by Bruce Wells | Apr 21, 2025 | This Week in Petroleum History
April 21, 1967 – GM celebrates its 100 Millionth Car –
General Motors celebrated its 100 millionth American-made car (a two-door Chevrolet Caprice). Founded in 1908 by William Durant, the Flint, Michigan, company began as a manufacturer of horse-drawn carriages. After leaving GM, Durant and partner Louis Chevrolet founded the Chevrolet Motor Company in 1911, which became part of GM five years later.
After World War II, GM was the first American corporation to pay more than $1 billion in taxes, according to the Detroit Historical Society, which also notes the company declared bankruptcy in 2009 and emerged less than 40 days later after a federal bailout that saved more than a million jobs. (more…)
by Bruce Wells | Jan 20, 2025 | This Week in Petroleum History
January 20, 1886 – Great Karg Well erupts Natural Gas in Ohio –
A well drilled for oil near Findlay, Ohio, erupted natural gas flowing at 12 million cubic feet per day from pressure that could not be controlled by technologies of the day. The “Great Karg Well” ignited into a flame that burned for four months and became a Findlay tourist attraction. Eight years earlier, a gas well in Pennsylvania had made similar headlines (see Natural Gas is King in Pittsburgh).

A plaque dedicated in 1937 at Findlay, Ohio, commemorated the state’s 1886 giant natural gas discovery.
Although Ohio’s first natural gas well was drilled in 1884 by the Findlay Natural Gas Company, the Karg well launched a gas-drilling boom that attracted manufacturing industries. Glass works companies were lured by the inexpensive gas (also see Indiana Natural Gas Boom), and new businesses included eight window glass factories, two bottle, two chimney lamp, one light bulb, one novelty, and five for tableware.
By 1887, Findlay was known as the “City of Light,” according to a historical marker erected in 1987 at the first field office of the Ohio Oil Company, which adopted the name Marathon Oil in 1962. The Hancock Historical Museum has preserved Great Karg Well history less than two miles from the well site.
January 21, 1865 – Testing the Roberts Torpedo
Civil War veteran Col. Edward A.L. Roberts (1829-1881) conducted his first experiment to increase oil production by using an explosive charge deep in the well. Roberts twice detonated eight pounds of black powder 465 feet deep in the bore of the “Ladies Well” on Watson’s Flats south of Titusville, Pennsylvania.

Civil War veteran Col. E.A.L. Roberts demonstrated his oil well “torpedo” south of Titusville, Pennsylvania.
The “shooting” of the well was a success, increasing daily production from a few barrels of oil to more than 40 barrels, according to Pennsylvania Heritage Magazine. By 1870, Roberts’ torpedoes using nitroglycerin became common in oilfields.
In April 1865, Roberts received the first of many patents for his “exploding torpedo,” and one year later the Titusville Morning Herald reported, “Our attention has been called to a series of experiments that have been made in the wells of various localities by Col. Roberts, with his newly patented torpedo. The results have in many cases been astonishing.”

January 22, 1861 – Pennsylvania Stills produce Kerosene
The first U.S. multiple-still oil refinery was brought on-stream one mile south of Titusville, Pennsylvania, by William Barnsdall, who had drilled the second successful well after Edwin Drake’s first U.S. oil discovery. Barnsdall and partners James Parker and W.H. Abbott spent about $15,000 to build six stills for refining kerosene. Equipment was purchased in Pittsburgh and shipped up the Allegheny River to Oil City where a refinery produced two grades of kerosene, white and the less expensive yellow.
January 22, 1910 – Standard Oil of California strikes Oil
Standard Oil Company of California (Socal) drilled its first successful oil well, a gusher in Kern County that initially produced 1,500 barrels of oil a day from the Midway-Sunset field. The discovery came after the 1906 merger of Pacific Coast Oil Company (see First California Oil Well) and Standard Oil Company of Iowa to create Socal.

Standard Oil Company of California (Socal) began in 1879 as the Pacific Coast Oil Company and was renamed Chevron in 1981. Image courtesy Chevron.
The new company needed more oil reserves after it had “stepped up its marketing efforts, particularly in gasoline sales, which nearly doubled between 1906 and 1910,” according to a company history. “Until now, Standard had left the hunt for oil to others.”
The U.S. Supreme Court in 1911 ordered Socal separated from its parent, Standard Oil Company of New Jersey. After absorbing Standard Oil of Kansas in 1961 and making other acquisitions, the California company in 1984 rebranded as Chevron, headquartered in San Ramon.

January 23, 1895 – Standard Oil closes Oil Exchanges
Standard Oil Company of New Jersey’s purchasing agency in Oil City, Pennsylvania, notified independent oil producers it would only buy their oil at a price “as high as the markets of the world will justify” — and not “the price bid on the oil exchange for certificate oil.”

The Oil City, Pennsylvania, Oil Exchange was incorporated in 1874. Three years later, it was the third-largest U.S. financial exchange.
Oil City’s exchange had become the third largest financial exchange of any kind in America, behind New York and San Francisco. But with the Standard Oil Company buying 90 percent of oil production and setting its own price for certificates, all other oil exchanges soon closed.
Learn more in End of Oil Exchanges.
January 23, 1957 – Wham-O launches a New Petroleum Product
Among the earliest mass-produced products made from plastic, the “Frisbee” was introduced by Wham-O Manufacturing Company of California. The polymer toy originated in 1948 when a company called Partners in Plastic sold its “Flyin’ Saucers” for 25 cents each. In 1955, Richard Knerr and Arthur “Spud” Melin’s Wham-O bought the rights.
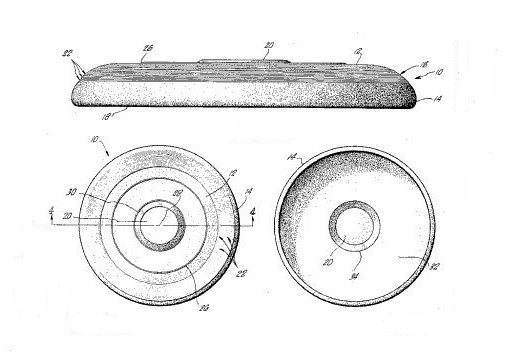
U.S. patent with mold details of a 1967 polyethylene plastic Frisbee.
The Wham-O founders discovered that Phillips Petroleum had invented a high-density polyethylene (called Marlex). They used the new plastic to meet phenomenal demand for manufacturing Frisbees – and Hula Hoops beginning in 1958.
Learn more in Petroleum Product Hoopla.
January 23, 1991 – Gulf War brings World’s Largest Oil Spill
The world’s largest oil spill began in the Persian Gulf when Saddam Hussein’s retreating Iraqi forces opened pipeline valves at oil terminals in Kuwait. About 11 million barrels of oil would cover an area extending 101 miles by 42 miles and reaching five inches thick in some places.
Iraqi soldiers sabotaged Kuwait’s main supertanker loading pier, dumping millions of gallons of oil into the Persian Gulf. By February, about 600 Kuwaiti wells had been set ablaze. It would take months to put out the well fires, with the last extinguished in early April (also see Oilfield Firefighting Technologies).

January 24, 1895 – Independent Producers found Pure Oil
To counter Standard Oil Company’s market dominance, Pennsylvania oil producers, refiners, and pipeline operators organized what would become a major Chicago-based oil venture. Originally based in Pittsburgh, Pure Oil Company quickly grew into the second vertically integrated U.S. petroleum company after Standard Oil.

Ohio Cities Gas acquired Pure Oil in 1920 and kept the popular Pennsylvania brand name.
Beginning in early 1896, Pure Oil marketed its petroleum products by horse-drawn tank wagons in Philadelphia and New York — successfully competing with Standard Oil’s monopoly. The Ohio Cities Gas Company of Columbus acquired Pure Oil and in 1920 adopted the former Pennsylvania venture’s brand name.
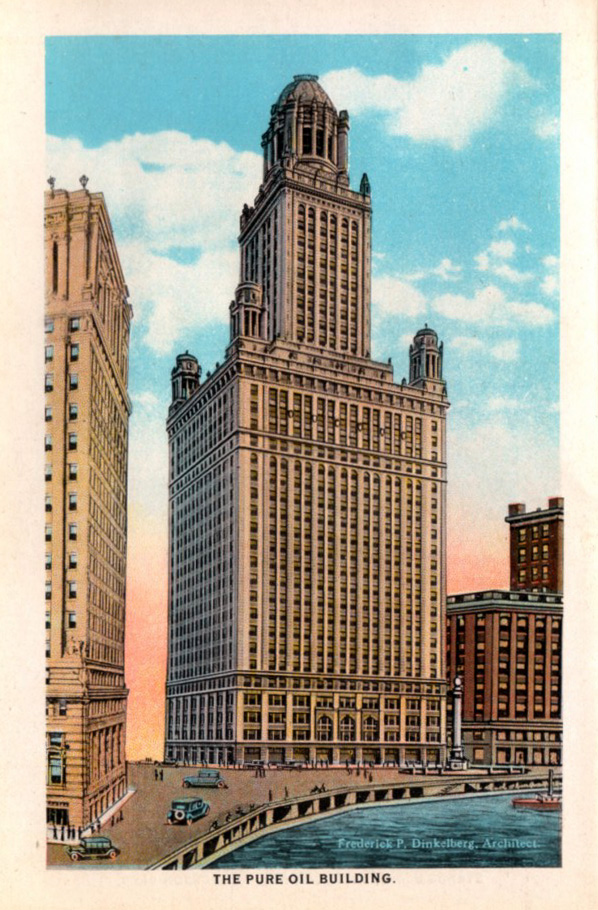

Pure Oil Company moved into its newly built 40-story Chicago headquarters on East Wacker Drive in 1926.
With a new Chicago headquarters opened in 1926, Pure Oil began exploring offshore technologies within a decade. The company developed early freestanding drilling platforms in the Gulf of Mexico.
January 25, 1930 – North Texas Oil Producers form Association
After meeting in Wichita Falls to protest “the recent drastic price cut in crude oil, inaugurated by some of the major purchasing companies,” 50 independent producers organized the North Texas Oil and Gas Association. Other issues included seeking a tariff on foreign oil imports and stopping “hot oil” oilfield thefts. The association merged with the West Central Texas Oil & Gas Association in 1998 to become the Texas Alliance of Energy Producers.

January 26, 1931 – Third Well reveals Extent of East Texas Oilfield
As East Texas farmers struggled to survive the Great Depression, an oil discovery confirmed the existence of a massive oilfield. W.A. “Monty” Moncrief of Fort Worth completed the Lathrop No. 1 well, which produced 7,680 barrels of oil a day from 3,587 feet deep. Geologists at first thought a third oilfield had been found.
Moncrief’s discovery well was 25 miles north of the famous Daisy Bradford No. 3 well of October 1930, drilled by Columbus Marion “Dad” Joiner. It was 15 miles north of the Lou Della Crim No. 1 well, completed at Kilgore three days after Christmas 1930. The 130,000-acre East Texas oilfield would become the largest in the lower 48 states.
Learn more in Moncrief makes East Texas History.
_______________________
Recommended Reading: Myth, Legend, Reality: Edwin Laurentine Drake and the Early Oil Industry (2009); Portrait in Oil: How Ohio Oil Company Grew to Become Marathon
(2009); Portrait in Oil: How Ohio Oil Company Grew to Become Marathon (1962); Ohio Oil and Gas, Images of America
(1962); Ohio Oil and Gas, Images of America (2008); Trek of the Oil Finders: A History of Exploration for Petroleum (1975). Titan: The Life of John D. Rockefeller, Sr.
(2008); Trek of the Oil Finders: A History of Exploration for Petroleum (1975). Titan: The Life of John D. Rockefeller, Sr. (2004); Plastic: The Making of a Synthetic Century
(2004); Plastic: The Making of a Synthetic Century (1996); Against the Fires of Hell: The Environmental Disaster of the Gulf War
(1996); Against the Fires of Hell: The Environmental Disaster of the Gulf War (1992); The Black Giant: A History of the East Texas Oil Field and Oil Industry Skulduggery & Trivia
(1992); The Black Giant: A History of the East Texas Oil Field and Oil Industry Skulduggery & Trivia (2003). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(2003). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Become an AOGHS annual supporting member and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2025 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.










