” because it had propelled company officials down U.S. Highway 66 at 66 mph on the way to a meeting at their Bartlesville headquarters. The roadway became part of Phillips Petroleum marketing plans for the new product, which boasted “controlled volatility,” the result of a higher-gravity mix of naphtha and gasoline.
By 1930, Phillips 66 gasoline was sold at 6,750 outlets in 12 states. Because the composition made Phillips 66 gas easier to start in cold weather, ads enticed motorists to try the “New Winter Gasoline.”
November 20, 1866 – Improved Well Torpedo patented
Col. Edward A.L. Roberts of New York City patented improvements to his Roberts Torpedo, an oilfield technology for increasing production by fracturing oil-bearing formations. “Our attention has been called to a series of experiments that have been made in the wells of various localities by Col. Roberts, with his newly patented torpedo,” noted the Titusville Morning Herald newspaper in 1865. “The results have in many cases been astonishing.”
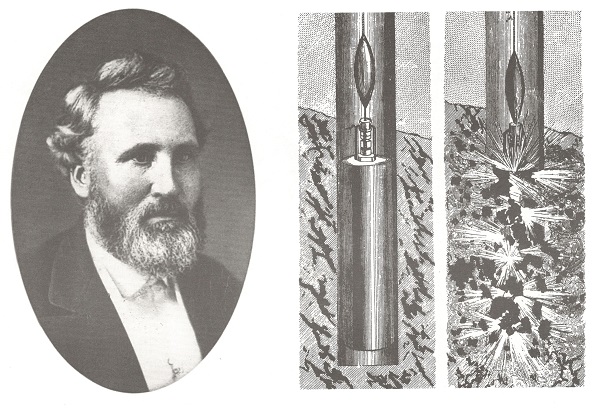
Portrait of Col. Edward Roberts, the Union Civil War veteran who patented well “torpedo” technologies that vastly improved oil production.
The Civil War Union Army veteran would receive many patents for his “Exploding Torpedoes in Artesian Wells” method to increase petroleum production (see Shooters – A “Fracking” History).
November 20, 1930 – Oil Booms bring Hilton Hotels to Texas
After buying his first hotel in the booming oil town of Cisco, Texas, Conrad Hilton opened a high-rise in El Paso. While visiting Cisco in 1919, Hilton had witnessed roughnecks from the Ranger oilfield waiting for rooms. Hilton’s first hotel, the Mobley, offered 40 rooms for eight-hour periods to coincide with workers’ shifts. Thanks to booming oilfields, Hilton was firmly established in Texas. His El Paso Hilton (now the Plaza Hotel) was placed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1980.

November 20, 1980 – Well taps Salt Mine, drains Louisiana Lake
Minutes after its drilling crew evacuated, a Texaco drilling platform overturned and disappeared into a whirlpool that drained Lake Peigneur, Louisiana, over the next three hours. The crew had accidentally penetrated a salt dome containing the mining operations of Diamond Crystal Salt Company.
All 50 miners working as deep as 1,500 feet below the surface escaped with no serious injuries as a maelstrom swallowed the $5 million Texaco platform — and 11 barges holding drilling supplies.
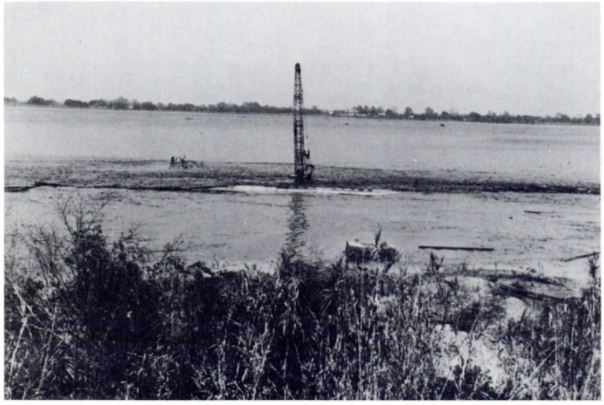

Photo from a 1981 government study of the “Jefferson Island Mine Inundation,” Texaco’s accidental drilling into a salt mine one year earlier. Photo courtesy Federal Mine Safety and Health Investigation Report.
“Texaco, who had ordered the oil probe, was aware of the salt mine’s presence and had planned accordingly; but somewhere a miscalculation had been made, which placed the drill site directly above one of the salt mine’s 80-foot-high, 50-foot-wide upper shafts,” noted a 2005 article about the Lake Peigneur vortex.
According to a 1981 government report, “Jefferson Island Mine Inundation,“ evidence for identifying the exact cause was washed away, but Texaco and Wilson Drilling paid $32 million to Diamond Crystal Salt Company and another $12.8 million to a nearby botanical garden. Changed from freshwater to saltwater with a depth reaching 200 feet, Lake Peigneur became the deepest lake in Louisiana.
November 21, 1925 – Magnolia Petroleum incorporates
Formerly an unincorporated joint-stock association with roots dating to an 1889 refinery in Corsicana, Texas, Magnolia Petroleum Company incorporated. The original association had sold many grades of refined petroleum products through more than 500 service stations in Texas, Oklahoma, and Arkansas.

Magnolia Petroleum operated gas stations throughout the Southeast.
Within a month of the new company’s founding, John D. Rockefeller’s Standard Oil of New York (Socony) purchased most Magnolia Petroleum assets and operated it as a subsidiary. Magnolia merged with the Socony Mobile Oil Company in 1959 and adopted the red Pegasus logo at gas stations. Magnolia Petroleum assets were part of the 1999 merger that created ExxonMobil.
Learn more in Mobil’s High-Flying Trademark.

November 21, 1980 – Millions watch “Dallas” Episode
The cliffhanger episode “Who shot J.R.?” on the prime-time soap opera “Dallas” was watched by 83 million people in the United States and 350 million worldwide. The CBS show debuted in 1978 and revolved around two Texas oil families, one featuring Larry Hagman as J.R. Ewing, “the character fans loved to hate,” according to History.com. Hagman’s portrayal of a “greedy, conniving, womanizing scoundrel” and the business dealings of Ewing Oil Company would stereotype the Texas petroleum industry for seasons.
November 22, 1878 – Tidewater Pipe Company established
Byron Benson organized the Tidewater Pipe Company in Pennsylvania. In 1879 his company would build the first oil pipeline to cross the Alleghenies from Coryville to the Philadelphia Reading Railroad 109 miles away in Williamsport. This technological achievement was considered by many as the first true oil pipeline in America, if not the world.

Despite protests from teamsters, a 109-mile oil pipeline revolutionized oil transportation. Photo courtesy explorepahistory.com.
The difficult work — much of it done in winter using sleds to move pipe sections — bypassed Standard Oil Company’s dominance in transporting petroleum. Tidewater made an arrangement with Reading Railroad to haul the oil in tank cars to Philadelphia and New York. In 1879, about 250 barrels of oil from the Bradford field was pumped across the mountains and into Williamsport.
More than 80 percent of America’s oil soon would come from Pennsylvania oilfields, according to Floyd Hartman Jr. in a 2009 article, “Birth of Coryville’s Tidewater Pipe Line.”
November 22, 1905 – Glenn Pool Field discovered in Indian Territory
Two years before Oklahoma statehood, the Glenn Pool (or Glenpool) oilfield was discovered in the Creek Indian Reservation south of Tulsa. The greatest oilfield in America at the time, it would help make Tulsa the “Oil Capital of the World.” Many independent oil producers, including Harry F. Sinclair and J. Paul Getty, got their start during the Glenn Pool boom.

An oilfield pioneers monument was dedicated in April 2008 at Glenpool, Oklahoma. Photo by Bruce Wells.
With production exceeding 120,000 barrels of oil a day, Glenn Pool exceeded Tulsa County’s earlier Red Fork Gusher. The giant oilfield even exceeded production from Spindletop Hill in Texas four years earlier. The Ida Glenn No. 1 well, drilled to about 1,500 feet deep, led to more prolific wells in the 12-square-mile Glenn Pool.
By the time of statehood in 1907, Tulsa area oilfields made Oklahoma the biggest U.S. oil-producing state. Learn more in Making Tulsa “Oil Capital of the World.”

November 22, 2003 – Smithsonian Museum features Transportation
A permanent exhibit about U.S. transportation history opened at the Smithsonian’s National Museum of American History in Washington, D.C. “Get your kicks on 40 feet of Route 66,” the Smithsonian exhibit noted on opening day of the $22 million renovation of the museum’s Hall of Transportation.

Opened in 2003 after a $22 million renovation, the Transportation Hall of the National Museum of American History exhibits 340 historic objects in 26,000 square feet. Photo by Bruce Wells.
Hundreds of artifacts are displayed in chronological order, allowing visitors “travel back in time and experience transportation as it changed America,” the hall today includes examples of the first models of Oldsmobile, Franklin, and Cadillac. Also preserved is the Duryea brothers’ 1893-1994 model, considered to be the first American car driven by an internal combustion engine.
Learn more in America on the Move.

November 23, 1947 – World’s First LPG Ship
The first U.S. seagoing Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) ship went into service as Warren Petroleum Corporation of Tulsa, Oklahoma, sent the Natalie O. Warren from the Houston Ship Channel to Newark, New Jersey. The vessel had an LPG capacity of 38,053 barrels in 68 vertical pressure tanks.

The Natalie O. Warren, a converted freighter, had an LPG capacity of 38,053 barrels in 68 vertical pressure tanks.
The one-of-a-kind ship was the former Cape Diamond dry-cargo freighter before being converted by the Bethlehem Steelyard in Beaumont, Texas. The experimental design led to innovative maritime construction standards for such vessels.
Warren Petroleum became the largest producer and marketer of natural gasoline and propane in the world by the early 1950s, according to an exhibit at the Tulsa Historical Society and Museum. LPG tankers today carry 20 times the capacity of the early vessels.
_______________________
Recommended Reading: The Extraction State, A History of Natural Gas in America (2021); Oil Man: The Story of Frank Phillips and the Birth of Phillips Petroleum (2016); History Of Oil Well Drilling
(2016); History Of Oil Well Drilling (2007); Be My Guest
(2007); Be My Guest (1957); Magnolia Oil News Magazine
(1957); Magnolia Oil News Magazine (January 1930); Oil and Gas Pipeline Fundamentals
(January 1930); Oil and Gas Pipeline Fundamentals (1993); Glenn Pool…and a little oil town of yesteryear
(1993); Glenn Pool…and a little oil town of yesteryear (1978); The American Highway: The History and Culture of Roads in the United States
(1978); The American Highway: The History and Culture of Roads in the United States (2000); Natural Gas: Fuel for the 21st Century
(2000); Natural Gas: Fuel for the 21st Century (2015). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(2015). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
he American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Please become an AOGHS annual supporter and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2025 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.













