by Bruce Wells | May 15, 2025 | Petroleum Transportation
Famous 1880s New York World reporter took charge of Iron Clad Manufacturing Company.
She was one of the most famous journalists of her day as a reporter for the New York World. Widely known as the remarkable Nellie Bly, Elizabeth J. Cochran Seaman, investigated conditions at an infamous mental institution, made a trip around the world in less than 80 days — and manufactured the first practical 55-gallon oil drum.
The 1901 Pan-American Exposition in Buffalo, N.Y., promoted her Iron Clad Manufacturing Company as “owned exclusively by Nellie Bly – the only woman in the world personally managing industries of such magnitude.”
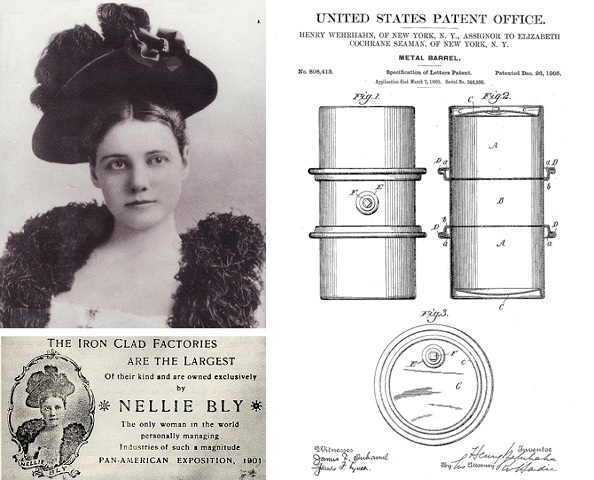
Recognizing the potential of an efficient metal barrel design, Nellie Bly acquired the 1905 patent rights from its inventor, Henry Wehrhahn, who worked at her Iron Clad Manufacturing Company.
(more…)
by Bruce Wells | Jun 23, 2024 | Petroleum Transportation
19th-century coopers made barrels of many capacities: hogsheads, puncheons, tierces, butts and tuns.
Soon after America’s first commercial oil well of 1859, a small group met in northwestern Pennsylvania and decided a 42-gallon wooden barrel was best for transporting their oil.
When filled with oil instead of fish or other commodities, a 42-gallon “tierce” weighed 300 pounds. The 42-gallon oil barrel was officially adopted in 1866. Today, a barrel’s refined products include about 20 gallons of gasoline, 12 gallons of diesel and four gallons of jet fuel (and rocket fuel) and other products, including asphalt.

By the 1860s, barges floated barrels of oil down the Allegheny River to Pittsburgh to be refined into a highly demanded product – kerosene for lamps. Image from an early oil company stock certificate.
In August 1866 a handful of America’s earliest independent oil producers met in Titusville, Pennsylvania, and agreed that henceforth, 42 gallons would constitute a barrel of oil. Pennsylvania led the world in oil production as demand soared for kerosene lamp fuel. (more…)



