This Week in Petroleum History: June 23 – 29
June 23, 1921 – Signal Hill brings California Oil Boom –
Another southern California drilling boom began when a geyser of “black gold” erupted 114 feet high at Signal Hill. The Alamitos No. 1 well, which revealed a giant oilfield, produced about 600 barrels of oil a day when it was completed.

The Signal Hill oil discovery helped make California the source of one-quarter of the world’s oil output. “Porcupine Hill” and the Long Beach field produced 260,000 barrels of oil a day by 1923. Photo courtesy of Los Angeles Museum of Natural History.
Soon known as “Porcupine Hill,” the Signal Hill oilfield 20 miles south of Los Angeles produced almost 260,000 barrels of oil a day by 1923. Combined with the 1892 Los Angeles Oilfield discovery and the 1920 Huntington Beach oilfield, California produced one-fourth of the world’s oil. A monument dedicated in 1952 at Signal Hill’s Discovery Well Park has served “as a tribute to the petroleum pioneers for their success here.”
Learn more in Signal Hill Oil Boom.
June 23, 1947 – Supreme Court limits State Rights to Continental Shelf
The U.S. Supreme Court ruled California could not claim rights to the continental shelf beyond three nautical miles. Litigation resulted from President Harry Truman’s September 1945 Continental Shelf Proclamation, which placed control with the federal government. The Supreme Court ruling on the Truman Proclamation affirmed federal jurisdiction “with respect to the natural resources of the subsoil and seabed of the continental shelf.” Similar rulings affecting Louisiana and Texas would be made in 1950.
June 24, 1937 – Traces of Oil found in Minnesota
In far western Minnesota, a remote wildcat well drilled in Traverse County began producing three barrels of oil a day from a depth of 864 feet. The unlikely discovery prompted more leasing, but no commercial quantities of oil.
The lack of an oilfield reaffirmed geologists’ conclusions since 1889 that conditions for significant petroleum deposits did not exist in Minnesota, despite some water wells in southern Minnesota containing small amounts of natural gas.
“Not much oil and gas is obtained from Precambrian rocks, with which Minnesota is very amply blessed,” noted the 1984 book Minnesota’s Geology.
June 25, 1889 – First Oil Tanker catches Fire in California
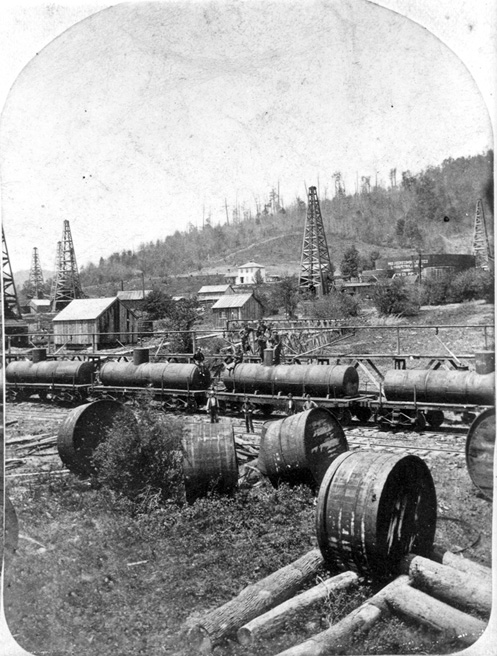
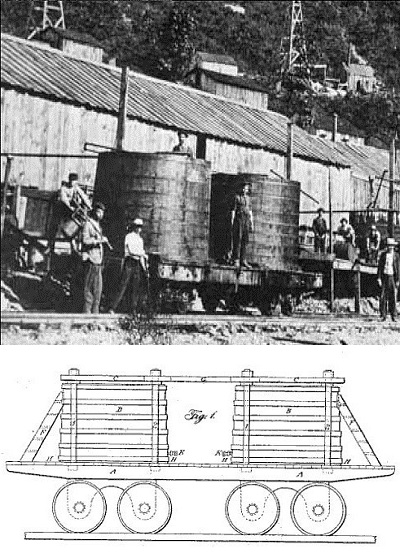
The first oil tanker built for that purpose, a schooner named W.L. Hardison, burned at its wharf in Ventura, California. The Hardison & Stewart Oil Company (later Union Oil) commissioned the experimental vessel, which offered an alternative to paying for railroad oil tank cars charging one dollar per oil barrel to reach markets in San Francisco.
With oil-fired steam boilers and supplemental sails, the schooner could ship up to 6,500 barrels of oil below deck in specially constructed steel tanks. After the fire, the tanks were recovered and used at the company’s Santa Paula refinery. It took 11 years before the company launched a replacement tanker, the Santa Paula.

Rare photographs of the doomed oil tanker W.L. Hardison and Ventura pier courtesy the Museum of Ventura County.
The Ventura Wharf Company by April 1898 had exported 518,204 barrels of bulk oil during the previous year, according to the Los Angeles Times. The pier remained a working wharf until 1936 when it became the longest recreational wooden pier in California.
Designated a Ventura Historic Landmark in 1976 and now 1,600 feet long, California’s oldest pier was refurbished for $2.2 million in 2000, according to the Museum of Ventura County, which also operates archaeological and agricultural museums. In nearby Santa Paula, the 1890 headquarters building of Union Oil Company is home to the California Oil Museum.
June 25, 1901 – Red Fork Discovery leads to Tulsa Boom
Six years before statehood, Oklahoma witnessed a second oil discovery (some say the third — see Another First Oklahoma Oil Well) when two drillers from the Pennsylvania oil regions discovered an oilfield at Red Fork in the Creek Indian Nation.
John Wick and Jesse Heydrick drilled the Sue A. Bland No. 1 well near the Creek village across the Arkansas River from Tulsa. Sue Bland, a Creek citizen, was the wife of homesteader Dr. John C. W. Bland. Their Red Fork well produced just 10 barrels of oil a day from a depth of 550 feet, but created a drilling boom attracting petroleum companies to nearby Tulsa.
Learn more in Red Fork Gusher.
June 25, 1999 – Texas Post Office named Historic Place
The former U.S. Post Office building in Graham, Texas, with its Great Depression-era oilfield mural by Alexandre Hogue, joined the National Register of Historic Places. Hogue’s 1939 “Oil Fields of Graham” has been joined by other art exhibits in its historic Art Deco building on Third Street.

“Oil Fields of Graham” by Alexandre Hogue, a 1939 mural in the Old Post Office Museum & Art Center of Graham, Texas. The white-haired gentleman was the mayor of Graham.
Hogue’s artwork included many southwestern scenes as part of the New Deal Federal Arts Program. His murals on the walls of public buildings often portrayed scenes of the Texas petroleum industry. In Graham’s historic building on Third Street, “Oil Fields of Graham,” 12 feet wide and 7 feet high, is among exhibits at the Old Post Office Museum & Art Center, which opened in 2002.
Learn more in Oil Art of Graham, Texas.
June 26, 1885 – Natural Gas Utility established in Pennsylvania
Peoples Natural Gas Company incorporated — the first Pennsylvania natural gas company chartered by the state to regulate production, transmission, and distribution of natural gas. A similar utility incorporation had taken place a year earlier in New York City when six competing companies combined to form Consolidated Edison.
By 1891, the Pittsburgh-based limited liability company had consolidated pipelines and facilities of Pittsburgh Natural Gas, Lawrence Natural Gas, Conemaugh Gas, and Columbia Natural Gas companies. More than a dozen more companies would be acquired between 1903 and 1961. The large utility added Saxonburg Heat and Light in 1979 and Equitable Gas in 2017, expanding natural gas services in West Virginia and Kentucky.
June 28, 1887 – Kansans celebrate First Natural Gas Jubilee
After erecting flambeau arches at the four corners of the town square, Paola, Kansas, hosted what local leaders described as “the first natural gas celebration ever held in the West.” Excursion trains from Kansas City brought about 2,000 people, “to witness the wonders of natural gas,” according to the Miami County Historical Museum, which preserves the region’s petroleum history.
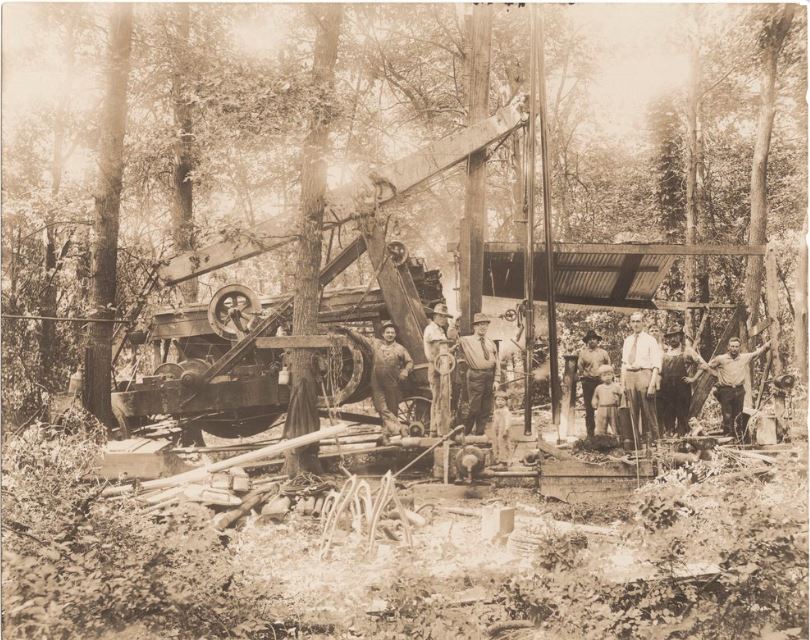

Paola’s giant natural gas field attracted more petroleum exploration to Miami County, including this circa 1920 oil well. Photo courtesy Kansas Historical Society.
The town’s special event included a “grand illumination” of natural gas street lights, where “gas was attached to a yard sprinkler by a rubber hose, and when it was ignited there appeared nests of small blazes which were beautiful and attractive.”
Learn more in First Kansas Oil Well.
June 28, 1967 – Hall of Petroleum opens in Smithsonian Museum
The Hall of Petroleum opened at the Smithsonian Institution’s Museum of History and Technology in Washington, D.C. Exhibits included cable-tool and rotary rig drilling technologies and counterbalanced pumping units, The Hall of Petroleum also featured 1967 developments in offshore exploration and production.
Visitors to what in 1980 became the National Museum of American History were greeted by a mural painted by Delbert Jackson of Tulsa, Oklahoma. Jackson spent two years creating his 13-foot by 56-foot painting with scenes of oil and natural gas exploration, production, refining, and transportation.

A “Panorama of Petroleum” once greeted visitors to the Smithsonian’s American History Museum in Washington, D.C. The 13-foot by 56-foot mural today is exhibited inside Tulsa International Airport.
Jackson’s “Panorama of Petroleum” featured industry pioneers and served as a visual map to the hall’s oilfield technology exhibits. “If the hall can increase the public’s knowledge of and respect for the technical skill and know-how of those who make this energy available, it will have served its purpose,” noted the exhibit’s 1967 catalog. The mural ended up in storage for three decades, until finding a home at Tulsa International Airport.
Learn more in Smithsonian’s “Hall of Petroleum.“
June 29, 1956 – Interstate Highway System enacted
The Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1956, popularly known as the National Interstate and Defense Highways Act, became law. Passed at the urging of President Dwight D. Eisenhower, the act provided 90 percent federal funding for a “system of interstate and defense highways,” and authorized spending $25 billion through 1969 for construction of about 41,000 miles of interstates.
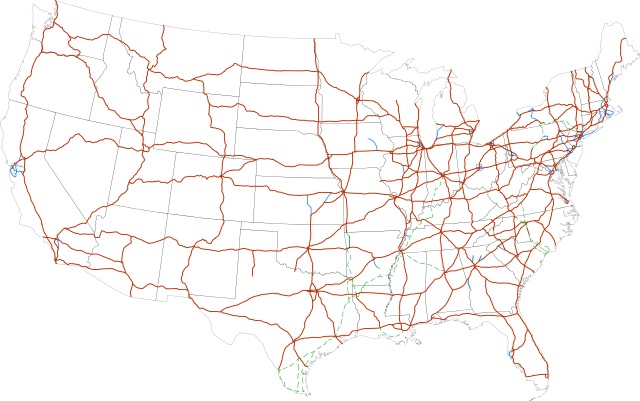
The interstate system reached 48,191 miles in 2016. Federal regulations banned collecting tolls but that would change.
“Of all his domestic programs, Eisenhower’s favorite by far was the Interstate System,” noted historian Stephen Ambrose. The thirty-fourth president urged passage of the act for national defense; interstates would be needed for evacuating major cities during a nuclear war.
_______________________
Recommended Reading: Signal Hill, California, Images of America (2006); Minnesota’s Geology (1982) Tulsa Oil Capital of the World, Images of America
(2004); Oil in West Texas and New Mexico
(1982); Minnesota’s Geology (1982); Black Gold in California: The Story of California Petroleum Industry
(2016); Early California Oil: A Photographic History, 1865-1940
(1985); Tulsa Oil Capital of the World, Images of America
(2004); Oil in West Texas and New Mexico
(1982); Official Guide to the Smithsonian
(2016); Eisenhower: Soldier and President
(1968). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Please become an AOGHS annual supporter and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. © 2025 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.