This Week in Petroleum History: September 30 – October 6
September 30, 2006 – Roughnecks Statue dedicated at Signal Hill –
A bronze “Tribute to the Roughnecks” statue was dedicated near the Alamitos No. 1 well, which in 1921 revealed California’s prolific Long Beach oilfield 20 miles south of Los Angeles.

Signal Hill once had so many derricks people called it Porcupine Hill. The city of Long Beach is visible in the distance from the “Tribute to the Roughnecks” statue by Cindy Jackson.
The statue by Cindy Jackson has since commemorated the Signal Hill Oil Boom, serving as “a tribute to the petroleum pioneers for their success here, a success which has, by aiding in the growth and expansion of the petroleum industry, contributed so much to the welfare of mankind.”
October 1, 1908 – Ford Motor Company produces First Model T
The first production Ford Model T rolled off the assembly line in Detroit. Between 1908 and 1927, Ford built about 15 million more, each fueled by inexpensive gasoline. The popularity of the Model T was timely for the U.S. petroleum industry, which faced falling demand for kerosene as consumers switched to electric lighting.

Ford Model T tires were white until 1910, when the petroleum product carbon black was added to improve durability.
New major oilfield discoveries, especially the 1901 “Lucas Gusher” at Spindletop Hill near Beaumont, Texas, helped meet growing demand for what had been a refining byproduct, gasoline.
October 1, 1942 – Water Injection begins in East Texas
The East Texas Salt Water Disposal Company drilled the first saltwater injection well in the 12-year-old East Texas oilfield near the towns of Tyler, Longview, and Kilgore. As early as 1929, the Federal Bureau of Mines had determined injecting recovered saltwater into formations could increase reservoir pressures and oil production.
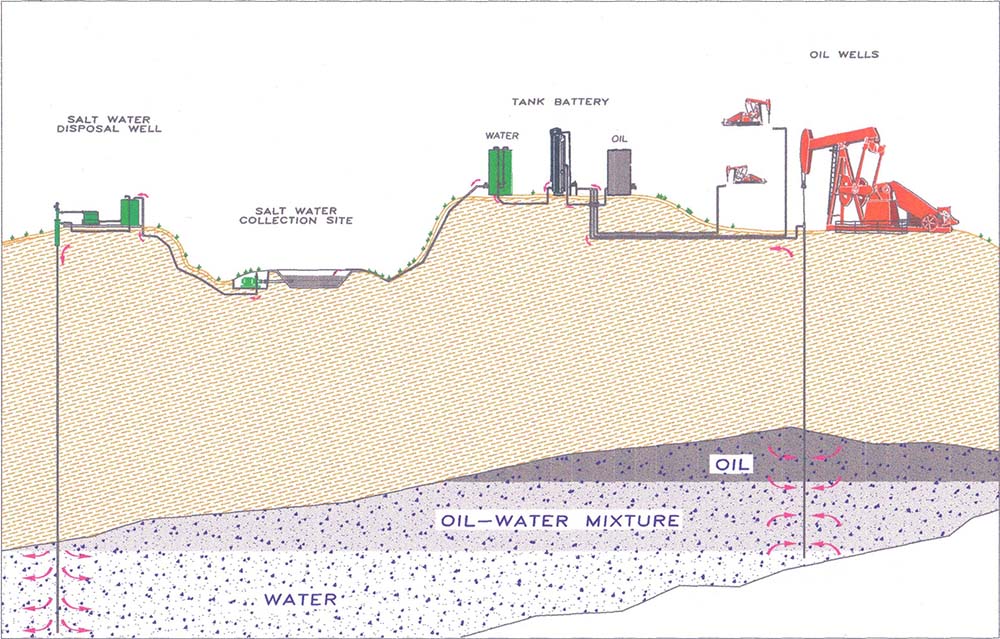
Saltwater injection wells have improved oil production. By disposing produced water at a low cost, marginal East Texas wells have remained viable. Illustration courtesy East Texas Salt Water Disposal Company.
The Texas Railroad Commission established the saltwater disposal company as a public utility to operate in the oilfield. The company treated and re-injected about 1.5 billion barrels of saltwater in its first 13 years, prompting the commission to proclaim saltwater injection as the “greatest oil conservation project in history.”
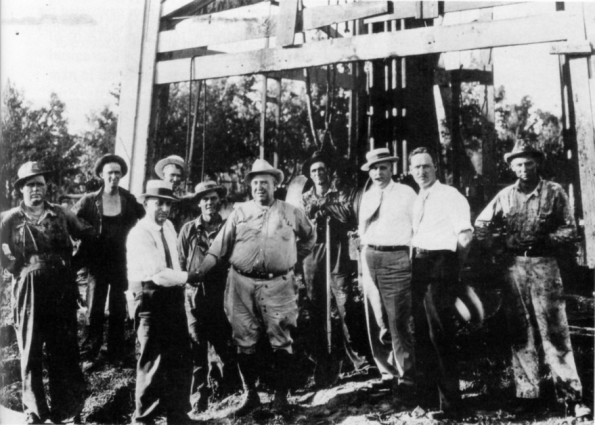
October 2, 1919 – Future “Mr. Tulsa” incorporates Skelly Oil
Skelly Oil Company incorporated in Tulsa, Oklahoma, with founder William Grove Skelly as president. He had been born in 1878 in Erie, Pennsylvania, where his father hauled oilfield equipment in a horse-drawn wagon.

Born near Pennsylvania’s early oilfields, independent oilman William Skelly’s company helped make Tulsa the “Oil Capital of the World.”
Skelly’s success in the El Dorado oilfield east of Wichita, Kansas, helped him launch Skelly Oil and other ventures, including Midland Refining Company, which he founded in 1917. As Tulsa promoted itself as “Oil Capital of the World,” Skelly became known as “Mr. Tulsa.”
Skelly served as president of Tulsa’s famous International Petroleum Exposition for 32 years until his death in 1957.
October 3, 1930 – East Texas Oilfield discovered on Widow’s Farm
With a crowd of more than 4,000 expectant landowners, leaseholders, creditors, and others watching, the Daisy Bradford No. 3 wildcat well was successfully shot with nitroglycerin near Kilgore, Texas.
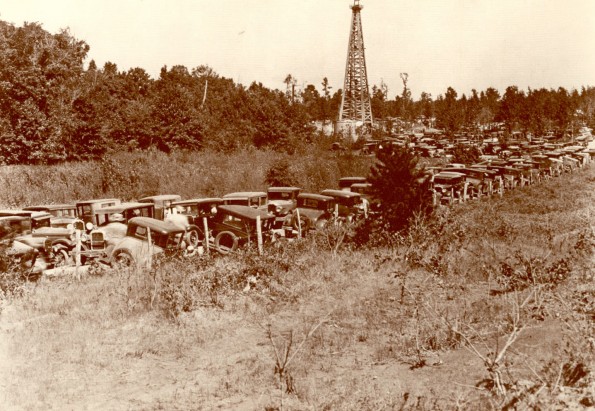

Spectators gathered on the widow Daisy Bradford’s farm near Kilgore, Texas, to watch the October 3, 1930, “shooting” of the discovery well of what proved to be the largest oilfield in the lower 48 states. Photo courtesy Jack Elder, The Glory Days.
“All of East Texas waited expectantly while Columbus ‘Dad’ Joiner inched his way toward oil,” explained historian Jack Elder in 1986. “Thousands crowded their way to the site of Daisy Bradford No. 3, hoping to be there when and if oil gushed from the well to wash away the misery of the Great Depression.”
Geologists were stunned when it became apparent the remote wildcat well on the widow Daisy Bradford’s farm — along with two other wells far to the north — were part of the same oil-producing formation (the Woodbine) that encompassed more than 140,000 acres. The “Black Giant” would produce billions of barrels of oil in coming decades.
Learn more in East Texas Oilfield Discovery.
October 3, 1980 – Museum opens in East Texas Oilfield
Fifty years after the discovery of the East Texas oilfield, the East Texas Oil Museum at Kilgore College opened as “a tribute to the independent oil producers and wildcatters, the men and women who dared to dream as they pursued the fruits of free enterprise.”

The East Texas Oil Museum since 1980 has hosted events and maintained exhibits preserving the “Black Giant” oilfield discovered during the Great Depression. Photos by Bruce Wells.
Established with funding from the Hunt Oil Company, the museum at Kilgore College recreated a 1930s boom town atmosphere.
October 4, 1866 – Oil Fever spreads to Allegheny River Valley
Just 15 miles east of Titusville, Pennsylvania, site of the first U.S. oil well, an oilfield discovery at Triumph Hill sparked another wild rush of speculators and new drilling. America’s petroleum industry was barely seven years old when wooden cable-tool derricks and engine houses replaced hemlock trees along the Allegheny River.
Learn more about post-Civil War oil boom towns in Derricks of Triumph Hill.
October 4, 1901 – Drake Memorial dedicated in Pennsylvania
More than 2,500 people, including his widow, Laura Dowd Drake, attended the unveiling of a monument to the “father of the petroleum industry,” Edwin L. Drake, who had died in relative obscurity 1880. Standard Oil Company executive Henry Rogers commissioned the marble, semi-circle memorial in Titusville, Pennsylvania.
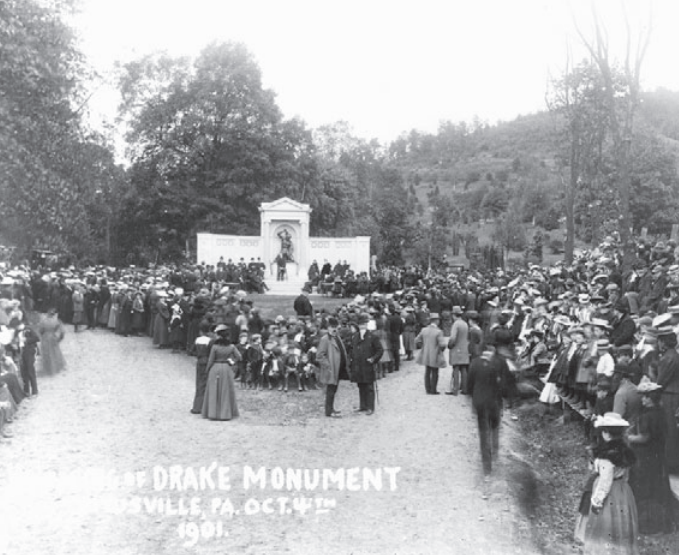

Unveiling of Drake Monument, Titusville, PA. Oct. 4th 1901. Thousands attended the dedication in Woodlawn Cemetery. Photo by John Mather courtesy Drake Well Museum.
The monument, which includes a bronze statue by Charles Henry Niehaus, was dedicated in Woodlawn Cemetery. Learn more by visiting Titusville’s Drake Well Museum and Park.
October 5, 1915 – Science of Petroleum Geology reveals Oilfield
Using the new earth science of petroleum geology for finding oil led to discovery of the giant Mid-Continent field in central Kansas. Drilled by Wichita Natural Gas Company, a subsidiary of Cities Service Company, the well revealed the 34-square-mile El Dorado oilfield.

The Stapleton No. 1 well discovered the El Dorado, Kansas, oilfield, which became one of the largest producing fields in the world. By 1919, Butler County had more than 1,800 producing oil wells. Photo by Bruce Wells.
“Pioneers named El Dorado, Kansas, in 1857 for the beauty of the site and the promise of future riches but not until 58 years later was black rather than mythical yellow gold discovered when the Stapleton No. 1 oil well came in on October 5, 1915,” explained geologist Lawrence Skelton in 1997.
The Stapleton No. 1 well east of Wichita initially found oil at a depth of 600 feet before being deepened to 2,500 feet to produce 110 barrels of oil a day from the Wilcox sands. Natural gas discoveries one year earlier at nearby Augusta had prompted El Dorado civic leaders to seek their own geological study.

The Stapleton No. 1 well and the Kansas Oil Museum preserve a 1915 oil discovery. Photo by Bruce Wells.
The Kansas Oil Museum preserves the state’s petroleum heritage with historic oilfield equipment displayed on 10 acres east of the city. Museum exhibits describe how lessons from the El Dorado field helped launch petroleum geology as a profession while establishing El Dorado as a center for refining.
Learn more in the Kansas Oil Boom.
October 5, 1958 – Water Park opens in West Texas for a Day
A water park inside a Depression-Era experimental concrete oil tank opened to public in West Texas. The day’s festivities at Monahans attracted swimmers, boaters, anglers, and even water skiers to the massive, manmade lake — before leaks at the seams forced it to close the next day.
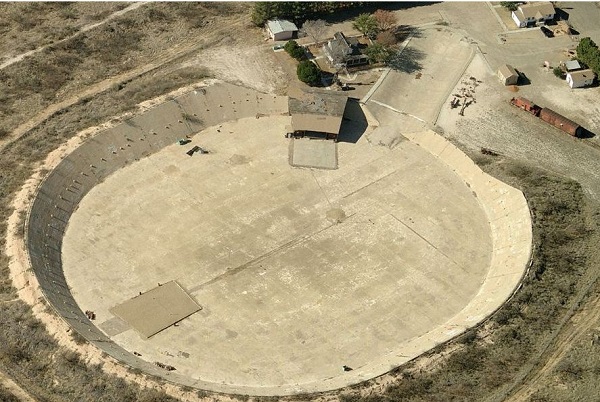

The Million Barrel Museum’s site was originally built to store Permian Basin oil. For scale, note the railroad car and caboose exhibit at upper right.
A local couple had attempted to find a good use for the 525-foot by 422-foot “million barrel reservoir” once covered by a redwood dome roof. The concrete tank had been completed in 1928 by Shell Oil due to a lack of pipelines for Permian Basin oil. Shell stopped using the tank because of the company could not prevent oil from leaking at the seams.
Learn more in Million Barrel Museum.
October 6, 1886 – Natural Gas fuels Glass Manufacturing
A 900-foot-deep natural gas well in a cornfield near Kokomo, Indiana, helped establish the Indiana Natural Gas Company and the Opalescent Glass Works, now Kokomo Opalescent Glass, which has been in continuous operation since 1888.
Although the glass company almost went bankrupt when natural gas supplies dwindled, it recovered and in 1893 sold thousands of pounds of stained glass to Tiffany Glass Company and electric insulators to Edison General Electric. Indiana’s first natural gas well had been drilled in 1867 seeking oil (see Indiana Natural Gas Boom).
_______________________
Recommended Reading: Signal Hill, California – Images of America (2006); From Here to Obscurity: An Illustrated History of the Model T Ford, 1909 – 1927
(1971); Artificial Lift-down Hole Pumping Systems
(1984); An adventure called Skelly: A history of Skelly Oil Company through fifty years, 1919-1969 (1970); The Black Giant: A History of the East Texas Oil Field and Oil Industry Skullduggery & Trivia
(2003); Early Texas Oil: A Photographic History, 1866-1936
(2000); Western Pennsylvania’s Oil Heritage
(2008); The fire in the rock: A history of the oil and gas industry in Kansas, 1855-1976
(1976); Chronicles of an Oil Boom: Unlocking the Permian Basin
(2014). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Please become an AOGHS annual supporter and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2024 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.