by Bruce Wells | Mar 31, 2025 | This Week in Petroleum History
March 31, 1919 – Oklahoma’s Other First Oil Well –
The Cherokee-Warren Oil and Gas Company incorporated — taking over the remaining assets of the exploration venture that drilled Oklahoma’s “other first oil well” in Indian Territory. That well, drilled in 1889 but abandoned by the United States Oil and Gas Company, was on a 100,000-acre lease in the Cherokee Nation.
Edward Byrd, a Cherokee by marriage, had found oil seeps southwest of Chelsea in 1882. Two years later the Cherokee Nation authorized his United States Oil and Gas Company, “for the purpose of finding petroleum, or rock oil, and thus increasing the revenue of the Cherokee Nation.”
Learn more in Another First Oklahoma Oil Well.
April 1, 1911 – First Gusher of “Pump Jack Capital of Texas”
South of the Red River border with Oklahoma, near Electra, Texas, the Clayco Oil & Pipe Line Company’s Clayco No. 1 well launched an oil boom that would last decades. “As news of the gusher spread through town, people thought it was an April Fools joke and didn’t take it seriously until they saw for themselves the plume of black oil spewing high into the sky,” noted a local historian. (more…)
by Bruce Wells | Oct 14, 2024 | This Week in Petroleum History
October 14, 1929 – Van Oilfield Discovery East of Dallas –
Pure Oil Company completed its Jarman No. 1 well in Van Zandt County and launched a drilling boom 60 miles east of Dallas. During its first hour, the oilfield discovery well produced 147 barrels of oil from the Woodbine sandstone at a depth of 2,700 feet. Three more wells followed as construction began on a camp for oilfield workers.

This Van Zandt County museum east of Dallas is in a warehouse originally built in 1930 by Pure Oil Company. Photo by Bruce Wells
By April 1930, the Van field produced 20,000 barrels of oil a day as companies adopted advanced production techniques. New pipelines linked the oilfield to the Pure refinery in Beaumont, Texas, and Standard Oil Company’s refinery in Baton Rouge, Louisiana.
Among the Van oilfield’s “Cook Camp” buildings was a sheet-metal warehouse, today home to the Van Area Oil and Historical Museum. Residents celebrate their oilfield’s discovery and the 45th Van Oil Festival will take place on October 19, 2024, in Van City Park.
October 15, 1895 – Patent for a Well Boring Machine
Oscar Benjamin of Lafayette, Louisiana, patented a compact, cable-tool drilling rig. His design for the “Well Boring Machine” used a framework mounted on wheels with a hinged derrick “adapted to swing over in transit.”
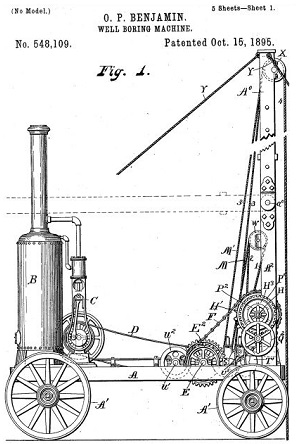
An 1895 patent for a portable cable-tool rig noted: Mounted on this framework (A) are the boiler (B) and the steam engine (C), which drives the belt (D).
Although Benjamin’s design included a boiler and steam engine mounted on the framework, any source of power could be used “independent of the portable boring machine,” he noted in his patent application (no. 548,109). The derrick could be steadied by stay-ropes and the velocity of the shaft controlled by using a band-brake (also see Making Hole — Drilling Technology).

October 15, 1966 – Johnson signs Historic Preservation Act
Recognizing the “spirit and direction of the nation are founded upon and reflected in its historic heritage,” Lyndon Johnson signed into law the National Historic Preservation Act to protect historical and archaeological sites. The Act authorized the Secretary of the Interior to maintain a National Register of Historic Places.
“The historical and cultural foundations of the nation should be preserved as a living part of our community life and development in order to give a sense of orientation to the American people,” the Act proclaimed.
October 15, 1997 – Kerosene fuels Land Speed Record
The current world land speed record was set at 763.035 miles per hour by the Thrust SSC, the British “supersonic car” fueled by a 19th-century petroleum product, kerosene. The vehicle’s twin turbofan engines burned JP-4, a fuel that first powered jet aircraft as early as 1951.
The latest SpaceX Falcon 9 rockets are fueled by highly refined kerosene rocket fuel, which also powered NASA’s Apollo moon launches. Liquefied natural gas fueled the world land speed record held from 1970 to 1983 (see Blue Flame Natural Gas Rocket Car).
October 16, 1931 – Natural Gas Pipeline sets Record
The first long-distance, high-pressure U.S. natural gas pipeline went into service during the Great Depression, linking prolific Texas Panhandle gas fields to consumers in Chicago.
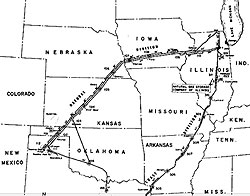
A 1931 natural gas pipeline extended 980 miles from North Texas to Illinois.
A.O. Smith Corporation developed the technology for a thin-walled pipe, and Continental Construction Corporation built the 980-mile bolted flange line for the Natural Gas Pipeline Company of America (NGPL).
The $75 million pipeline consumed 209,000 tons of specially fabricated 24-inch wide steel pipe, which filled 6,500 freight cars. The project required 2,600 separate right-of-way leases (also see Big Inch Pipelines of WWII).

October 17, 1890 – Union Oil of California founded
Lyman Stewart, Thomas Bard and Wallace Hardison founded the Union Oil Company of California by merging their petroleum properties to compete with Standard Oil of California, founded 20 years earlier. Union Oil made strategic alliances with smaller oil companies to build pipelines from Kern County oilfields to the Pacific Coast.
“This gave the independent producers an alternative to what they perceived as the low prices paid by Standard Oil and the high freight rates charged by the railroads to move crude oil,” noted the American Institute of Mining in 1914. Union Oil moved the company headquarters from Santa Paula to Los Angeles in 1901.
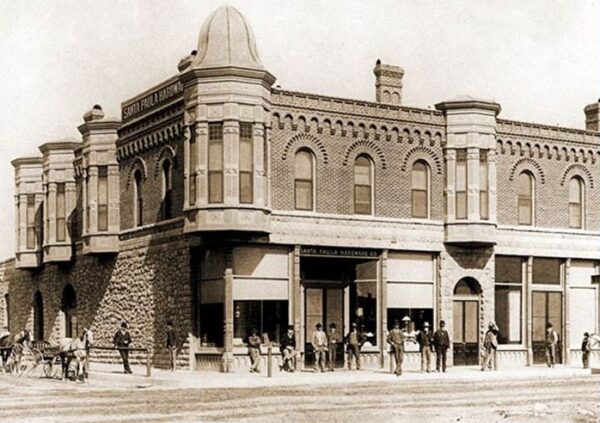

After becoming the Union Oil Museum in 1950, the company’s Santa Paula headquarters building in 1990 was restored to its original appearance and reopened as the California Oil Museum.
In 1910, Union Oil lost control of its Midway-Sunset field’s Lakeview No. 1 well, which would take 18 months to control. The purchase of Pennsylvania-based Pure Oil in 1965 made the Unocal Union 76 brand a nationwide company. Chevron acquired Unocal in 2005.
Union Oil’s original Santa Paula headquarters building, a California Historical Landmark, became home to the California Oil Museum in 1990.
October 17, 1917 – “Roaring Ranger” launches Texas Drilling Boom
A wildcat well drilled between Abilene and Dallas launched the Texas drilling boom that helped fuel the Allied victory in World War I. The J.H. McCleskey No. 1 well erupted oil about two miles south of the small town of Ranger, which had been founded in the 1870s near a Texas Ranger camp in Eastland County.
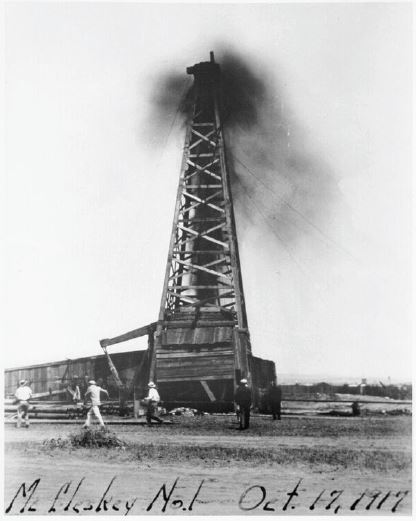

The 1917 McCleskey No. 1 oil gusher in Texas made headlines as the “Roaring Ranger” that helped win World War I.
William Knox Gordon of the Texas and Pacific Coal Company completed the oilfield discovery well at a depth of 3,432 feet. It initially produced 1,600 barrels a day of quality, high-gravity oil. Within 20 months the exploration company’s stock value jumped from $30 a share to $1,250 a share.
“Roaring Ranger” launched a drilling boom that extended to nearby towns. More gushers followed, some producing up to 10,000 barrels of oil every day, and Ranger’s population grew from 1,000 to 30,000.

Eastland County discoveries included oil wells near Cisco, where Conrad Hilton bought his first hotel.
Petroleum proved essential in World War I. After the armistice was signed in 1918, a member of the British War Cabinet declared, “The Allied cause floated to victory upon a wave of oil.”
After the war, a veteran named Conrad Hilton visited Eastland County intending to buy a bank at Cisco. When his deal fell through, Hilton — at the Cisco train station ready to leave — noticed a small hotel with a line of roughnecks waiting for a room (see Oil Boom Brings First Hilton Hotel).
Learn more in “Roaring Ranger” wins WWI.

October 17, 1973 – OPEC Embargo brings Gas Lines, Recession
Fifty years ago, the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) implemented what it called “oil diplomacy,” prohibiting any nation that had supported Israel in the Yom Kippur War from buying the cartel’s oil. The embargo brought an end to years of cheap gasoline and caused the New York Stock Exchange to drop by almost $100 billion. It also created one of the worst recessions in U.S. history. The United States became the world’s top petroleum producer in 2017, surpassing Russia and Saudi Arabia.
October 18, 2008 – Derrick dedicated at First Oklahoma Well
A re-enactment of the dramatic moment that changed Oklahoma history highlighted the 2008 dedication of a 84-foot replica derrick at Discovery 1 Park in Bartlesville, Oklahoma. Events included roughneck reenactors and a water gusher from an 84-foot derrick that replaced one dedicated in 1948.
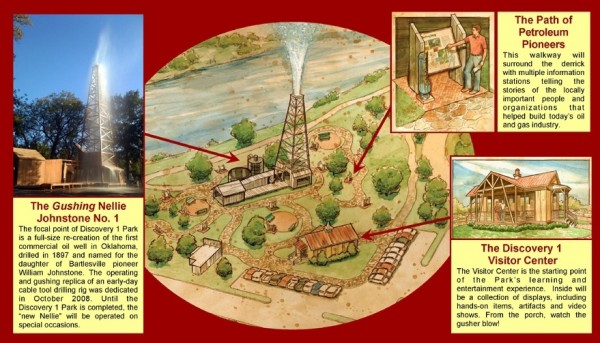
Discovery 1 Park in Bartlesville includes a replica derrick on the original site of Oklahoma’s first oil well.
In 1897, a cable-tool drilling rig at the site of Oklahoma’s first commercial oil well had thrilled another group of spectators when Jenny Cass, stepdaughter of Bartlesville founder George W. Keeler, was given the honor of “shooting” the well in what today is Discovery 1 Park.
October 19, 1990 – First Emergency Use of Strategic Petroleum Reserve
As world oil prices spiked after the August 1990 invasion of Kuwait by Saddam Hussein’s Iraqi troops, the first presidentially mandated emergency use of the Strategic Petroleum Reserve was authorized by George H. W. Bush, who ordered the sale of five million barrels of SPR oil as a test to “demonstrate the readiness of the system under real life conditions,” according to the Department of Energy.
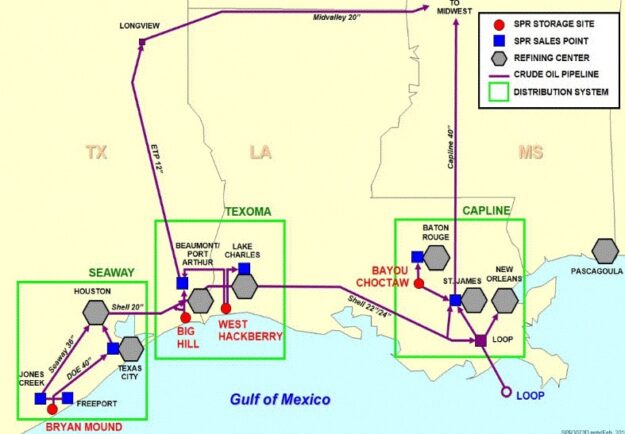
The Strategic Petroleum Reserve’s four oil storage facilities are grouped into three geographical pipeline distribution systems
in Texas and Louisiana. Map courtesy U.S. Department of Energy, Report to Congress, December 2018.
President Ford established the SPR in 1975 as a protection against severe supply interruptions. By 2020, four underground salt dome sites along the Gulf Coast stored 735 million barrels of oil — the largest stockpile of government-owned emergency oil in the world.
October 20, 1924 – First Tubular Goods Standards
Shortages of equipment and drilling delays during World War I revealed the petroleum industry’s struggle with a lack of uniformity of pipe sizes, threads and coupling. Founded in 1919, the American Petroleum Industry (API) gathered experts to develop industry-wide standards to promote equipment compatibility. “After bringing these experts together to agree upon design and requirements, the first standard Specifications for Steel and Iron Pipe for Oil Country Tubular Goods was published on October 20, 1924,” notes API, which has since published more than 800 standards and guidelines.
October 20, 1944 – Liquefied Natural Gas Tank explosion in Ohio
An explosion and fire from liquefied natural gas tanks in Cleveland, Ohio, killed 131 people and caused more than $10 million in damage. Temperatures inside of one of the East Ohio Gas Company’s tanks had been allowed to fall below minus 250 degrees, which caused the steel plates to contract and rupture. Investigators never discovered a cause for the explosion, but witnesses reported a leak in one of the tanks, according to Ohio History Central. “Some spark must have then ignited the gas, although, with World War II currently raging, some residents initially suspected a German saboteur.”

October 20, 1949 – Maryland produces Some Natural Gas
The first commercially successful natural gas well in Maryland was drilled by the Cumberland Allegheny Gas Company in the town of Mountain Lake Park, Garrett County. The Elmer Beachy well produced about 500 thousand cubic feet of natural gas per day.
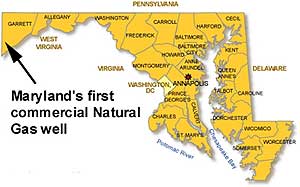
No oil has been produced in Maryland.
The discovery well prompted a rush of competing companies and high-density drilling (an average of nine wells per acre), which depleted the field. Twenty of 29 wells drilled within the town produced natural gas, but overall production from the field was low. No oil has been found in Maryland.
_______________________
Recommended Reading: Early Texas Oil: A Photographic History, 1866-1936 (2000); Oil and Gas Pipeline Fundamentals
(2000); Oil and Gas Pipeline Fundamentals (1993); The 76 bonanza: The fabulous life and times of the Union Oil Company of California
(1993); The 76 bonanza: The fabulous life and times of the Union Oil Company of California (1966); Ranger, Images of America
(1966); Ranger, Images of America (2010); Desert Kingdoms to Global Powers: The Rise of the Arab Gulf
(2010); Desert Kingdoms to Global Powers: The Rise of the Arab Gulf (2016); Bartlesville, Oklahoma, Postcard History Series
(2016); Bartlesville, Oklahoma, Postcard History Series  (2000); The Extraction State, A History of Natural Gas in America (2021). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(2000); The Extraction State, A History of Natural Gas in America (2021). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Please become an AOGHS annual supporter and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2024 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.











