May 14, 1906 – Louisiana Law conserves Natural Gas –
Joining the growing number of states producing natural gas, Louisiana enacted conservation measures to prevent waste. Lawmakers passed “an Act to Protect the Natural Gas Fields of this State” empowering the governor “to close, cap, or plug offending wells” at the owner’s expense.
Expanded in 1910, the act marked the beginning of legislative control of the state’s petroleum industry, according to the Department of Natural Resources (DNR). Penalties were imposed for “failure to cap out of control wells, doing injury to pipe lines, or wastefully burning natural gas from any well into the air.” Louisiana sought to avoid the waste of natural gas that had depleted fields during the Indiana gas boom.
May 14, 1953 – Golden Driller debuts at Petroleum Exposition
A golden, 76-foot-tall statue of a roughneck appeared at the 30th annual International Petroleum Exposition in Tulsa, Oklahoma. Sponsored by the Mid-Continent Supply Company of Fort Worth, Texas, the oilfield worker would appear again for the 1959 expo.
Because of the roughneck’s popularity with the public, the company decided to refurbish and donate it to the Tulsa County Fairgrounds. Completely rebuilt in 1966, the “golden driller” would be refurbished several more times by 1980.

The original Golden Driller of 1953, left, proved so popular that a more permanent version (supported with steel rods) returned for the 1966 Petroleum Expo. Photos courtesy Tulsa Historical Society.
Now a Tulsa tourist attraction, the mustard-shaded driller, weighing 43,500 pounds, stands among the largest freestanding statues in the world, according to city officials. Promotional t-shirts, ties, and scarfs — and in 2020 a Covid-19 mask — have occasionally adorned the statue.
Learn more in Golden Driller of Tulsa.
May 14, 2004 – Museum Opens in Oil City, Louisiana
Louisiana’s first publicly funded museum dedicated to the petroleum industry opened in Oil City, about 20 miles north of Shreveport. The Louisiana State Oil and Gas Museum, originally called the Caddo-Pine Island Oil and Historical Museum, opened at a former depot of the Kansas City Southern Railroad.

The museum in Caddo Parish, Louisiana, includes outdoor exhibits of modern oil production technology.
The museum has since preserved the Caddo Parish oilfield discoveries, which began in 1905 and brought sustained economic prosperity to North Louisiana. Museum exhibits reveal the technologies behind a 1911 well drilled by Gulf Refining Company that was among the earliest “offshore” oil wells. The Ferry Lake No. 1, completed on Caddo Lake, produced 450 barrels of oil per day from a depth of 2,185 feet (see First Louisiana Oil Wells).
May 15, 1911 – Supreme Court mandates Break Up of Standard Oil
After reviewing 12,000 pages of court documents, the Supreme Court issued its majority opinion mandating dissolution of the Standard Oil Company of New Jersey into 34 separate companies. The Justice Department had filed an antitrust lawsuit against Standard Oil in 1909. The Supreme Court’s ruling upheld a circuit court decision that Standard Oil’s practices violated the Sherman Antitrust Act. The company was given six months to spin off its subsidiaries.
May 15, 1940 — Nylon Stockings Go on Sale
One year after being unveiled at the 1939 New York World’s Fair, nylon stockings went on sale for the first time at Gimbels Department Store in Manhattan. Promoted as “strong as steel, as fine as spiderweb,” first-year sales reached about 64 million pairs at $1.35 each for the DuPont Company petroleum product, according to ABC News.
“Women’s love affair with nylon stockings has had a long run,” the network proclaimed in 2010. Nylon had been used for toothbrush bristles for “Dr. West’s Miracle-Tuft” as early as February 1938 (see Nylon, a Petroleum Polymer).
May 16, 1817 – U.S. Geology Described and Mapped
Scottish American geologist William Maclure presented his detailed study of U.S. geology to the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia. He would be named president of the Academy, a post he would hold for 22 years, and become known as the “father of American Geology.”
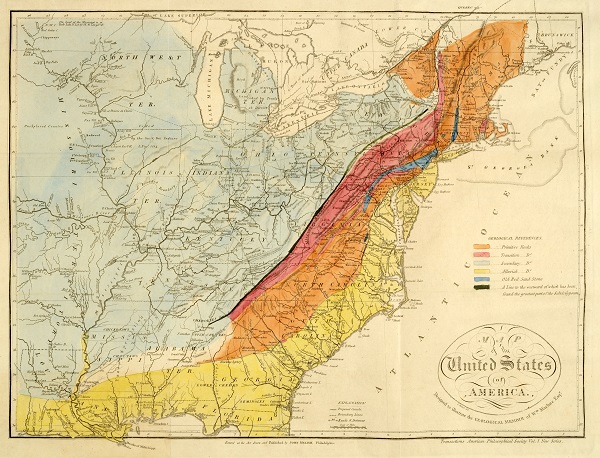
An 1818 map by William Maclure provided a more detailed version of a geological map he published in 1809. Image courtesy the Historic Maps Collection, Princeton Library.
The American Philosophical Society published Maclure’s detailed study in 1818 as “Observations on the Geology of the United States of North America.”
May 16, 1934 – National Stripper Well Association established
The National Stripper Well Association (NSWA) organized in Tulsa, Oklahoma, to represent operators of stripper wells — marginal wells that produce less than 15 barrels of oil a day or less than 90 thousand cubic feet of natural gas a day. In 2023, about 400,000 oil stripper wells accounted for more than 7.4 percent of U.S. oil production, according to NSWA. About 360,000 natural gas stripper wells accounted for 8.2 percent of gas production.
May 16, 1961 – Museum opens over Natural Gas Field
In southwestern Kansas, the Stevens County Gas & Historical Museum in Hugoton opened above a natural gas producing formation extending 8,500 square miles into the Oklahoma and Texas panhandles. The town’s museum has since educated visitors about one of the largest natural gas fields in North America — the Hugoton field. A gas well drilled in 1945 still produces on the museum grounds.

A small Stevens County natural gas museum in Hugoton, Kansas, preserves the history of a gas field that extends into two other states.
Although the Hugoton field’s once dominant natural gas production gave way to gas shale and coalbed methane regions, including production from Fayetteville, Arkansas, (2004) and Haynesville, Louisiana (2008), the Hugoton-Panhandle gas continues to be a leading source of helium.
Learn more in Hugoton Natural Gas Museum.
May 17, 1882 – Mystery Well Production revealed
The true oil production of a closely guarded discovery well in the Warren County, Pennsylvania, township was revealed to be 1,000 barrels of oil a day. News about Jamestown Oil Company’s “Mystery Well” sent shock waves through petroleum market centers.
“The excitement in the oil exchanges was indescribable,” noted Paul H. Giddens in his 1938 classic, The Birth of the Oil Industry. “Over 4,500,000 barrels of oil were sold in one day on the exchanges in Titusville, Oil City and Bradford.”

In 2007, Cherry Grove, Pennsylvania, oil patch volunteers rebuilt a derrick to celebrate their historic 1882 Mystery Well.
Although the Cherry Grove discovery demoralized the market and drove oil prices down to less than 50 cents per barrel, hundreds of derricks appeared around Cherry Grove and thousands of people moved there while the boom lasted. It was short lived, according to volunteers of Cherry Grove Old Home and Community Day Committee, which has kept the “Oil Excitement” alive with special events.
Learn more in Cherry Grove Mystery Well.
May 17, 1901 – Gulf Oil begins at Spindletop Hill
James M. Guffey organized Guffey Petroleum Company to buy the famous “Lucas Gusher” well drilled the previous January at Spindletop Hill near Beaumont, Texas. Guffey purchased about half of the well’s high-volume oil production (the Mellon family of Pittsburgh owned the remainder). Guffey created Gulf Refining Company to refine and market the oil produced by Guffey Petroleum. In 1907, Andrew Mellon acquired J.M. Guffey Petroleum and Gulf Refining companies of Texas and reorganized them as Gulf Oil.
May 17, 1973 – Last Nuclear fracturing of Natural Gas Well
Atomic Energy Commission scientists conducted the last experiment of the Plowshare Program with a nearly simultaneous detonation of three 33-kiloton devices in a Colorado natural gas well. Project Rio Blanco was the third and final underground detonation to test nuclear fracturing of gas wells.
The first had been Project Gasbuggy in 1967, when a 29-kiloton nuclear device fractured a New Mexico well. A second experiment, Project Rulison, detonated a 40-kiloton device in a Colorado well in 1969. All three projects improved production, but the natural gas proved too radioactive.
May 19, 1885 – Lima Oilfield discovered in Ohio
Ohio’s petroleum industry began when Benjamin Faurot found oil at Lima in the northwestern part of the state. He had been searching for natural gas in the prolific Trenton Rock Limestone (see Indiana Natural Gas Boom). “If the well turns out, as it looks now that it will, look out for the biggest boom Lima ever had,” proclaimed Lima’s Daily Republican newspaper.

A postcard promotes the oil wealth of Lima, Ohio, and the giant oilfield discovered there in 1885. Circa 1909 postcard published by Robbins Bros., Boston.
Faurot organized the Trenton Rock Oil Company, and by 1886 the Lima oilfield was producing more than 20 million barrels of oil, the most in the nation. The Lima field’s heavy oil needed special refining, and Standard Oil Company of New Jersey in 1889 began construction on the Whiting refinery.
Learn more in Great Oil Boom of Lima, Ohio.

May 19, 1942 – Oklahoma Inventor patents Portable Drilling Rig
A pioneer in oilfield technologies, George E. Failing of Enid, Oklahoma, received a patent for his design of a drilling rig on a truck bed. “I designate the rear portion of a drilling rig such as used in drilling shallow wells, the taking of cores, drilling of shot-holes, and performing similar oil field operations,” Failing noted in his patent.
In 1931, he had mounted a rig on a 1927 Ford farm truck, “adding a power take-off assembly to transfer power from the truck engine to the drill,” according to the Oklahoma Historical Society. Failing would receive more than 300 patents for oilfield tools, “from rock bit cores to an apparatus for seismic surveying.”
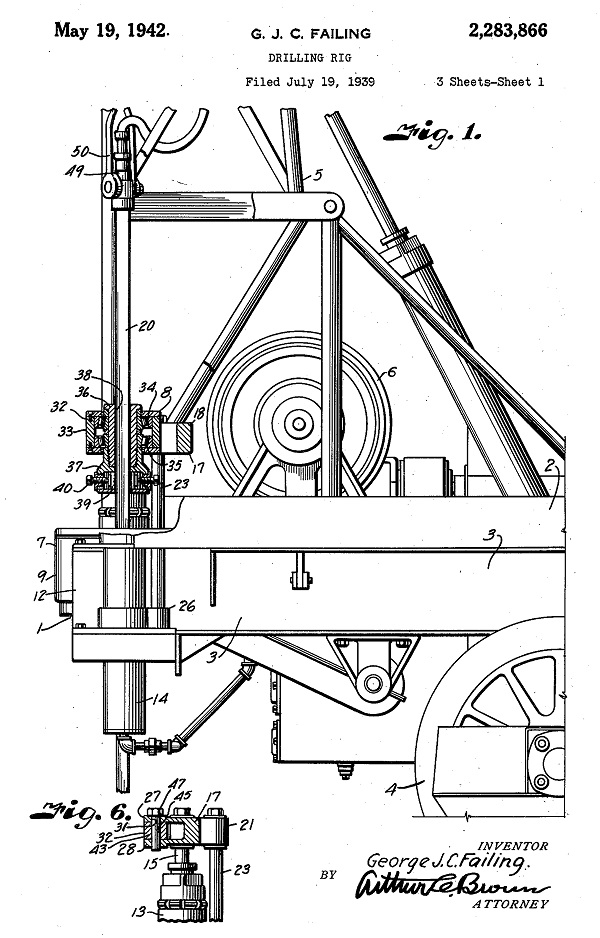
George Failing’s drilling rig — powered by its truck’s engine — will prove ideal for slanted wells.
Failing’s portable rig could drill ten slanted, 50-foot holes in a single day, while a traditional rotary rig took about a week to set up and drill to a similar depth. He demonstrated his portable drilling technology at a 1933 well disaster in Conroe, Texas, working with H. John Eastman, today considered the father of directional drilling (see Technology and the “Conroe Crater”).
_______________________
Recommended Reading: Louisiana’s Oil Heritage, Images of America (2012); Oil in Oklahoma
(1976); Titan: The Life of John D. Rockefeller, Sr.
(2004); The Extraction State, A History of Natural Gas in America (2021); Cherry Run Valley: Plumer, Pithole, and Oil City, Pennsylvania
(2000); Trek of the Oil Finders: A History of Exploration for Petroleum (1975); The Birth of the Oil Industry (1938); Ohio Oil and Gas, Images of America
(2008); History Of Oil Well Drilling
(2007); Drilling Technology in Nontechnical Language
(2012). Your Amazon purchase benefits the American Oil & Gas Historical Society. As an Amazon Associate, AOGHS earns a commission from qualifying purchases.
_______________________
The American Oil & Gas Historical Society (AOGHS) preserves U.S. petroleum history. Become an AOGHS annual supporting member and help maintain this energy education website and expand historical research. For more information, contact bawells@aoghs.org. Copyright © 2024 Bruce A. Wells. All rights reserved.


