Eccentric Wheels and Jerk Lines
Oilfield production technologies began in Pennsylvania with an economical way to pump multiple wells.
In the earliest days of the petroleum industry, which began with an 1859 oil discovery in Pennsylvania, production technologies used steam power and a walking beam pump system that evolved into ways for economically producing oil from multiple wells.
Just as drilling technologies evolved from spring poles to steam-powered cable tools to modern rotary rigs, oilfield production also improved.
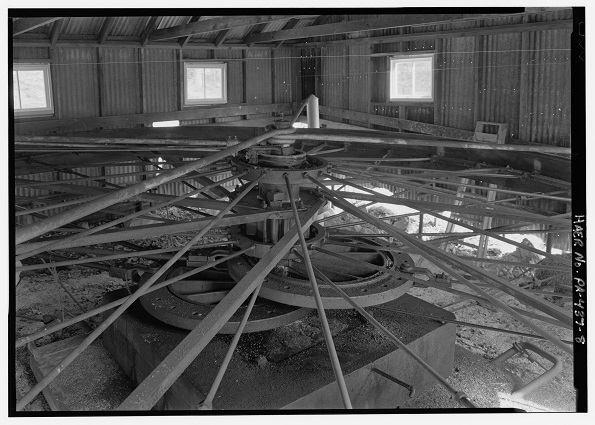

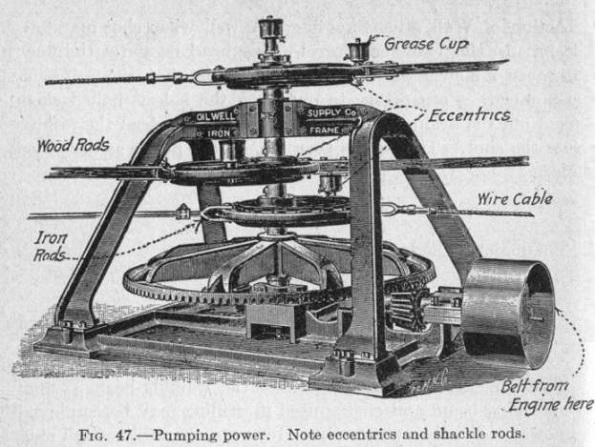
This image of a circa 1909 double eccentric power wheel manufactured by the Titusville (Pennsylvania) Iron Works is just one example of what can be discovered online at public domain resources. Photo courtesy Library of Congress Prints and Photographs Collections.
In the early days of the industry, oil production technology used steam power and a wooden walking beam. A steam engine at each well raised and lowered one end of the beam. An oil production technique perfected in Pennsylvania used central power for pumping low-production wells to economically recover oil.
Eccentric Wheels
A Library of Congress (LOC) photograph from 1909 shows a “double eccentric power wheel,” part of an innovative centralized power system. The oilfield technology from a South Penn Oil Company (the future Pennzoil) lease between the towns of Warren and Bradford, Pennsylvania.
The LOC photograph preserves the oilfield technology that used the two wheels’ elliptical rotation for simultaneously pumping multiple oil wells. The wheels’ elliptical rotation simultaneously pumped eleven remote wells. This central pump unit operated in the Morris Run oilfield, discovered in 1883. It was manufactured at the Titusville Iron Works.
Many oilfield history resources can be found in the Library of Congress Digital Collections and the related images of petroleum history photography. The development of centralized pumping systems — eccentric wheels and jerk lines — often are preserved in high-resolution files.
The Morris Run field in Pennsylvania produced oil from two shallow “pay sands,” both at depths of less than 1,400 feet. It was part of a series of other early important discoveries.
Late 18th-century Oil Well Supply Company illustration of pumping system using rods, cables, and an eccentric wheel.
In 1881, the Bradford field alone accounted for 83 percent of all the oil produced in the United States (see Mrs. Alford’s Nitro Factory). In 2004, new technologies began producing natural gas from a far deeper formation, the Marcellus Shale.
Oil production from some of the earliest shallow Pennsylvania wells declined to only about half a barrel of oil a day, but some continued pumping into 1960. On the West Coast, a 1913 central pumping unit produced from California’s largest oilfield three decades longer.
Midway-Sunset Jack Plant
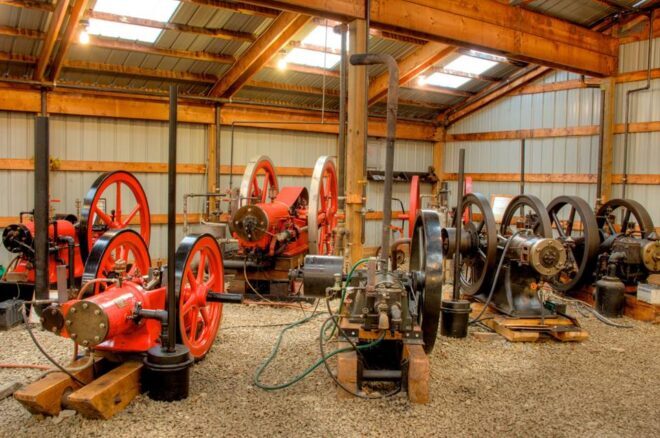
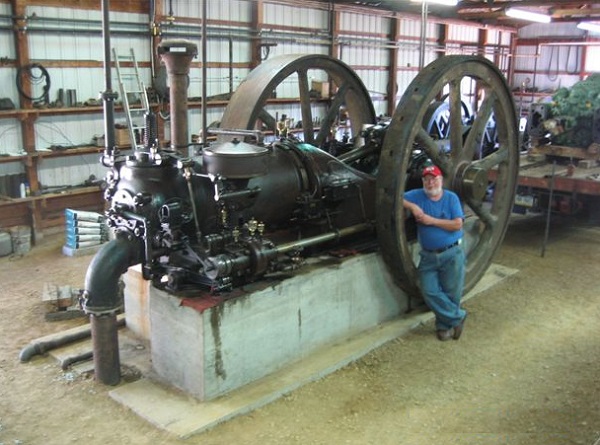
On June 9, 2023, the National Park Service added the Midway-Sunset Jack Plant to the National Register of Historic Places — thanks to Mark Smith, who submitted the application to preserve the facility. Installed by the Engineers Oil Company in 1913, the Kern County jack plant pumped oil until 1990.
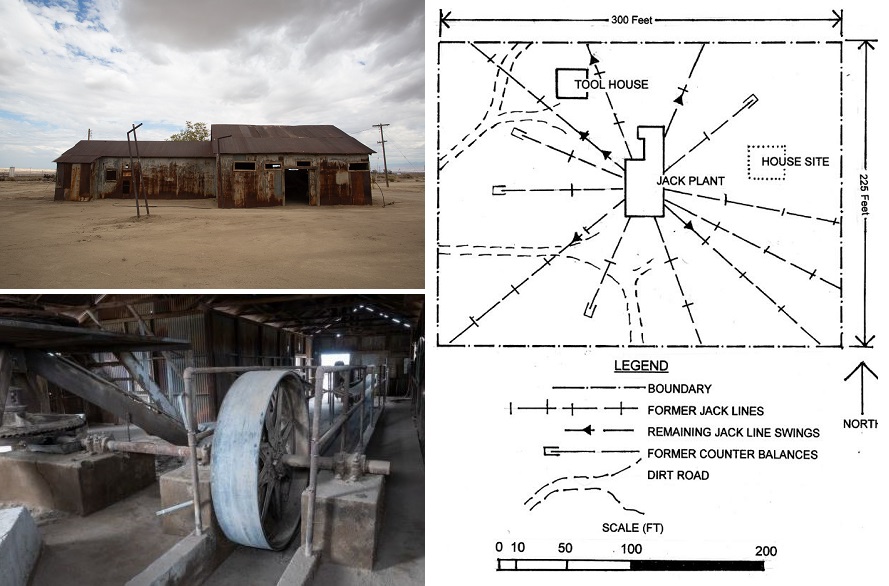
In operation until 1990, California’s Midway-Sunset Jack Plant used eccentric-wheel technologies from the late 19th century. The Kern County plant pumped more than 1.5 million barrels of oil. Photos courtesy John Harte. Illustration courtesy San Joaquin Geological Society.
“The Midway-Sunset Jack Plant is an extremely rare example of central power and ‘jack-line’ oil pumping technology on its original site and housed in its original building,” Smith noted in his 45-page draft application to the State Historical Resources Commission. “Its design and operational history reflect significant advancements in oil extraction technology.”
According to company records, the jack plant’s slowly rotating eccentric wheels produced 1.5 million barrels of oil during its lifetime. The end came when the bearing of the vertical shaft became worn, causing the shaft to wobble. The wobble of the eccentric gears made the pumping of the wells out of balance.
Pumping Multiple Wells
As the number of oil wells grew in the early days of America’s petroleum industry in Pennsylvania, simple water-well pumping technologies began to be replaced with steam-driven walking-beam pumping systems.
At first, each well had an engine house where a steam engine raised and lowered one end of a sturdy wooden beam, which pivoted on the cable-tool well’s “Samson Post.” The walking beam’s other end cranked a long string of sucker rods up and down to pump oil to the surface.
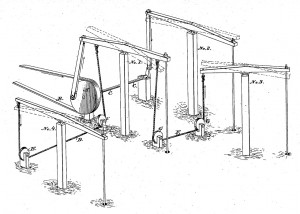
America’s oilfield technologies advanced in 1875 with this “Improvement In Means For Pumping Wells” invented in Pennsylvania.
Recognizing that pumping multiple wells with a single steam engine would boost efficiency, on April 20, 1875, Albert Nickerson and Levi Streeter of Venango County, Pennsylvania, patented their “Improvement in Means for Pumping Wells.”
Their system was the forerunner of wooden or iron rod jerk line systems for centrally powered oil production. This technology, eventually replaced by counter-balanced pumping units, will operate well into the 20th century – and remain an icon of early oilfield production.
“By an examination of the drawing it will be seen that the walking beam to well No. 1 is lifting or raising fluid from the well. Well No. 3 is also lifting, while at the same time wells 2 and 4 are moving in an opposite direction, or plunging, and vice versa,” the inventors explained in their patent application (No. 162,406).
Central Power Units
“Heretofore it has been necessary to have a separate engine for each well, although often several such engines are supplied with steam from the same boiler,” noted Nickerson and Streeter.
“The object of our invention is to enable the pumping of two or more wells with one engine…By it the walking beams of the different wells are made to move in different directions at the same time, thereby counterbalancing each other, and equalizing the strain upon the engine.”
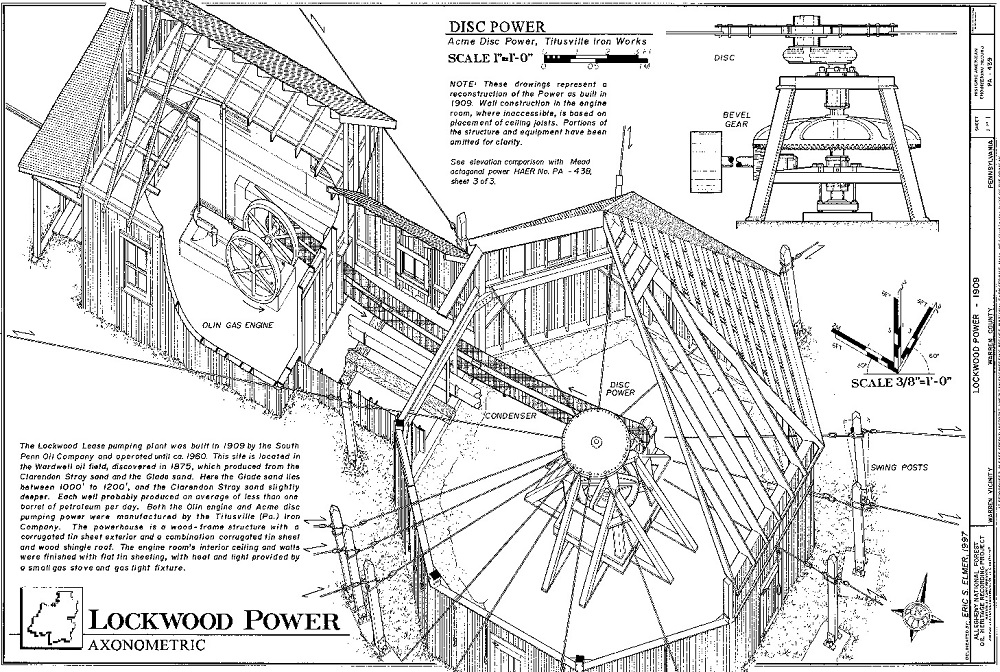
An Allegheny National Forest Oil Heritage Series illustration of an oilfield “jack plant” in McKean County, Pennsylvania.
Steam initially drove many of these central power units, but others were converted to burn natural gas or casing-head gas at the wellhead – often using single-cylinder horizontal engines. Examples of the engines, popularly called “one lungers” by oilfield workers, have been collected and restored (see Coolspring Power Museum).
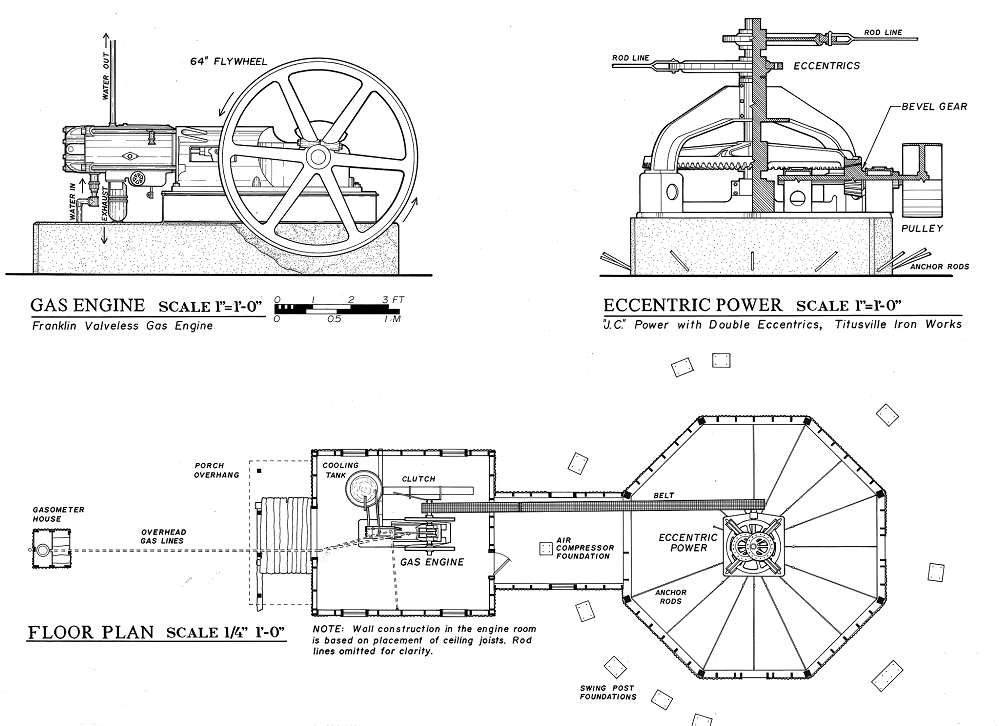
Many widely used techniques of drilling and pumping oil were developed to recover the high-quality “Pennsylvania Grade” oil. Image courtesy Library of Congress.
The heavy and powerful engine — started by kicking down on one of the iron spokes — transferred power to rotate an eccentric wheel, which alternately pushed and pulled on a system of rods linked to pump jacks at distant oil wells.
Pump Jacks
“Transmitting power hundreds of yards, over and around obstacles, etc., to numerous pump jacks required an ingenious system of reciprocating rods or cables called Central Power and jerker lines,” explains documentation from an Allegheny National Forest Oil Heritage Series.
The series documentation includes an early illustration of an oilfield “jack plant” in McKean County, Pennsylvania. The long rod lines were also called shackle lines or jack lines.
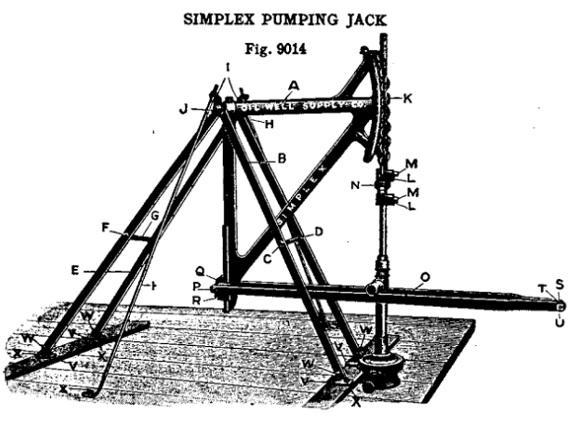
A single engine with eccentric wheel connecting rod lines could economically pump oil using Oil Well Supply Company’s “Simplex Pumping Jacks.”
Around 1913, with electricity not readily available, the Simplex Pumping Jack became a popular offering from Oil Well Supply Company of Oil City, Pennsylvania. The simple and effective technology could often be found at the very end of long jerk lines.
A central power unit could connect and run several of these dispersed Simplex pumps. Those equipped with a double eccentric wheel could power twice as many.
Roger Riddle, a retired field guide for the West Virginia Oil & Gas Museum in Parkersburg, grew up around central power units and recalls the rhythmic clanking of rod lines.
Riddle guided visitors through dense nearby woods where remnants of the elaborate systems rust. The heavy equipment once “pumped with just these steel rods, just dangling through the woods,” he said. “You could hear them banging along – it was really something to see those work. The cost of pumping wells was pretty cheap.”
The heyday of central power units passed when electrification arrived, nonetheless, a few such systems remain in use today. Learn more about the evolution of petroleum production methods, the first counter-balanced “Nodding Donkeys” in All Pumped Up – Oilfield Technology.
______________________
Recommended Reading: Drilling Technology in Nontechnical Language (2012); Trek of the Oil Finders: A History of Exploration for Petroleum (1975). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Please become an AOGHS annual supporter and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2025 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
Citation Information: Article Title: “Eccentric Wheels and Jerk Lines.” Authors: B.A. Wells and K.L. Wells. Website Name: American Oil & Gas Historical Society. URL: https://aoghs.org/technology/jerk-lines-eccentric-wheels. Last Updated: June 15, 2025. Original Published Date: November 20, 2017.







