by Bruce Wells | May 15, 2025 | Petroleum Transportation
Famous 1880s New York World reporter took charge of Iron Clad Manufacturing Company.
She was one of the most famous journalists of her day as a reporter for the New York World. Widely known as the remarkable Nellie Bly, Elizabeth J. Cochran Seaman, investigated conditions at an infamous mental institution, made a trip around the world in less than 80 days — and manufactured the first practical 55-gallon oil drum.
The 1901 Pan-American Exposition in Buffalo, N.Y., promoted her Iron Clad Manufacturing Company as “owned exclusively by Nellie Bly – the only woman in the world personally managing industries of such magnitude.”
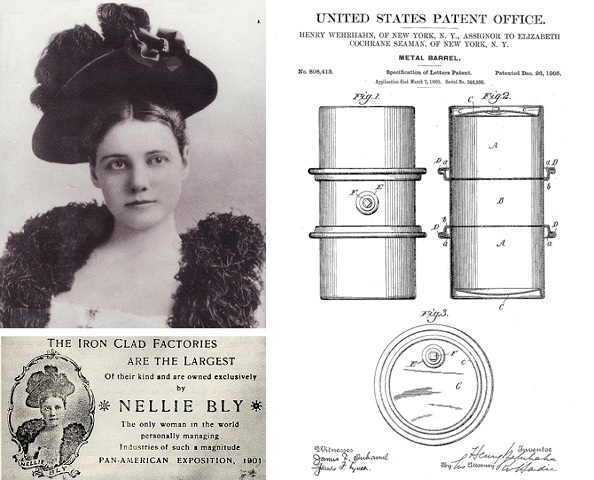
Recognizing the potential of an efficient metal barrel design, Nellie Bly acquired the 1905 patent rights from its inventor, Henry Wehrhahn, who worked at her Iron Clad Manufacturing Company.
(more…)
by Bruce Wells | Dec 23, 2024 | This Week in Petroleum History
December 23, 1919 – Home Gas Heating System –
When most American homeowners were stocking up on wood and coal to heat their homes, Alice H. Parker patented a gas furnace system with adjustable ducts. The 1910 graduate of Howard University described her patent (no. 1,325,905) as a reliable gas-heating furnace, with “individual hot air ducts leading to different parts of the building, so that heating of the various rooms or floors can be regulated as required.”
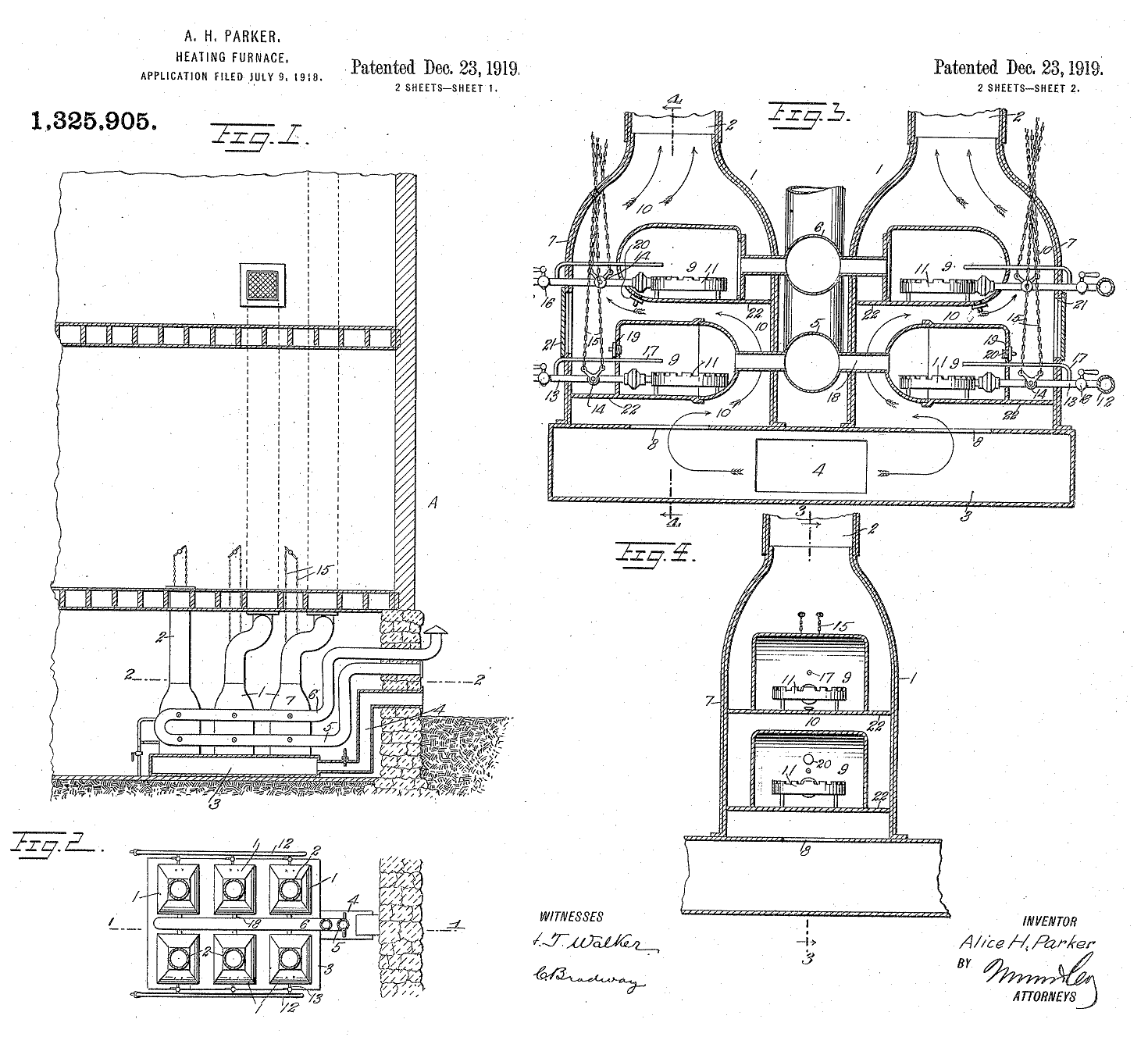
Alice Parker in 1919 patented her design for a gas furnace with adjustable hot air ducts.
Although Parker’s patent was not the first for a gas furnace design, according to Heat Treat Today, “It was unique in that it incorporated a multiple yet individually controlled burner system.” By 1927, more than 250,000 U.S. homeowners were heating with natural gas.

December 23, 1943 – Oilfield discovered in Mississippi
Gulf Oil Company discovered a new Mississippi oilfield at Heidelberg in Jasper County. The company’s surveyors had recognized the geological potential of the area southeast of Jackson as early as 1929, and Gulf Oil used newly developed seismography methods and core drilling technologies to look for oil-bearing formations.

Mississippi’s petroleum industry began with a 1939 oilfield discovery in Yazoo County.
The 1943 discovery well revealed one of the state’s largest oilfields since the Tinsley oil-producing formation in 1939. The first major Mississippi oil well was drilled following a geological survey by a young geologist — who had sought a suitable Yazoo County clay to mold cereal bowls for children. “It all began quite independently of any search for oil,” a historian later explained.
Learn more in the First Mississippi Ol Wells.
December 24, 1997 – Petroleum Products in a Holiday Classic
The TNT network began airing “24 Hours of A Christmas Story,” an annual marathon of an independent film made in 1983. The circa 1940 movie’s popularity — and merchandise sales — led to more marathons on TBS. In addition to the plastic leg lamp with black nylon polymer stocking, another petroleum product featured: a paraffin-based novelty candy.

“A Christmas Story” featured Ralphie, his 4th-grade classmates, and an unusual petroleum product. Photos courtesy MGM Home Entertainment.
Paraffin makes its appearance when Ralphie Parker and his fourth-grade classmates smuggle Wax Fangs into class. An older generation may recall the peculiar disintegrating flavor of Wax Lips, Wax Moustaches, and Wax Bottles. Few realize the candy started in the U.S. oil patch — as did another oilfield paraffin product, Crayola Crayons.
Learn more in the Oleaginous History of Wax Lips.
December 26, 1905 – Nellie Bly’s Ironclad 55-Gallon Metal Barrel
Inventor Henry Wehrhahn of Brooklyn, New York, received two patents that would lead to the modern 55-gallon steel drum. He assigned both to his employer, the famous journalist Nellie Bly, who was president of the Iron Clad Manufacturing Company.
“My invention has for its object to provide a metal barrel which shall be simple and strong in construction and effective and durable in operation,” Wehrhahn noted. After receiving a second patent for detaching and securing a lid, he assigned them to Elizabeth Cochrane Seaman (Nellie Bly), the recent widow of the company’s founder, Robert Seaman.
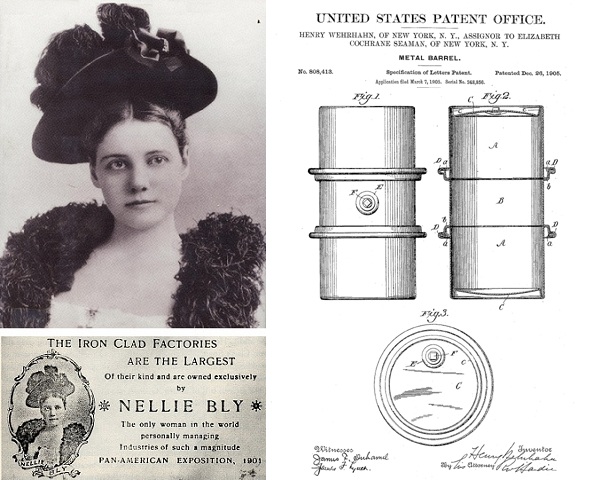
Nellie Bly was assigned a 1905 patent for the “Metal Barrel” by its inventor, Henry Wehrhahn, who worked at her Iron Clad Manufacturing Company.
Well-known as a reporter for the New York World, Bly manufactured early versions of the “Metal Barrel” that would become today’s 55-gallon steel drum. Wehrhahn later became superintendent of a steel tank company in Milwaukee, Wisconsin.
Learn more in the Remarkable Nellie Bly’s Oil Drum.

December 28, 2017 – Smithsonian features Oilfield Nitro Factory
“The True Story of Mrs. Alford’s Nitroglycerin Factory,” proclaimed an article in Smithsonian magazine about the early oil industry. “Mary Alford remains the only woman known to own a dynamite and nitroglycerin factory,” the magazine added about the 19th-century nitroglycerin factory owner. With the Bradford, Pennsylvania, oilfield in 1881 accounting for 83 percent of all U.S. oil production, Mrs. Alford was reported to be “an astute businesswoman in the midst of America’s first billion-dollar oilfield.”
Learn more in Mrs. Alford’s Nitro Factory.
December 28, 1930 – Well reveals extent of East Texas Oilfield
Three days after Christmas, a major oil discovery on the farm of the widow Lou Della Crim of Kilgore revealed the extent of the giant East Texas oilfield. Her son, J. Malcolm Crim, had ignored advice from most geologists and explored about 10 miles north of the field’s discovery well, drilled in October by Columbus “Dad” Joiner on the farm of another widow, Daisy Bradford.
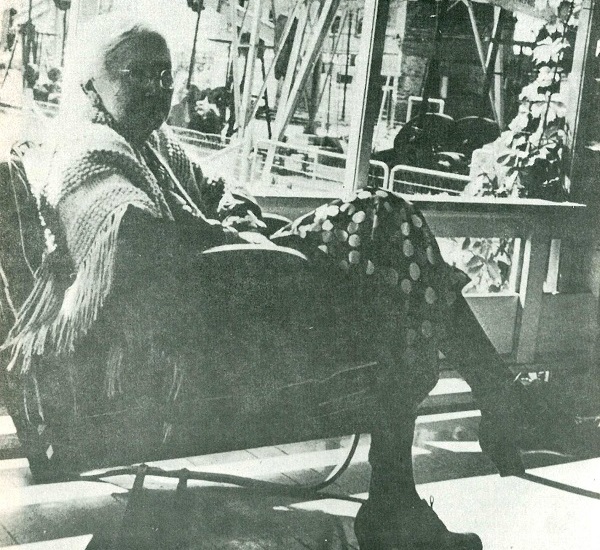

“Mrs. Lou Della Crim sits on the porch of her house and contemplates the three producing wells in her front yard,” notes the caption of this undated photo courtesy Neal Campbell, Words and Pictures.
The Lou Della Crim No. 1 well erupted oil on a Sunday morning while “Mamma” Crim was attending church. The well initially produced 20,000 barrels of oil a day.
One month later and 15 miles farther north, a third wildcat well drilled by Fort Worth wildcatter W.A. “Monty” Moncrief confirmed the true size of the largest oilfield in the continental United States. The East Texas field would encompass more than 480 square miles.
Learn more in Lou Della Crim Revealed.
_______________________
Recommended Reading: Oil in the Deep South: A History of the Oil Business in Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida, 1859-1945 (1993); How Sweet It Is (and Was): The History of Candy (2003); Nellie Bly: Daredevil, Reporter, Feminist
(1993); How Sweet It Is (and Was): The History of Candy (2003); Nellie Bly: Daredevil, Reporter, Feminist (1994); Breaking the Gas Ceiling: Women in the Offshore Oil and Gas Industry (2019); Anomalies, Pioneering Women in Petroleum Geology, 1917-2017 (2017); Images of America: Around Bradford
(1994); Breaking the Gas Ceiling: Women in the Offshore Oil and Gas Industry (2019); Anomalies, Pioneering Women in Petroleum Geology, 1917-2017 (2017); Images of America: Around Bradford (1997); The Black Giant: A History of the East Texas Oil Field
(1997); The Black Giant: A History of the East Texas Oil Field (2003). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
(2003). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Please become an AOGHS annual supporter and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2024 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.








