by Bruce Wells | Oct 28, 2024 | This Week in Petroleum History
October 28, 1868 – Newspaper praises Explosive Technology –
The Titusville Morning Herald praised the results of an explosive oilfield production technology — Civil War veteran Colonel E.A.L. Roberts’ patented nitroglycerin torpedo. “It would be superfluous, at this late day, to speak of the merits of the Roberts Torpedo,” explained the first daily newspaper of the Pennsylvania oil region.

Front page of the first issue of the Titusville Morning Herald, which ceased publication in 2022 after 157 years. Photo courtesy TheDerrick.com.
“For the past three years, it has been a most successful operation and has increased the production of oil in hundreds upon hundreds of oil wells to an extent which could hardly be overestimated” (see Shooters — a “Fracking” History). The Titusville Herald ceased publication in 2022 after 157 years.

October 28, 1926 – Giant Yates Field discovered West of the Pecos
The 26,400-acre Yates oilfield was discovered in a remote area of Pecos County, Texas, in the Permian Basin. Drilled in 1926 with a $15,000 cable-tool rig, the Ira Yates 1-A produced 450 barrels of oil a day from almost 1,000 feet deep. Before the giant oilfield discovery, Ira Yates had struggled to keep his ranch on the northern border of the Chihuahua Desert.
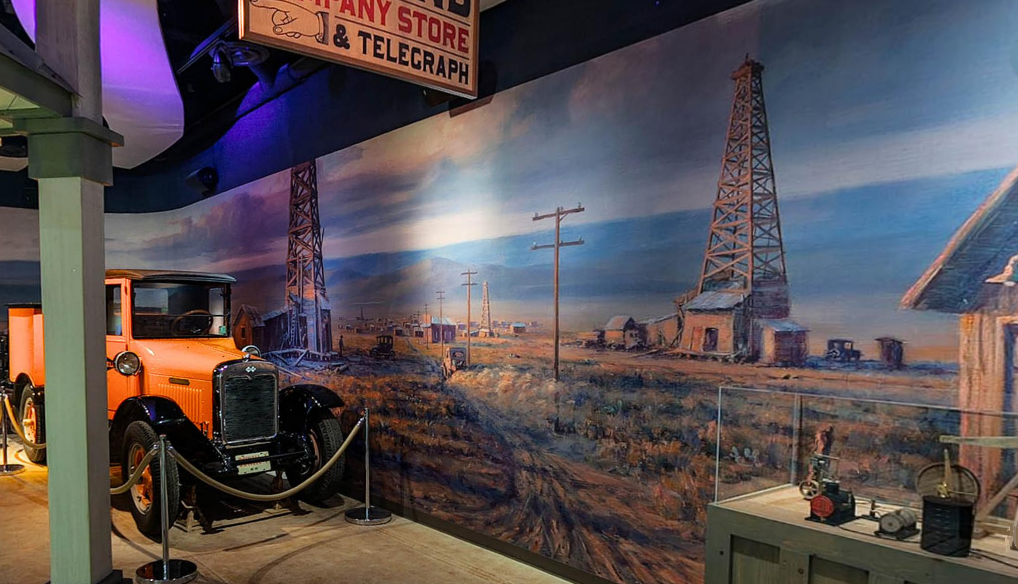

The Permian Basin’s 1926 Yates oilfield discovery followed the 1923 gusher at Big Lake (Santa Rita No. 1) and led to giant oilfield discoveries at Hendrick and Hobbs. “Midland Comes of Age” exhibit photo courtesy of the Petroleum Museum.
“Drought and predators nearly did him in” noted one historian, until Yates convinced a San Angelo company to explore for oil west of the Pecos River. With the Pecos County well 30 miles from the nearest oil pipeline and a storage tank under construction, four more Yates wells yielded another 12,000 barrels of oil a day. On his 67th birthday, Yates received an $18 million royalty check (also see Santa Rita taps Permian Basin).
October 30, 1894 – “Golden Rule” Jones invents a Better Sucker Rod
Samuel M. Jones patented a sucker rod design for his Acme Sucker Rod Company, which he had founded in 1892 in Toledo, Ohio. With his “Coupling for Pipes or Rods,” Jones applied his oilfield experience in mechanics to solve the frequent and time-consuming problem of broken sucker rods. His innovation would soon make him a millionaire.
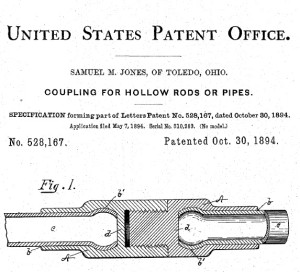
Samuel M. Jones, future mayor of Toledo, Ohio, worked as a potboiler, pumper, tool dresser, blacksmith, and pipe layer before starting an oilfield service company.
Jones had worked in Pennsylvania’s oil region as a potboiler, pumper, tool dresser, blacksmith, and pipe layer. He became known as “Golden Rule” Jones by establishing a better workplace for employees at his factory, where he shortened the work day and started a revenue-sharing program.
Jones ran for Toledo mayor as a progressive Republican in 1887 and was elected. He was reelected three times and served until dying on the job in 1904.
Learn more in “Golden Rule” Jones of Ohio.
October 31, 1871 – Modern Refinery Method patented
Petroleum refining would become more efficient thanks to an invention by Henry Rogers of Brooklyn, New York, who patented an “apparatus for separating volatile hydrocarbons by repeated vaporization and condensation.”
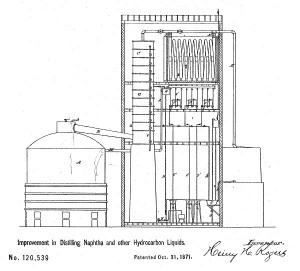
Henry Rogers patented his “improvement to distilling naphtha and other hydrocarbon liquids,” including kerosene.
Rogers introduced many elements of modern refineries, including “fractionating” towers that improved earlier processes of extracting kerosene by simple distillation in kettle stills.
“The apparatus which I use is, in many respects, similar to what is known as the column-still for distilling alcoholic spirits, but modified in all the details, so as to make it available for distilling oils,” Rogers noted in his 1871 patent application. More technological advancements would lead to giant refining operations like the Standard Oil of Indiana Whiting Refinery, which opened in 1889.
October 31, 1903 – Salt-Dome Oilfield discovered in Texas
One mile north of Batson, Texas, a discovery well drilled by W.L. Douglas’ Paraffine Oil Company produced 600 barrels of oil a day from a depth of 790 feet. A second well drilled two months later in the Batson field produced 4,000 barrels of oil a day from 1,000 feet deep. Many new ventures joined the drilling boom (see Buffalo Oil Company).
When combined with other newly discovered prolific salt-dome fields, Spindletop (1901), Sour Lake (1903), and Humble (1904), “Batson helped to establish the basis of the Texas oil industry when these shallow fields gave up the first Texas Gulf Coast oil,” noted the Texas State Historical Association in 2010.

October 31, 1913 – First Paved U.S. Highway dedicated
Towns nationwide celebrated the opening of the Lincoln Highway, a 3,389-mile-long “Main Street Across America” connecting Times Square in New York City to San Francisco’s Lincoln Park. The Lincoln Highway was the first national memorial dedicated to President Abraham Lincoln. In 1919, the Army Motor Transport Corps organized a transcontinental convoy to test vehicles and highlight the need for more paved roads.
October 31, 1924 – Olinda Oil Wells Pitcher plays Exhibition Game
Former California oilfield worker Walter “Big Train” Johnson returned to his oil patch roots in Brea for an exhibition game with famed slugger Babe Ruth, who swatted two home runs off the future Hall of Fame pitcher. Three decades earlier, Johnson began his baseball career as a 16-year-old pitcher for the Olinda Oil Wells.

The former star player for the Olinda Oil Wells pitched against Babe Ruth in a 1924 exhibition game in nearby Brea.
Playing for the Washington Senators years later, the former oilfield roustabout became major league baseball’s all-time career leader in shutouts with 110. Many oilfield towns like Brea fielded teams with names reflecting their communities’ livelihood.
Learn more in Oilfields of Dreams – Gassers, Oilers, and Drillers Baseball Teams.
October 31, 1930 – C.M. “Dad” Joiner’s Properties placed into Receivership
After it was learned that 70-year-old wildcatter Columbus Marion “Dad” Joiner had oversold his East Texas oilfield leases in Rusk County, District Judge R.T. Brown placed the properties into receivership.

The Baker Hotel in Dallas was where Columbus “Dad” Joiner, discoverer of the East Texas oilfield, met with H.L. Hunt and sold Hunt 5,580 acres for $1.34 million. Built in 1925, the hotel was torn down in 1980.
With the field’s Daisy Bradford No. 3 and other wells tied up in conflicting claims, Joiner took refuge from creditors in the Baker Hotel in Dallas, where Haroldson Lafayette (H.L.) Hunt negotiated a $1.34 million deal with him for the discovery well and 5,580 acres of leases. In the 300 lawsuits and 10 years of litigation that followed, Hunt sustained every title.
November 1, 1865 – First Railroad Oil Tank Car arrives
The first of James and Amos Densmore’s innovative railroad oil tank cars arrived at the Miller Farm, four miles south of Titusville, Pennsylvania. The inventors would be awarded a U.S. patent on April 10, 1866, for their dual tank design.

Brothers Amos and James Densmore designed and built the first successful railroad tank cars used in the Pennsylvania oilfields in 1865. Photo courtesy Drake Well Museum.
The crude oil for the iron-banded wooden tanks on a flatcar was delivered by Samuel Van Syckle’s two-inch iron pipeline (another oil industry first) from the oilfield boom town at Pithole Creek. Oil from large storage tanks on the farm filled the Densmore tanks for the Oil Creek Railroad, which connected to lines reaching Pittsburgh, New York City, and other markets.
Learn more in Densmore Brothers Oil Tank Car.

November 2, 1902 – First Gas-Powered Locomobile delivered
Known for building luxury steam-powered automobiles, the Locomobile Company of America delivered its first gasoline-powered auto to a buyer in New York City. The company had hired Andrew Riker, a self-taught engineer and racecar driver, to create the four-cylinder, 12-horsepower vehicle, which sold for $4,000.

The four-cylinder gasoline engine of Locomobile “Old 16” racing car on display in the Henry Ford Museum, Dearborn, Michigan.
In 1908, a Locomobile “Old 16,” a four-cylinder, 16-liter, two-seater, won America’s first international racing victory — the Vanderbilt Cup at the Long Island Motor Parkway, one of the first paved parkways. The Locomobile Company would “reign supreme in the niche category of luxury American cars for decades,” according to Today in Connecticut History.
November 3, 1878 – Haymaker Natural Gas Well lights Pittsburgh
While drilling for oil in 1878, a well drilled by Michael and Obediah Haymaker erupted with natural gas from a depth of almost 1,400 feet. “Every piece of rigging went sky high, whirling around like so much paper caught in a gust of wind. But instead of oil, we had struck gas,” Michael Haymaker recalled.
Eighteen miles east of Pittsburgh, the out-of-control well in Murrysville, Pennsylvania, produced an estimated 34 million cubic feet of natural gas daily. It was considered the largest natural gas well ever drilled up to that time.

“A sight that can be seen in no other city in the world,” noted Harper’s Weekly in 1885.
Given oilfield technologies of the late 1880s, there was no way to cap the well and no pipeline to exploit commercial possibilities. The Haymaker well drew thousands of curious onlookers to a flaming torch that burned for 18 months and was visible miles away.
“Outlet of a natural gas well near Pittsburgh — a sight that can be seen in no other city in the world,” noted Harper’s Weekly. When finally brought under control, the Haymaker well provided inexpensive gas light to Pittsburgh for many years.
Learn more in Natural Gas is King in Pittsburgh.

November 3, 1900 – New York City hosts First U.S. Auto Show
America’s first gathering of the latest automotive technologies attracted thousands to New York City’s Madison Square Garden. Manufacturers presented 160 different vehicles and conducted driving and maneuverability demonstrations on a 20-foot-wide wooden track that encircled the exhibits.

The Winton Motor Carriage of 1898 was the first American automobile advertisement.
Almost 50,000 visitors paid 50 cents each to witness autos driving up a 200-foot ramp to test hill-climbing power. The most popular models proved to be electric, steam, and gasoline…in that order. New Yorkers welcomed the new models as a way to reduce the 450,000 tons of manure, 21 million gallons of urine, and 15,000 horse carcasses that had to be removed from city streets every year.
Of the 4,200 automobiles sold in 1900, less than a thousand were powered by gasoline. But within five years, consumer preference established the dominance of gasoline-powered autos.
Learn more in Cantankerous Combustion — 1st U.S. Auto Show and First Gas Pump and Service Station.
_______________________
Recommended Reading: The Boom: How Fracking Ignited the American Energy Revolution and Changed the World (2015); Wildcatters: Texas Independent Oilmen
(2015); Wildcatters: Texas Independent Oilmen (1984); Holy Toledo: Religion and Politics in the Life of “Golden Rule” Jones
(1984); Holy Toledo: Religion and Politics in the Life of “Golden Rule” Jones (1998); The Bradford Oil Refinery, Pennsylvania, Images of America
(1998); The Bradford Oil Refinery, Pennsylvania, Images of America (2006); Early Texas Oil: A Photographic History, 1866-1936
(2006); Early Texas Oil: A Photographic History, 1866-1936 (2000); The Lincoln Highway: Coast to Coast from Times Square to the Golden Gate
(2000); The Lincoln Highway: Coast to Coast from Times Square to the Golden Gate (2011); Oil on the Brain: Petroleum’s Long, Strange Trip to Your Tank
(2011); Oil on the Brain: Petroleum’s Long, Strange Trip to Your Tank (2008); The Extraction State, A History of Natural Gas in America (2021); A History of the New York International Auto Show: 1900-2000
(2008); The Extraction State, A History of Natural Gas in America (2021); A History of the New York International Auto Show: 1900-2000 (2000). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(2000). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Please become an AOGHS annual supporter and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2024 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
.
by Bruce Wells | Oct 21, 2024 | This Week in Petroleum History
October 21, 1921 – First Natural Gas Well in New Mexico –
The New Mexico natural gas industry began when the newly established Aztec Oil Syndicate’s State No. 1 well found a gas field about 15 miles northeast of Farmington in San Juan County. The drilling crew used a tree trunk with a two-inch pipe and shut-off valve to control the well until a wellhead could be shipped from Colorado. The well produced 10 million cubic feet of natural gas a day.
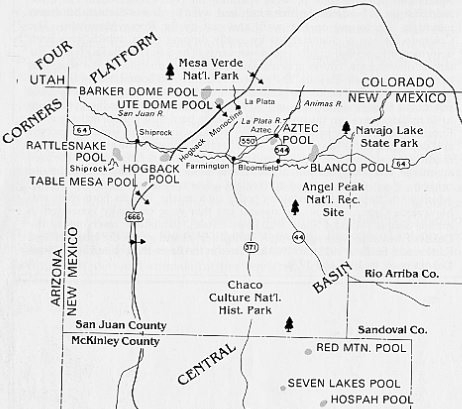
New Mexico’s first commercial natural gas service began after a 1921 discovery near Aztec. Oil discoveries followed in the southeast.
By the end of December 1921, a pipeline reached two miles into the town of Aztec, where citizens enjoyed New Mexico’s first commercial natural gas service. In 1922, natural gas could be purchased in Aztec at a flat rate of $2 a month (for a gas heater) and $2.25 (for a gas stove). Learn more about the state’s petroleum history in First New Mexico Oil Wells.

October 23, 1908 – Salt Creek Well launches Wyoming Boom
Wyoming’s first oil boom began when the Dutch company Petroleum Maatschappij Salt Creek completed its “Big Dutch” well about 40 miles north of Casper.
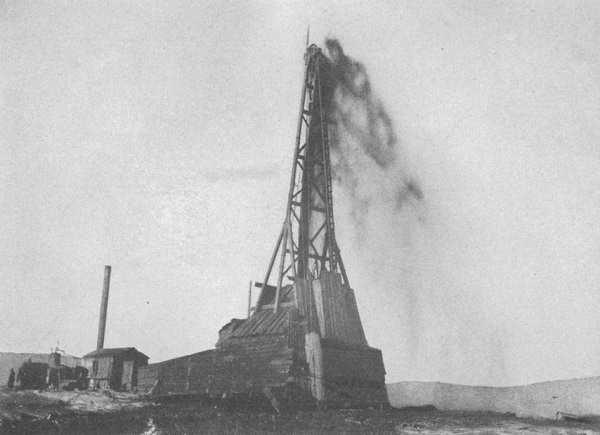

The “Big Dutch” No. 1 well, above, launched a Wyoming drilling boom in 1908. Photo courtesy U.S. Geological Survey.
Salt Creek’s potential had been known since the 1880s, but the area’s central geological salt dome received little attention until Italian geologist Cesare Porro recommended drilling there in 1906. Another salt dome formation had been revealed with the 1901 Spindletop oilfield discovery in Texas.
At Salt Creek, the Oil Wells Drilling Syndicate, a British company, drilled the “Big Dutch” well, which produced 600 barrels of oil a day from a depth of 1,050 feet deep and launched a Wyoming drilling boom. By 1930, about one-fifth of all U.S. oil came from the Salt Creek oilfield. Production continued in the 1960s with water-flooding technologies and the use of carbon dioxide injection beginning in 2004.
Learn more in First Wyoming Oil Wells.

October 23, 1948 – “Smart Pig” advances Pipeline Inspection
Northern Natural Gas Company recorded the first use of an X-ray machine for internal testing of petroleum pipeline welds. The company examined a 20-inch diameter pipe north of its Clifton, Kansas, compressor station. The device — today known as a “smart pig” — traveled up to 1,800 feet inside the pipe, imaging each weld.

A pipeline worker inspects a “smart pig.” Photo courtesy Pacific L.A. Marine Terminal.
As early as 1926, U.S. Navy researchers had investigated the use of gamma-ray radiation to detect flaws in welded steel. In 1944, Cormack Boucher patented a “radiographic apparatus” suitable for many large pipelines. Modern inspection tools employ magnetic particle, ultrasonic, eddy current, and other methods to verify pipeline and weld integrity.
October 23, 1970 – LNG powers World Land Speed Record
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) powered the Blue Flame to a new world land speed record of 630.388 miles per hour. A rocket motor combining LNG and hydrogen peroxide fueled the 38-foot, 4,950-pound Blue Flame, which set the record at the Bonneville Salt Flats in Utah. The rocket motor could produce up to 22,000 pounds of thrust — about 58,000 horsepower.

In 1970, the Blue Flame achieved, “the greenest world land speed record set in the 20th century.”
Sponsored by the American Gas Association (AGA) and the Institute of Gas Technology, the Blue Flame design came from three Milwaukee, Wisconsin, automotive engineers: Dick Keller, Ray Dausman, and Pete Farnsworth. Building a record-setting rocket dragster in 1967 got the attention of AGA executives.

The American Oil & Gas Historical Society interviewed Dick Keller in 2013 to help produce a YouTube video using his 8mm home movies.
Interviewed by the American Oil & Gas Historical Society in 2013, Keller explained how the growing environmental movement of the late 1960s encouraged AGA “suits” to see value in supporting a new racer fueled by LNG. Keller in 2020 published Speedquest: Inside the Blue Flame, noting natural gas powered “the greenest world land speed record set in the 20th century.”
Learn more in Blue Flame Natural Gas Rocket Car.

October 25, 1929 – Cabinet Member guilty in Teapot Dome Scandal
Albert B. Fall, appointed Interior Secretary in 1921 by President Warren G. Harding, was found guilty of accepting a bribe while in office, becoming the first cabinet official in U.S. history to be convicted of a felony. An executive order from President Harding had given Fall full control of the Naval Petroleum Reserves.

Wyoming’s Teapot Dome oilfield was named after Teapot Rock, seen here circa 1922 (the “spout” later fell off). Photo courtesy Casper College Western History Center.
Fall was found guilty of secretly leasing the Navy’s oil reserve lands to Harry Sinclair of Sinclair Oil Company and to Edward Doheny, discoverer of the Los Angeles oilfield.
The noncompetitive leases were awarded to Doheny’s Pan American Petroleum Company (reserves at Elk Hills and Buena Vista Hills, California), and Sinclair’s Mammoth Oil Company (reserve at Teapot Dome, Wyoming). Fall received more than $400,000 from the two oil companies.
It emerged during Senate hearings that cash was delivered to Secretary Fall in a Washington, D.C., hotel. He was convicted of taking a bribe, fined $100,000, and sentenced to one year in prison. Sinclair and Doheny were acquitted, but Sinclair spent six-and-a-half months in prison for contempt of court and the U.S. Senate.
October 26, 1970 – Joe Roughneck Statue dedicated in Texas
Texas Governor Preston Smith dedicated a “Joe Roughneck” memorial in Boonsville to mark the 20th anniversary of a giant natural gas field discovery in East Texas.
In 1950, the Lone Star Gas Company Vaught No. 1 well discovered the Boonsville field, which produced 2.5 billion cubic feet of natural gas over the next 20 years. By 2001 the field reached production of 3.1 trillion cubic feet of gas from more than 3,500 wells.

“Joe Roughneck” in Boonsville, Texas. Photo, courtesy Mike Price.
Joe Roughneck began as a character in Lone Star Steel Company advertising in the 1950s. Until discontinued in 2020, the bronze bust was presented each year during the Chief Roughneck Award ceremony of the Independent Petroleum Association of America (IPAA).
In addition to the Boonsville monument, Joe’s bust sits atop three different Texas oilfield monuments: Joinerville (1957), Conroe (1957) and Kilgore (1986).
Learn more in Meet Joe Roughneck.

October 27, 1763 – Birth of Pioneer American Geologist
William Maclure, who would become a renowned American geologist and “stratigrapher,” was born in Ayr, Scotland. He created the earliest geological maps of North America in 1809 and later earned the title, “Father of American Geology.”
After settling in the United States in 1797, Maclure explored the eastern part of North America to prepare the first geological map of the United States. His travels from Maine to Georgia in 1808 resulted in the map’s sequence of rock layers.
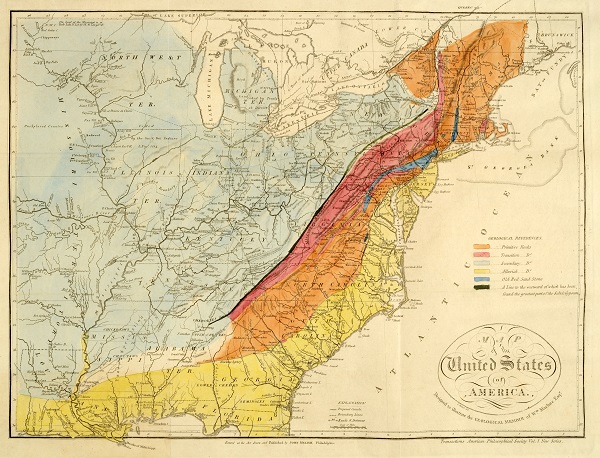
“Map of the United States of America, Designed to Illustrate the Geological Memoir of Wm. Maclure, Esqr.” This 1818 version is more detailed than the first geological map he published in 1809. Image courtesy the Historic Maps Collection, Princeton Library.
“Here, in broad strokes, he identifies six different geological classes,” a Princeton geologist reported. “Note that the chain of the Appalachian Mountains is correctly labeled as containing the most primitive, or oldest, rock.”
In the 1850s, a chemist at Yale analyzed samples of Pennsylvania “rock oil” for refining into kerosene; his report led to the drilling of the first U.S. oil well in 1859 (also see Rocky Beginnings of Petroleum Geology).
October 27, 1923 – Refining Company founded in Arkansas
Lion Oil Company was founded as a refining Company in El Dorado, Arkansas, by Texan Thomas Harry Barton. He earlier had organized the El Dorado Natural Gas Company and acquired a 2,000-barrel-a-day refinery in 1922.
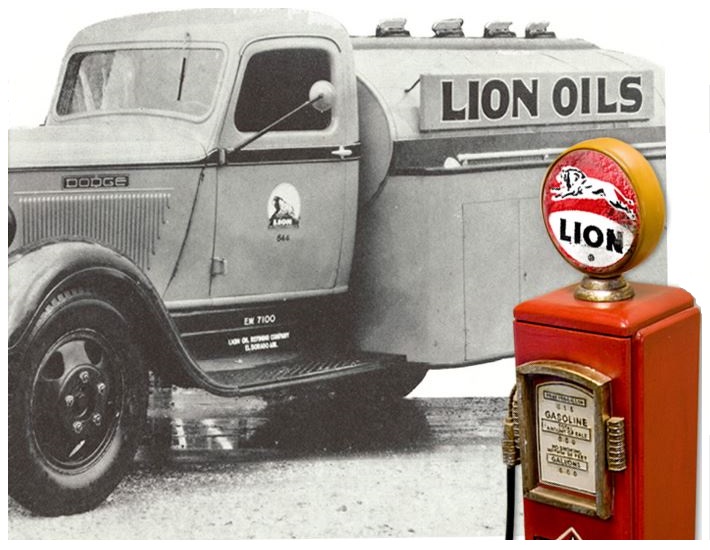

Founded in 1923 in El Dorado, Arkansas, Lion Oil will operate about 2,000 service stations in the south in the 1950s. Photo courtesy Lion Oil.
Production from the nearby Smackover oilfield helped the Lion Oil Refining Company’s refining capacity grow to 10,000 barrels a day. By 1925, the company acquired oil wells producing 1.4 million barrels of oil. A merger with Monsanto Chemical in 1955 brought the gradual disappearance of the once familiar “Beauregard Lion” logo.
Learn more Arkansas history in Arkansas Oil and Gas Boom Towns.

October 27, 1938 – DuPont names Petroleum Product Nylon
DuPont chemical company announced that Nylon would be the name of its newly invented synthetic fiber yarn made from petroleum. Discovered in 1935 by Wallace Carothers at a DuPont research facility, nylon is considered the first commercially successful synthetic polymer. Carothers would become known as the father of the science of man-made polymers (see Nylon, a Petroleum Polymer).
_______________________
Recommended Reading: Oil in West Texas and New Mexico (1982); The Salt Creek Oil Field: Natrona County, Wyoming, 1912
(1982); The Salt Creek Oil Field: Natrona County, Wyoming, 1912 (2017); Oil and Gas Pipeline Fundamentals
(2017); Oil and Gas Pipeline Fundamentals (1993); The Reluctant Rocketman: A Curious Journey in World Record Breaking
(1993); The Reluctant Rocketman: A Curious Journey in World Record Breaking (2013); Speedquest: Inside the Blue Flame (2020); The Bradford Oil Refinery, Pennsylvania, Images of America
(2013); Speedquest: Inside the Blue Flame (2020); The Bradford Oil Refinery, Pennsylvania, Images of America 2006); Early Louisiana and Arkansas Oil: A Photographic History, 1901-1946
2006); Early Louisiana and Arkansas Oil: A Photographic History, 1901-1946 (1982); Du Pont Dynasty: Behind the Nylon Curtain
(1982); Du Pont Dynasty: Behind the Nylon Curtain (1984). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(1984). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Please become an AOGHS annual supporter and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2024 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
by Bruce Wells | Oct 14, 2024 | This Week in Petroleum History
October 14, 1929 – Van Oilfield Discovery East of Dallas –
Pure Oil Company completed its Jarman No. 1 well in Van Zandt County and launched a drilling boom 60 miles east of Dallas. During its first hour, the oilfield discovery well produced 147 barrels of oil from the Woodbine sandstone at a depth of 2,700 feet. Three more wells followed as construction began on a camp for oilfield workers.

This Van Zandt County museum east of Dallas is in a warehouse originally built in 1930 by Pure Oil Company. Photo by Bruce Wells
By April 1930, the Van field produced 20,000 barrels of oil a day as companies adopted advanced production techniques. New pipelines linked the oilfield to the Pure refinery in Beaumont, Texas, and Standard Oil Company’s refinery in Baton Rouge, Louisiana.
Among the Van oilfield’s “Cook Camp” buildings was a sheet-metal warehouse, today home to the Van Area Oil and Historical Museum. Residents celebrate their oilfield’s discovery and the 45th Van Oil Festival will take place on October 19, 2024, in Van City Park.
October 15, 1895 – Patent for a Well Boring Machine
Oscar Benjamin of Lafayette, Louisiana, patented a compact, cable-tool drilling rig. His design for the “Well Boring Machine” used a framework mounted on wheels with a hinged derrick “adapted to swing over in transit.”
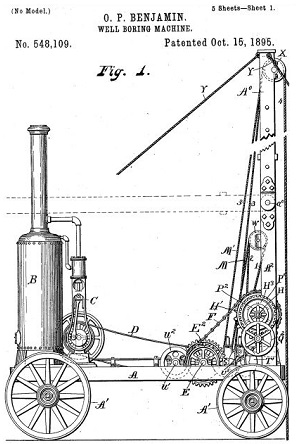
An 1895 patent for a portable cable-tool rig noted: Mounted on this framework (A) are the boiler (B) and the steam engine (C), which drives the belt (D).
Although Benjamin’s design included a boiler and steam engine mounted on the framework, any source of power could be used “independent of the portable boring machine,” he noted in his patent application (no. 548,109). The derrick could be steadied by stay-ropes and the velocity of the shaft controlled by using a band-brake (also see Making Hole — Drilling Technology).

October 15, 1966 – Johnson signs Historic Preservation Act
Recognizing the “spirit and direction of the nation are founded upon and reflected in its historic heritage,” Lyndon Johnson signed into law the National Historic Preservation Act to protect historical and archaeological sites. The Act authorized the Secretary of the Interior to maintain a National Register of Historic Places.
“The historical and cultural foundations of the nation should be preserved as a living part of our community life and development in order to give a sense of orientation to the American people,” the Act proclaimed.
October 15, 1997 – Kerosene fuels Land Speed Record
The current world land speed record was set at 763.035 miles per hour by the Thrust SSC, the British “supersonic car” fueled by a 19th-century petroleum product, kerosene. The vehicle’s twin turbofan engines burned JP-4, a fuel that first powered jet aircraft as early as 1951.
The latest SpaceX Falcon 9 rockets are fueled by highly refined kerosene rocket fuel, which also powered NASA’s Apollo moon launches. Liquefied natural gas fueled the world land speed record held from 1970 to 1983 (see Blue Flame Natural Gas Rocket Car).
October 16, 1931 – Natural Gas Pipeline sets Record
The first long-distance, high-pressure U.S. natural gas pipeline went into service during the Great Depression, linking prolific Texas Panhandle gas fields to consumers in Chicago.
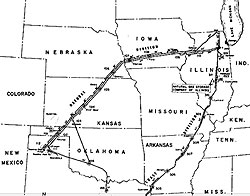
A 1931 natural gas pipeline extended 980 miles from North Texas to Illinois.
A.O. Smith Corporation developed the technology for a thin-walled pipe, and Continental Construction Corporation built the 980-mile bolted flange line for the Natural Gas Pipeline Company of America (NGPL).
The $75 million pipeline consumed 209,000 tons of specially fabricated 24-inch wide steel pipe, which filled 6,500 freight cars. The project required 2,600 separate right-of-way leases (also see Big Inch Pipelines of WWII).

October 17, 1890 – Union Oil of California founded
Lyman Stewart, Thomas Bard and Wallace Hardison founded the Union Oil Company of California by merging their petroleum properties to compete with Standard Oil of California, founded 20 years earlier. Union Oil made strategic alliances with smaller oil companies to build pipelines from Kern County oilfields to the Pacific Coast.
“This gave the independent producers an alternative to what they perceived as the low prices paid by Standard Oil and the high freight rates charged by the railroads to move crude oil,” noted the American Institute of Mining in 1914. Union Oil moved the company headquarters from Santa Paula to Los Angeles in 1901.
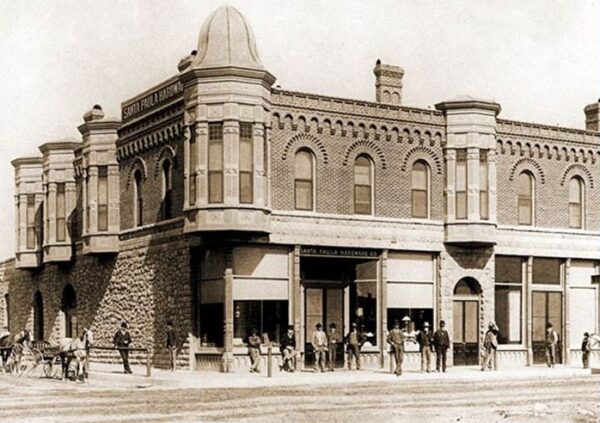

After becoming the Union Oil Museum in 1950, the company’s Santa Paula headquarters building in 1990 was restored to its original appearance and reopened as the California Oil Museum.
In 1910, Union Oil lost control of its Midway-Sunset field’s Lakeview No. 1 well, which would take 18 months to control. The purchase of Pennsylvania-based Pure Oil in 1965 made the Unocal Union 76 brand a nationwide company. Chevron acquired Unocal in 2005.
Union Oil’s original Santa Paula headquarters building, a California Historical Landmark, became home to the California Oil Museum in 1990.
October 17, 1917 – “Roaring Ranger” launches Texas Drilling Boom
A wildcat well drilled between Abilene and Dallas launched the Texas drilling boom that helped fuel the Allied victory in World War I. The J.H. McCleskey No. 1 well erupted oil about two miles south of the small town of Ranger, which had been founded in the 1870s near a Texas Ranger camp in Eastland County.
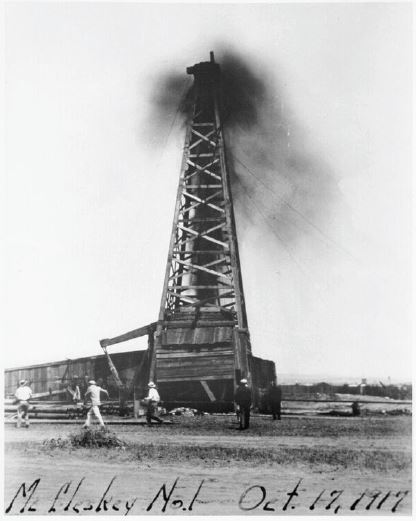

The 1917 McCleskey No. 1 oil gusher in Texas made headlines as the “Roaring Ranger” that helped win World War I.
William Knox Gordon of the Texas and Pacific Coal Company completed the oilfield discovery well at a depth of 3,432 feet. It initially produced 1,600 barrels a day of quality, high-gravity oil. Within 20 months the exploration company’s stock value jumped from $30 a share to $1,250 a share.
“Roaring Ranger” launched a drilling boom that extended to nearby towns. More gushers followed, some producing up to 10,000 barrels of oil every day, and Ranger’s population grew from 1,000 to 30,000.

Eastland County discoveries included oil wells near Cisco, where Conrad Hilton bought his first hotel.
Petroleum proved essential in World War I. After the armistice was signed in 1918, a member of the British War Cabinet declared, “The Allied cause floated to victory upon a wave of oil.”
After the war, a veteran named Conrad Hilton visited Eastland County intending to buy a bank at Cisco. When his deal fell through, Hilton — at the Cisco train station ready to leave — noticed a small hotel with a line of roughnecks waiting for a room (see Oil Boom Brings First Hilton Hotel).
Learn more in “Roaring Ranger” wins WWI.

October 17, 1973 – OPEC Embargo brings Gas Lines, Recession
Fifty years ago, the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) implemented what it called “oil diplomacy,” prohibiting any nation that had supported Israel in the Yom Kippur War from buying the cartel’s oil. The embargo brought an end to years of cheap gasoline and caused the New York Stock Exchange to drop by almost $100 billion. It also created one of the worst recessions in U.S. history. The United States became the world’s top petroleum producer in 2017, surpassing Russia and Saudi Arabia.
October 18, 2008 – Derrick dedicated at First Oklahoma Well
A re-enactment of the dramatic moment that changed Oklahoma history highlighted the 2008 dedication of a 84-foot replica derrick at Discovery 1 Park in Bartlesville, Oklahoma. Events included roughneck reenactors and a water gusher from an 84-foot derrick that replaced one dedicated in 1948.
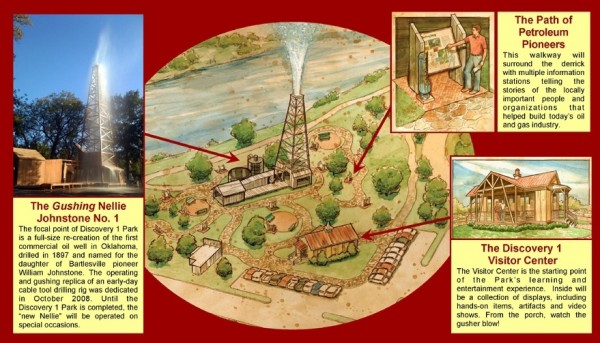
Discovery 1 Park in Bartlesville includes a replica derrick on the original site of Oklahoma’s first oil well.
In 1897, a cable-tool drilling rig at the site of Oklahoma’s first commercial oil well had thrilled another group of spectators when Jenny Cass, stepdaughter of Bartlesville founder George W. Keeler, was given the honor of “shooting” the well in what today is Discovery 1 Park.
October 19, 1990 – First Emergency Use of Strategic Petroleum Reserve
As world oil prices spiked after the August 1990 invasion of Kuwait by Saddam Hussein’s Iraqi troops, the first presidentially mandated emergency use of the Strategic Petroleum Reserve was authorized by George H. W. Bush, who ordered the sale of five million barrels of SPR oil as a test to “demonstrate the readiness of the system under real life conditions,” according to the Department of Energy.
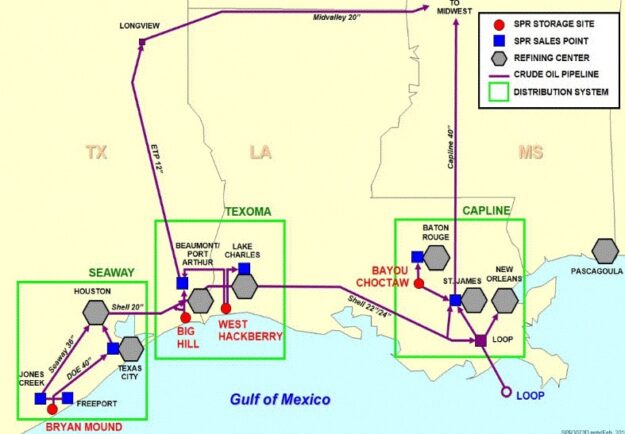
The Strategic Petroleum Reserve’s four oil storage facilities are grouped into three geographical pipeline distribution systems
in Texas and Louisiana. Map courtesy U.S. Department of Energy, Report to Congress, December 2018.
President Ford established the SPR in 1975 as a protection against severe supply interruptions. By 2020, four underground salt dome sites along the Gulf Coast stored 735 million barrels of oil — the largest stockpile of government-owned emergency oil in the world.
October 20, 1924 – First Tubular Goods Standards
Shortages of equipment and drilling delays during World War I revealed the petroleum industry’s struggle with a lack of uniformity of pipe sizes, threads and coupling. Founded in 1919, the American Petroleum Industry (API) gathered experts to develop industry-wide standards to promote equipment compatibility. “After bringing these experts together to agree upon design and requirements, the first standard Specifications for Steel and Iron Pipe for Oil Country Tubular Goods was published on October 20, 1924,” notes API, which has since published more than 800 standards and guidelines.
October 20, 1944 – Liquefied Natural Gas Tank explosion in Ohio
An explosion and fire from liquefied natural gas tanks in Cleveland, Ohio, killed 131 people and caused more than $10 million in damage. Temperatures inside of one of the East Ohio Gas Company’s tanks had been allowed to fall below minus 250 degrees, which caused the steel plates to contract and rupture. Investigators never discovered a cause for the explosion, but witnesses reported a leak in one of the tanks, according to Ohio History Central. “Some spark must have then ignited the gas, although, with World War II currently raging, some residents initially suspected a German saboteur.”

October 20, 1949 – Maryland produces Some Natural Gas
The first commercially successful natural gas well in Maryland was drilled by the Cumberland Allegheny Gas Company in the town of Mountain Lake Park, Garrett County. The Elmer Beachy well produced about 500 thousand cubic feet of natural gas per day.
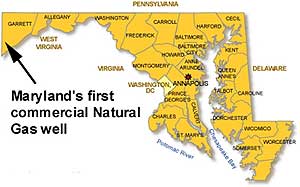
No oil has been produced in Maryland.
The discovery well prompted a rush of competing companies and high-density drilling (an average of nine wells per acre), which depleted the field. Twenty of 29 wells drilled within the town produced natural gas, but overall production from the field was low. No oil has been found in Maryland.
_______________________
Recommended Reading: Early Texas Oil: A Photographic History, 1866-1936 (2000); Oil and Gas Pipeline Fundamentals
(2000); Oil and Gas Pipeline Fundamentals (1993); The 76 bonanza: The fabulous life and times of the Union Oil Company of California
(1993); The 76 bonanza: The fabulous life and times of the Union Oil Company of California (1966); Ranger, Images of America
(1966); Ranger, Images of America (2010); Desert Kingdoms to Global Powers: The Rise of the Arab Gulf
(2010); Desert Kingdoms to Global Powers: The Rise of the Arab Gulf (2016); Bartlesville, Oklahoma, Postcard History Series
(2016); Bartlesville, Oklahoma, Postcard History Series  (2000); The Extraction State, A History of Natural Gas in America (2021). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(2000); The Extraction State, A History of Natural Gas in America (2021). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Please become an AOGHS annual supporter and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2024 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
by Bruce Wells | Oct 7, 2024 | This Week in Petroleum History
October 7, 1859 – First U.S. Oil Well catches Fire –
The wooden derrick and engine house of America’s first oil well erupted in flames along Oil Creek at Titusville, Pennsylvania. The well had been completed the previous August by Edwin L. Drake for George Bissell and the Seneca Oil Company of New Haven, Connecticut. Working with driller William “Uncle Billy” Smith, Drake used steam-powered cable-tool technology.
The first U.S. oil well fire began when Uncle Billy inspected a vat of oil with an open lamp. When the lamp’s flame set gases alight, the conflagration consumed the derrick, the stored oil, and the driller’s home. Drake and Seneca Oil Company would quickly rebuild at the already famous well site.
Learn more in First Oil Well Fire.

October 8, 1915 – Elk Basin oilfield discovered in Wyoming
An exploratory well drilled in a remote Wyoming valley opened the giant Elk Basin oilfield. Completed by the Midwest Refining Company near the Montana border, the wildcat well produced 150 barrels of high-grade “light oil” a day. The oil needed little refining to provide quality lubricants.

“Gusher coming in, south rim of the Elk Basin field, 1917.” Photo courtesy American Heritage Center, University of Wyoming.
Geologist George Ketchum first recognized the potential of the basin as a source of oil deposits. Ketchum had explored the remote area in 1906 with C.A. Fisher while farming near Cowley, Wyoming. The Elk Basin extended from Carbon County, Montana, into northeastern Park County, Wyoming.
Fisher was the first geologist to map sections of the Bighorn Basin southeast of Cody, Wyoming, where oil seeps had been found as early as 1883. The Wyoming oilfield discovery in unproved territory attracted new ventures like Elk Basin United Oil Company, investors, and oilfield service companies.
Learn more in First Wyoming Oil Wells.

October 8, 1923 – First International Petroleum Exposition and Congress
Five thousand visitors attended the rainy opening day of the first International Petroleum Exposition and Congress in downtown Tulsa, an event that would return for almost six decades.

Although still a tourist attraction, the 76-foot-tall Golden Driller arrived decades after Tulsa’s first International Petroleum Exposition in 1923.
With annual attendance growing to more than 120,000, Mid-Continent Supply Company of Fort Worth introduced the original Golden Driller of Tulsa at the expo in 1953. Economic shocks beginning with the 1973 OPEC oil embargo depressed the industry and after 57 years, the International Petroleum Exposition ended in 1979.
October 9, 1999 – Converted Offshore Platform launches Rocket
Sea Launch, a Boeing-led consortium of companies from the United States, Russia, Ukraine and Norway, launched its first commercial rocket using the Ocean Odyssey, a modified semi-submersible drilling platform. After a demonstration flight in March, a Russian Zenit-3SL rocket carried a DirecTV satellite to geostationary orbit.

Ocean Odyssey, a modified semi-submersible drilling platform, became the world’s first floating equatorial launch pad in 1999. Photo courtesy Sea Launch.
In 1988, the former drilling platform had been used by Atlantic Richfield Company (ARCO) for North Sea explorations. The Ocean Odyssey made 36 more rocket launches until 2014, when the consortium ended after Russia illegally annexed Ukraine’s Crimean peninsula.
Learn more in Offshore Rocket Launcher.

October 10, 1865 – Oil Pipeline constructed in Pennsylvania
A two-inch iron pipeline began transporting oil five miles through hilly terrain from a well at booming Pithole, Pennsylvania, to the Miller Farm Railroad Station at Oil Creek. With their livelihoods threatened, teamsters attempted to sabotage the pipeline, until armed guards intervened. A second oil pipeline would begin operating in December.
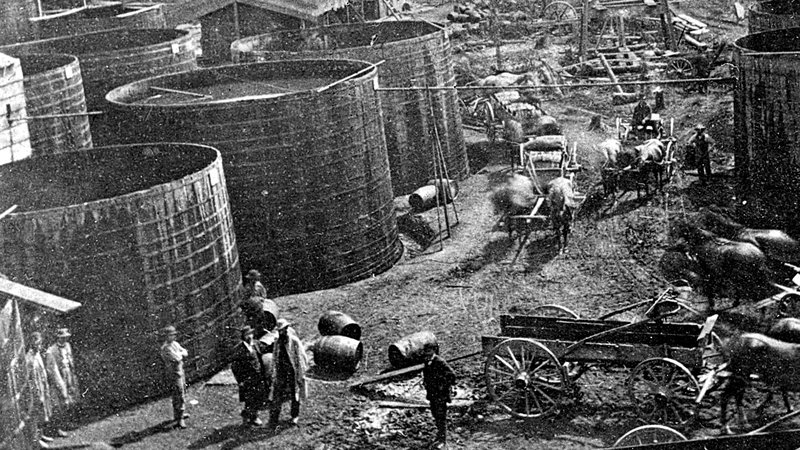

Oil tanks at the boom town of Pithole, Pennsylvania, where Samuel Van Syckel built a five-mile pipeline in 1865. Photo courtesy Drake Well Museum.
Built by Samuel Van Syckel, who had formed the Oil Transportation Association, the pipeline used 15-foot welded joints. Three 10-horsepower Reed and Cogswell steam pumps pushed the oil at a rate of 81 barrels per hour. With up to 2,000 barrels of oil arriving daily at the terminal, more storage tanks were soon added. The pipeline transported the equivalent of 300 teamster wagons working for 10 hours.
“The day that the Van Syckel pipeline began to run oil a revolution began in the business,” proclaimed Ida Tarbell in her 1904 History of the Standard Oil Company. “After the Drake well, it is the most important event in the history of the Oil Regions.”
October 13, 1917 – U.S. Oil & Gas Association founded
The United States Oil & Gas Association was founded as the Mid-Continent Oil & Gas Association in Tulsa, Oklahoma, six months after the United States entered World War I. Independent producers Frank Phillips, E.W. Marland, Bill Skelly, Robert Kerr and others established the association to help increase petroleum supplies for the Allies. In 1919, the association formed an Oklahoma-Kansas Division, now the Petroleum Alliance of Oklahoma.

October 13, 1954 – First Arizona Gas Well
After decades of searching for oil, Arizona became the 30th petroleum-producing state when Shell Oil Company completed a natural gas well one mile south of the Utah border on Apache County’s Navajo Indian Reservation. The East Boundary Butte No. 2 well indicated gas production of about 3 million cubic feet per day from depths between 4,540 feet to 4,690 feet, but just a few barrels of oil a day.
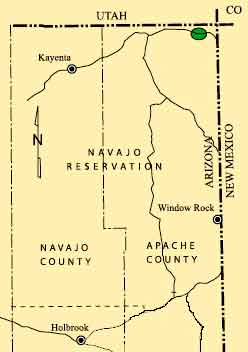
Arizona produces oil only from Apache County.
A rancher had reported finding natural oil seeps in central Arizona in the late 1890s, and by 1902, a part-time prospector from Pennsylvania, Joseph Heslet, began a lengthy exploration effort that ended in 1916 after finding traces of oil.
Arizona’s oil production declined after 2015, occasionally reaching 1,000 barrels of crude oil per month. There were no significant proven reserves by 2023, and the state’s few oil wells produced only about 6,000 barrels of oil, according to the Energy Information Administration (EIA).
Learn more in First Arizona Oil and Gas Wells.
_______________________
Recommended Reading: Myth, Legend, Reality: Edwin Laurentine Drake and the Early Oil Industry (2009); Black Gold, Patterns in the Development of Wyoming’s Oil Industry (1997); Tulsa Where the Streets Were Paved With Gold – Images of America
(2009); Black Gold, Patterns in the Development of Wyoming’s Oil Industry (1997); Tulsa Where the Streets Were Paved With Gold – Images of America (2000); Offshore Pioneers: Brown & Root and the History of Offshore Oil and Gas
(2000); Offshore Pioneers: Brown & Root and the History of Offshore Oil and Gas (1997); Western Pennsylvania’s Oil Heritage
(1997); Western Pennsylvania’s Oil Heritage (2008); Oil and Gas Pipeline Fundamentals
(2008); Oil and Gas Pipeline Fundamentals (1993); Arizona Rocks & Minerals: A Field Guide to the Grand Canyon State
(1993); Arizona Rocks & Minerals: A Field Guide to the Grand Canyon State (2010). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(2010). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Please become an AOGHS annual supporter and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2024 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.
by Bruce Wells | Sep 30, 2024 | This Week in Petroleum History
September 30, 2006 – Roughnecks Statue dedicated at Signal Hill –
A bronze “Tribute to the Roughnecks” statue was dedicated near the Alamitos No. 1 well, which in 1921 revealed California’s prolific Long Beach oilfield 20 miles south of Los Angeles.

Signal Hill once had so many derricks people called it Porcupine Hill. The city of Long Beach is visible in the distance from the “Tribute to the Roughnecks” statue by Cindy Jackson.
The statue by Cindy Jackson has since commemorated the Signal Hill Oil Boom, serving as “a tribute to the petroleum pioneers for their success here, a success which has, by aiding in the growth and expansion of the petroleum industry, contributed so much to the welfare of mankind.”

October 1, 1908 – Ford Motor Company produces First Model T
The first production Ford Model T rolled off the assembly line in Detroit. Between 1908 and 1927, Ford built about 15 million more, each fueled by inexpensive gasoline. The popularity of the Model T was timely for the U.S. petroleum industry, which faced falling demand for kerosene as consumers switched to electric lighting.

Ford Model T tires were white until 1910, when the petroleum product carbon black was added to improve durability.
New major oilfield discoveries, especially the 1901 “Lucas Gusher” at Spindletop Hill near Beaumont, Texas, helped meet growing demand for what had been a refining byproduct, gasoline.
October 1, 1942 – Water Injection begins in East Texas
The East Texas Salt Water Disposal Company drilled the first saltwater injection well in the 12-year-old East Texas oilfield near the towns of Tyler, Longview, and Kilgore. As early as 1929, the Federal Bureau of Mines had determined injecting recovered saltwater into formations could increase reservoir pressures and oil production.
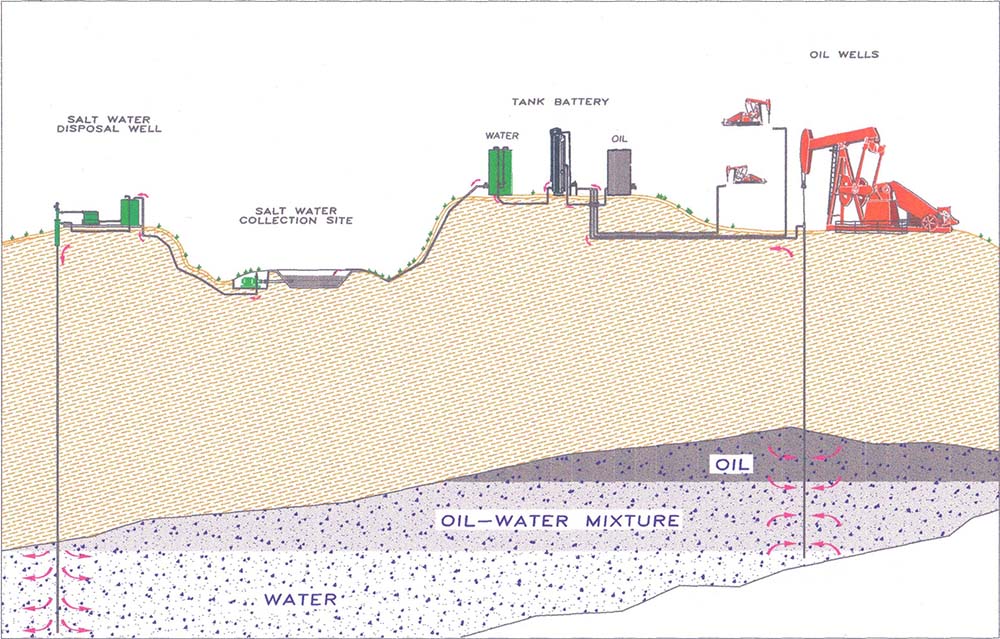
Saltwater injection wells have improved oil production. By disposing produced water at a low cost, marginal East Texas wells have remained viable. Illustration courtesy East Texas Salt Water Disposal Company.
The Texas Railroad Commission established the saltwater disposal company as a public utility to operate in the oilfield. The company treated and re-injected about 1.5 billion barrels of saltwater in its first 13 years, prompting the commission to proclaim saltwater injection as the “greatest oil conservation project in history.”
October 2, 1919 – Future “Mr. Tulsa” incorporates Skelly Oil
Skelly Oil Company incorporated in Tulsa, Oklahoma, with founder William Grove Skelly as president. He had been born in 1878 in Erie, Pennsylvania, where his father hauled oilfield equipment in a horse-drawn wagon.

Born near Pennsylvania’s early oilfields, independent oilman William Skelly’s company helped make Tulsa the “Oil Capital of the World.”
Skelly’s success in the El Dorado oilfield east of Wichita, Kansas, helped him launch Skelly Oil and other ventures, including Midland Refining Company, which he founded in 1917. As Tulsa promoted itself as “Oil Capital of the World,” Skelly became known as “Mr. Tulsa.”
Skelly served as president of Tulsa’s famous International Petroleum Exposition for 32 years until his death in 1957.

October 3, 1930 – East Texas Oilfield discovered on Widow’s Farm
With a crowd of more than 4,000 expectant landowners, leaseholders, creditors, and others watching, the Daisy Bradford No. 3 wildcat well was successfully shot with nitroglycerin near Kilgore, Texas.
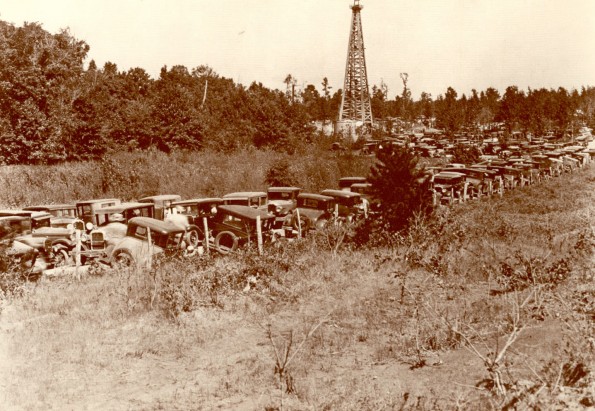

Spectators gathered on the widow Daisy Bradford’s farm near Kilgore, Texas, to watch the October 3, 1930, “shooting” of the discovery well of what proved to be the largest oilfield in the lower 48 states. Photo courtesy Jack Elder, The Glory Days.
“All of East Texas waited expectantly while Columbus ‘Dad’ Joiner inched his way toward oil,” explained historian Jack Elder in 1986. “Thousands crowded their way to the site of Daisy Bradford No. 3, hoping to be there when and if oil gushed from the well to wash away the misery of the Great Depression.”
Geologists were stunned when it became apparent the remote wildcat well on the widow Daisy Bradford’s farm — along with two other wells far to the north — were part of the same oil-producing formation (the Woodbine) that encompassed more than 140,000 acres. The “Black Giant” would produce billions of barrels of oil in coming decades.
Learn more in East Texas Oilfield Discovery.
October 3, 1980 – Museum opens in East Texas Oilfield
Fifty years after the discovery of the East Texas oilfield, the East Texas Oil Museum at Kilgore College opened as “a tribute to the independent oil producers and wildcatters, the men and women who dared to dream as they pursued the fruits of free enterprise.”

The East Texas Oil Museum since 1980 has hosted events and maintained exhibits preserving the “Black Giant” oilfield discovered during the Great Depression. Photos by Bruce Wells.
Established with funding from the Hunt Oil Company, the museum at Kilgore College recreated a 1930s boom town atmosphere.

October 4, 1866 – Oil Fever spreads to Allegheny River Valley
Just 15 miles east of Titusville, Pennsylvania, site of the first U.S. oil well, an oilfield discovery at Triumph Hill sparked another wild rush of speculators and new drilling. America’s petroleum industry was barely seven years old when wooden cable-tool derricks and engine houses replaced hemlock trees along the Allegheny River.
Learn more about post-Civil War oil boom towns in Derricks of Triumph Hill.
October 4, 1901 – Drake Memorial dedicated in Pennsylvania
More than 2,500 people, including his widow, Laura Dowd Drake, attended the unveiling of a monument to the “father of the petroleum industry,” Edwin L. Drake, who had died in relative obscurity 1880. Standard Oil Company executive Henry Rogers commissioned the marble, semi-circle memorial in Titusville, Pennsylvania.
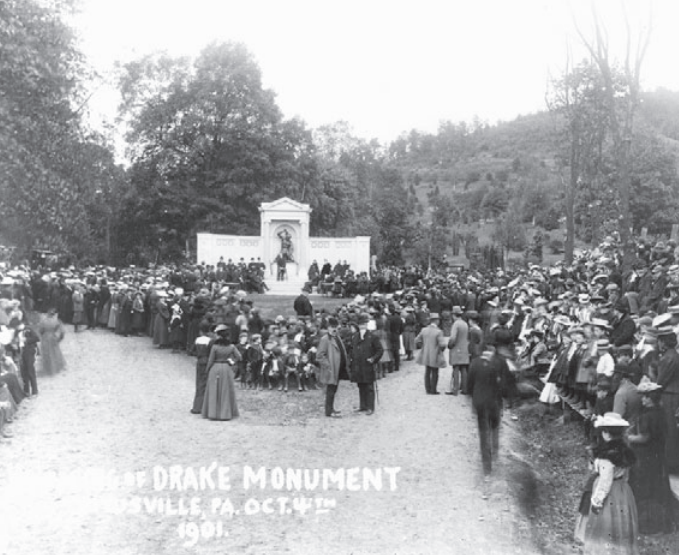

Unveiling of Drake Monument, Titusville, PA. Oct. 4th 1901. Thousands attended the dedication in Woodlawn Cemetery. Photo by John Mather courtesy Drake Well Museum.
The monument, which includes a bronze statue by Charles Henry Niehaus, was dedicated in Woodlawn Cemetery. Learn more by visiting Titusville’s Drake Well Museum and Park.

October 5, 1915 – Science of Petroleum Geology reveals Oilfield
Using the new earth science of petroleum geology for finding oil led to discovery of the giant Mid-Continent field in central Kansas. Drilled by Wichita Natural Gas Company, a subsidiary of Cities Service Company, the well revealed the 34-square-mile El Dorado oilfield.

The Stapleton No. 1 well discovered the El Dorado, Kansas, oilfield, which became one of the largest producing fields in the world. By 1919, Butler County had more than 1,800 producing oil wells. Photo by Bruce Wells.
“Pioneers named El Dorado, Kansas, in 1857 for the beauty of the site and the promise of future riches but not until 58 years later was black rather than mythical yellow gold discovered when the Stapleton No. 1 oil well came in on October 5, 1915,” explained geologist Lawrence Skelton in 1997.
The Stapleton No. 1 well east of Wichita initially found oil at a depth of 600 feet before being deepened to 2,500 feet to produce 110 barrels of oil a day from the Wilcox sands. Natural gas discoveries one year earlier at nearby Augusta had prompted El Dorado civic leaders to seek their own geological study.

The Stapleton No. 1 well and the Kansas Oil Museum preserve a 1915 oil discovery. Photo by Bruce Wells.
The Kansas Oil Museum preserves the state’s petroleum heritage with historic oilfield equipment displayed on 10 acres east of the city. Museum exhibits describe how lessons from the El Dorado field helped launch petroleum geology as a profession while establishing El Dorado as a center for refining.
Learn more in the Kansas Oil Boom.
October 5, 1958 – Water Park opens in West Texas for a Day
A water park inside a Depression-Era experimental concrete oil tank opened to public in West Texas. The day’s festivities at Monahans attracted swimmers, boaters, anglers, and even water skiers to the massive, manmade lake — before leaks at the seams forced it to close the next day.
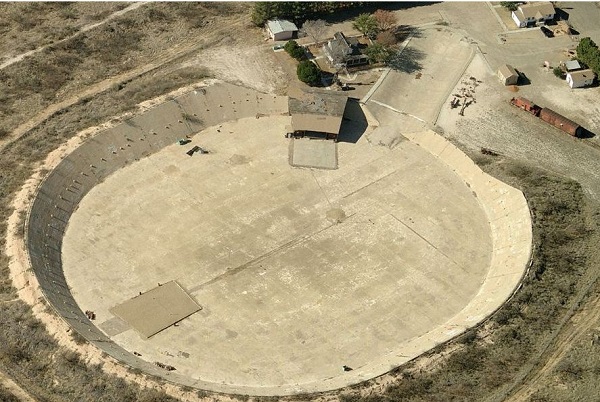

The Million Barrel Museum’s site was originally built to store Permian Basin oil. For scale, note the railroad car and caboose exhibit at upper right.
A local couple had attempted to find a good use for the 525-foot by 422-foot “million barrel reservoir” once covered by a redwood dome roof. The concrete tank had been completed in 1928 by Shell Oil due to a lack of pipelines for Permian Basin oil. Shell stopped using the tank because of the company could not prevent oil from leaking at the seams.
Learn more in Million Barrel Museum.

October 6, 1886 – Natural Gas fuels Glass Manufacturing
A 900-foot-deep natural gas well in a cornfield near Kokomo, Indiana, helped establish the Indiana Natural Gas Company and the Opalescent Glass Works, now Kokomo Opalescent Glass, which has been in continuous operation since 1888.
Although the glass company almost went bankrupt when natural gas supplies dwindled, it recovered and in 1893 sold thousands of pounds of stained glass to Tiffany Glass Company and electric insulators to Edison General Electric. Indiana’s first natural gas well had been drilled in 1867 seeking oil (see Indiana Natural Gas Boom).
_______________________
Recommended Reading: Signal Hill, California – Images of America (2006); From Here to Obscurity: An Illustrated History of the Model T Ford, 1909 – 1927
(2006); From Here to Obscurity: An Illustrated History of the Model T Ford, 1909 – 1927 (1971); Artificial Lift-down Hole Pumping Systems
(1971); Artificial Lift-down Hole Pumping Systems (1984); An adventure called Skelly: A history of Skelly Oil Company through fifty years, 1919-1969 (1970); The Black Giant: A History of the East Texas Oil Field and Oil Industry Skullduggery & Trivia
(1984); An adventure called Skelly: A history of Skelly Oil Company through fifty years, 1919-1969 (1970); The Black Giant: A History of the East Texas Oil Field and Oil Industry Skullduggery & Trivia (2003); Early Texas Oil: A Photographic History, 1866-1936
(2003); Early Texas Oil: A Photographic History, 1866-1936 (2000); Western Pennsylvania’s Oil Heritage
(2000); Western Pennsylvania’s Oil Heritage (2008); The fire in the rock: A history of the oil and gas industry in Kansas, 1855-1976
(2008); The fire in the rock: A history of the oil and gas industry in Kansas, 1855-1976 (1976); Chronicles of an Oil Boom: Unlocking the Permian Basin
(1976); Chronicles of an Oil Boom: Unlocking the Permian Basin (2014). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(2014). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Please become an AOGHS annual supporter and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2024 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.








(2015); Wildcatters: Texas Independent Oilmen
(1984); Holy Toledo: Religion and Politics in the Life of “Golden Rule” Jones
(1998); The Bradford Oil Refinery, Pennsylvania, Images of America
(2006); Early Texas Oil: A Photographic History, 1866-1936
(2000); The Lincoln Highway: Coast to Coast from Times Square to the Golden Gate
(2011); Oil on the Brain: Petroleum’s Long, Strange Trip to Your Tank
(2008); The Extraction State, A History of Natural Gas in America (2021); A History of the New York International Auto Show: 1900-2000
(2000). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.






































